Humanity punched this asteroid! NASA shows how hard in numbers
What happened after NASA's DART spacecraft collided with Asteroid Dimorphos? Find it out here.





 View all Images
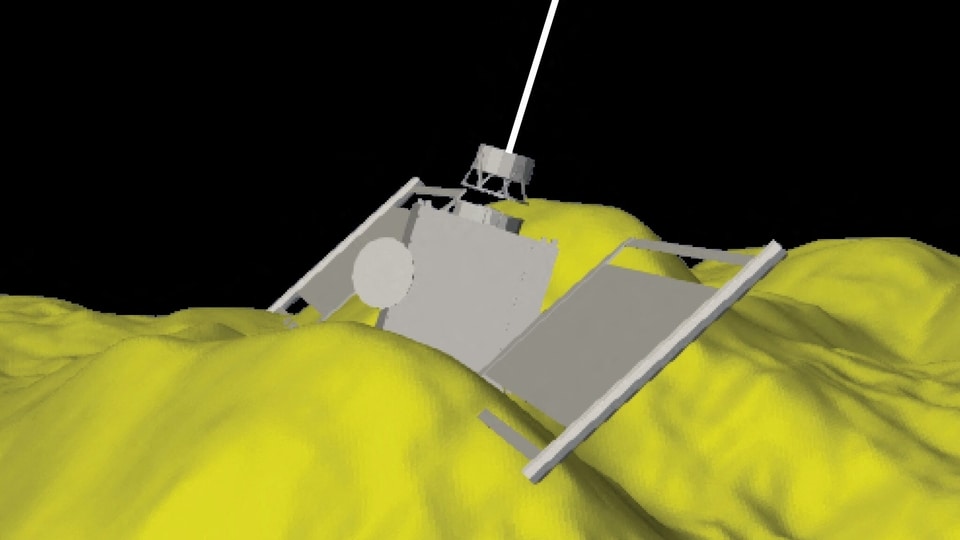
View all ImagesPotentially hazardous asteroids can pose a risk for planet Earth at any time. In order to avoid any kind of a dangerous situation and to deflect the direction of any asteroid nearing Earth, NASA had on September 26, 2022 launched Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) spacecraft which deliberately smashed into an asteroid called Asteroid Dimorphos leading to successfully altering its trajectory. The primary objective of DART was to test NASA's ability to alter the asteroid's direction. Asteroid Dimorphos orbits around another asteroid called Didymos. The separation between the centers of the two asteroids is 1.18 kilometers (0.73 miles), says Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory.
Data from this mission will help inform researchers how to potentially divert a threatening asteroid's path away from Earth, if ever necessary. The DART experiment also provided fresh insights into planetary collisions that may have been common in the early solar system.
So, if you are wondering what happened after the collision, then know that scientists have just revealed the same.
According to a report by Nature, "The impact caused the asteroid's orbit around another space rock to shrink — Dimorphos now completes an orbit 33 minutes faster than before the impact."
The report further added, "now, five studies in Nature describe the final moments of the crash and how it affected the asteroid. One group combined data on the spacecraft's trajectory with photographs of the asteroid's surface just before impact. As DART hurtled towards Dimorphos at more than 6 kilometres per second, the first part that hit was one of its solar panels, which smashed into a 6.5-metre-wide boulder. Microseconds later, the main body of the spacecraft collided with the rocky surface next to the boulder — and the US$330-million DART shattered to bits."
Amazingly, at least one million kilograms of rock from Dimorphos's 4.3-billion-kilogram mass ejected due to the collision. NASA's Hubble Space Telescope also captured a series of photos of asteroid Dimorphos when it was deliberately hit by a 1,200-pound NASA spacecraft.
Hubble's time-lapse movie of the aftermath of DART's collision reveals hour-by-hour changes as dust and chunks of debris were flung into space. "Smashing head on into the asteroid at 13,000 miles per hour, the DART impactor blasted over 1,000 tons of dust and rock off of the asteroid," NASA said in an earlier report.
The movie shows three overlapping stages of the impact aftermath: the formation of an ejecta cone, the spiral swirl of debris caught up along the asteroid's orbit about its companion asteroid, and the tail swept behind the asteroid by the pressure of sunlight (resembling a windsock caught in a breeze).
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.