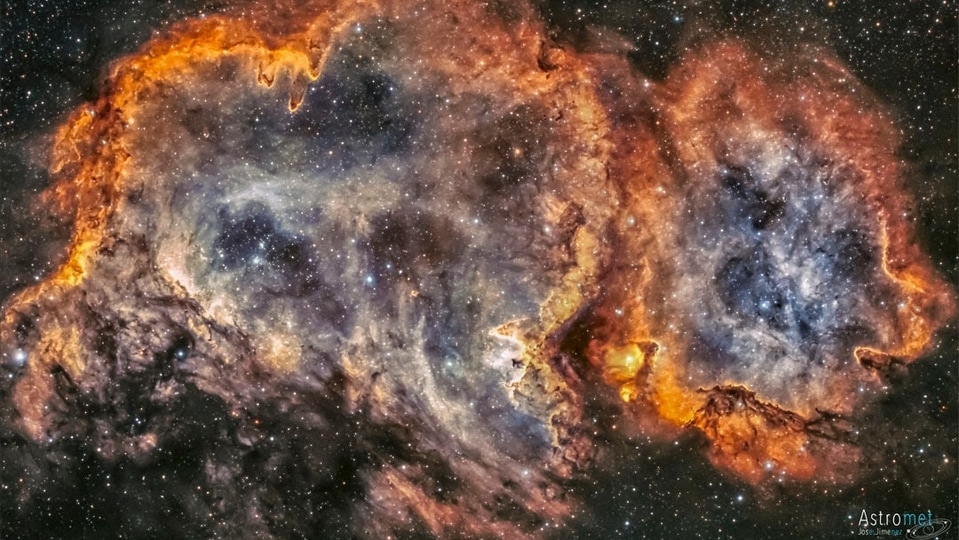
NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day 21 March 2023: Dark Nebulae and the Taurus Molecular Cloud
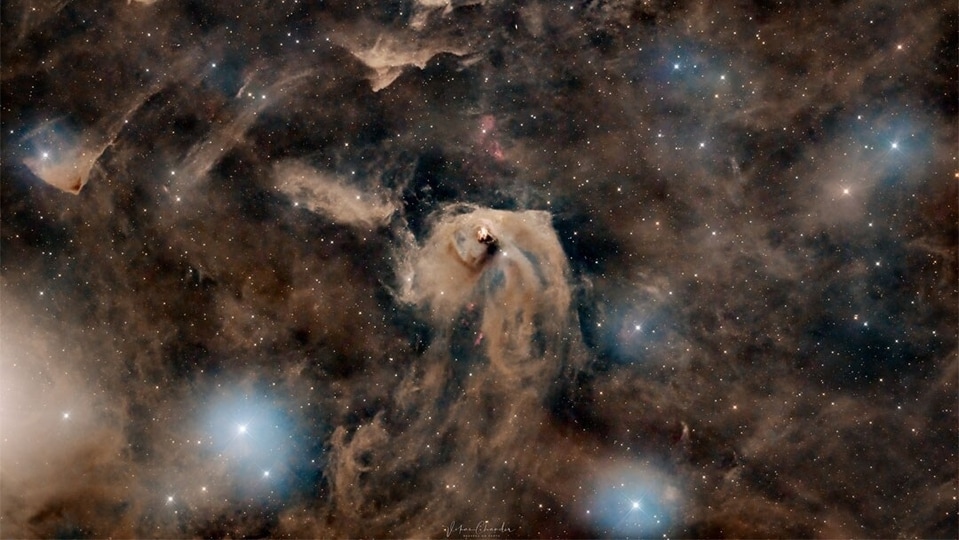
NASA’s Astronomy Picture of the Day is a fascinating snapshot of the dark nebulae and the star formation in the Taurus Molecular Cloud (TMC).






 View all Images
View all ImagesWhen gas, dust and plasma get accumulated in space, it usually leads to the formation of interstellar clouds. Initially, these clouds are hot in nature but when they become dense and cool enough, molecules form inside them, giving them the name of Interstellar Molecular Clouds. Molecular clouds are places where stars first form and they help astronomers in learning about the earliest stages of stars. According to NASA, these celestial objects are so dense that the dust within blocks visible wavelengths of light. Telescopes that see visible light only detect ghostly dark patches in the sky, called Dark Nebulae.
Today's NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day is a fascinating snapshot of the dark nebulae and the star formation in the Taurus Molecular Cloud (TMC). Located about 400 light-years away, TMC is one of the closest molecular clouds to our solar system. The Taurus Molecular Cloud is also home to Hind's Variable Nebula (NGC 1555) about 650 light-years away as well as the star T Tauri.
The picture was captured by astrophotographer Vikas Chander.
NASA's description of the picture
Can dust be beautiful? Yes, and it can also be useful. The Taurus molecular cloud has several bright stars, but it is the dark dust that really draws attention. The pervasive dust has waves and ripples and makes picturesque dust bunnies, but perhaps more importantly, it marks regions where interstellar gas is dense enough to gravitationally contract to form stars. In the image center is a light cloud lit by neighboring stars that is home not only to a famous nebula, but to a very young and massive famous star.
Both the star, T Tauri, and the nebula, Hind's Variable Nebula, are seen to vary dramatically in brightness -- but not necessarily at the same time, adding to the mystery of this intriguing region. T Tauri and similar stars are now generally recognized to be Sun-like stars that are less than a few million years old and so still in the early stages of formation.
The featured image spans about four degrees not far from the Pleiades star cluster, while the featured dust field lies about 400 light-
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.