US infiltrates big ransomware gang: ''We hacked the hackers''
The FBI quietly gained access to its control panel in July and was able to obtain software keys to decrypt the network of some 1,300 victims globally.








 View all Images
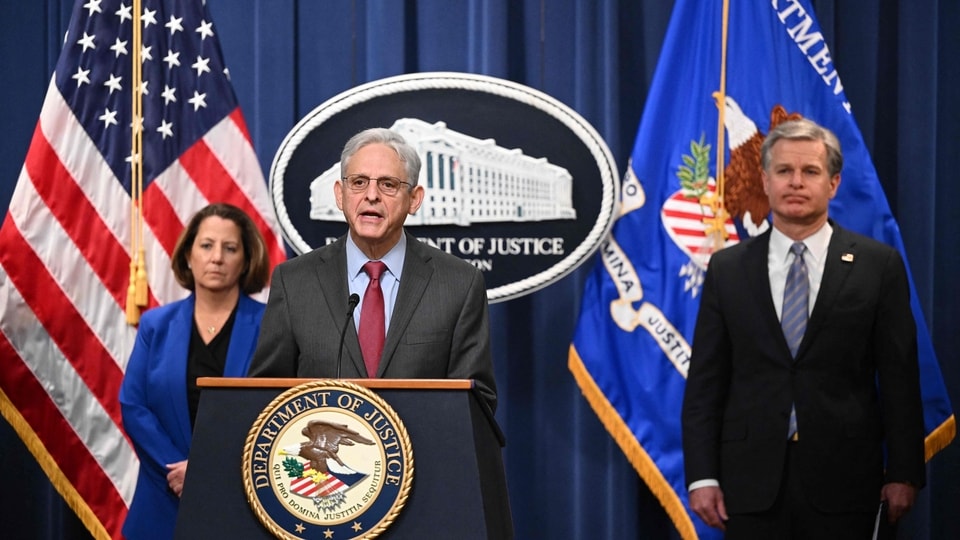
View all ImagesThe FBI and international partners have at least temporarily dismantled the network of a prolific ransomware gang they infiltrated last year, saving victims including hospitals and school districts a potential USD 130 million in ransom payments, Attorney General Merrick Garland and other US officials announced on Thursday.
“Simply put, using lawful means we hacked the hackers,” Deputy Attorney General Lisa Monaco said at a news conference.
Officials said the targeted syndicate, known as Hive, operates one of the world's top five ransomware networks and has heavily targeted hospitals and other health care providers.
The FBI quietly gained access to its control panel in July and was able to obtain software keys to decrypt the network of some 1,300 victims globally, said FBI Director Christopher Wray. Officials credited German police and other international partners.
It was not immediately clear how the takedown will affect Hive's long-term operations, however. Officials did not announce any arrests but said they were building a map of Hive's administrators, who manage the software, and affiliates, who infect targets and negotiate with victims, to pursue prosecutions.
“I think anyone involved with Hive should be concerned because this investigation is ongoing,” Wray said.
On Wednesday night, FBI agents seized computer infrastructure in Los Angeles that was used to support the network. Two Hive dark web sites were seized: one used for leaking data of non-paying victims, the other for negotiating extortion payments.
“Cybercrime is a constantly evolving threat, but as I have said before, the Justice Department will spare no resource to bring to justice anyone anywhere that targets the United States with a ransomware attack,” Wray said.
Garland said that thanks to the infiltration, led by the FBI's Tampa office, agents were able in one instance to disrupt a Hive attack against a Texas school district, stopping it from making a USD 5 million payment.
The operation is a big win for the Justice Department. The ransomware scourge is the world's biggest cybercrime headache with everything from Britain's postal service and Ireland's national health service to Costa Rica's government crippled by Russian-speaking syndicates that enjoy Kremlin protection.
The criminals lock up, or encrypt, victims' computer networks, steal sensitive data and demand large sums.
As an example of Hive's threat, Garland said it had prevented a hospital in the Midwest in 2021 from accepting new patients at the height of the COVID-19 epidemic.
The online takedown notice, alternating in English and Russian, mentions Europol and German federal and state police as partners in the effort.
In a statement, Europol said companies in more than 80 countries, including oil multinationals, have been compromised by Hive. It said Europol assisted with cryptocurrency, malware and other analysis, and that law enforcement agencies from 13 countries were involved in the effort.
A US government advisory last year said Hive ransomware actors victimized over 1,300 companies worldwide from June 2021 through November 2022, receiving approximately USD 100 million in ransom payments.
It said criminals using Hive ransomware targeted a wide range of businesses and critical infrastructure, including government, manufacturing and especially health care and public health facilities.
Even though the FBI offered decryption keys to some 1,300 victims around the world, Wray said only about 20 per cent of them reported potential issues to law enforcement.
“Here, fortunately, we were still able to identify and help many victims who didn't report. But that is not always the case,” Wray said. “When victims report attacks to us, we can help them and others, too.”
John Hultquist, the head of threat intelligence at the cybersecurity firm Mandiant, said the Hive disruption won't cause a major drop in overall ransomware activity but is nonetheless “a blow to a dangerous group”.
“Unfortunately, the criminal marketplace at the heart of the ransomware problem ensures a Hive competitor will be standing by to offer a similar service in their absence, but they may think twice before allowing their ransomware to be used to target hospitals,” Hultquist said.
But Brett Callow, an analyst with the cybersecurity firm Emsisoft, said the operation is apt to lessen ransomware crooks' confidence in what has been a very high reward-low risk business.
“The information collected may point to affiliates, launderers and others involved in the ransomware supply chain," Callow said.
And analyst Allan Liska of the cybersecurity firm Recorded Future said the operation shows “law enforcement's multi-pronged strategy of arrests, sanctions, seizures and more is working to slow down ransomware attacks.” He predicted it would lead to indictments, if not actual arrests, in the next few months.
The ransomware threat captured the attention of the highest levels of the Biden administration two years ago after a series of high-profile attacks that threatened critical infrastructure and global industry. In May 2021, for instance, hackers targeted the nation's largest fuel pipeline, causing the operators to briefly shut it down and make a multimillion-dollar ransom payment that the US government largely recovered.
Federal officials have used a variety of tools to try to combat the problem, but conventional law enforcement measures such as arrests and prosecutions have done little to frustrate the criminals.
The FBI has obtained access to decryption keys before. It did so in the case of a major 2021 ransomware attack on Kaseya, a company whose software runs hundreds of websites. It took some heat, however, for waiting several weeks to help victims unlock afflicted networks.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.