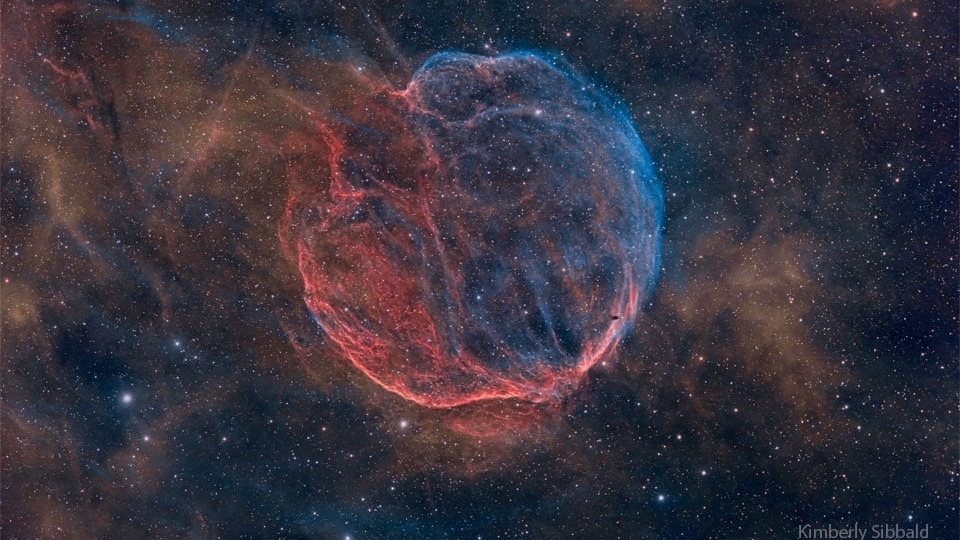
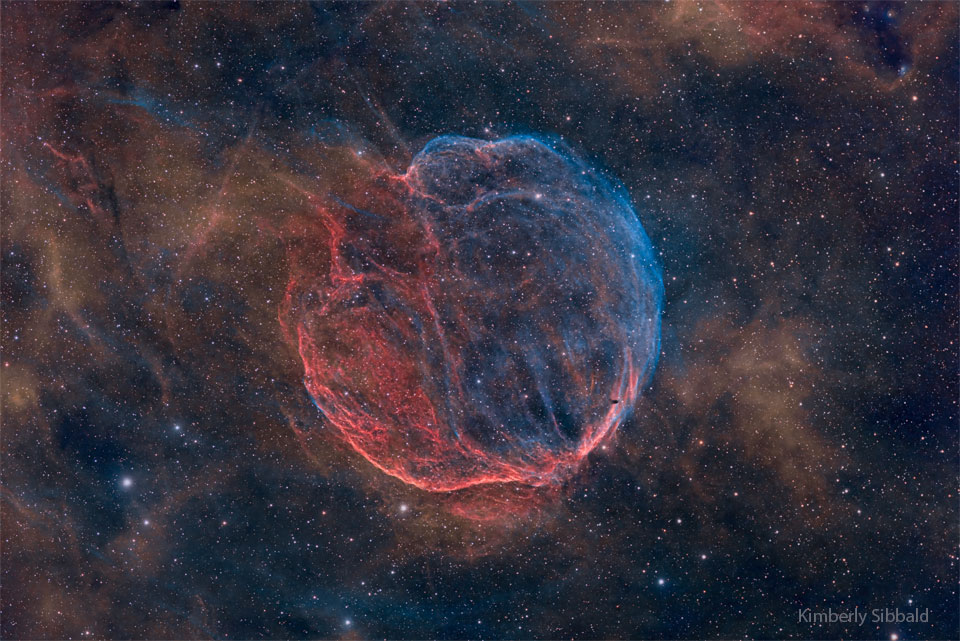
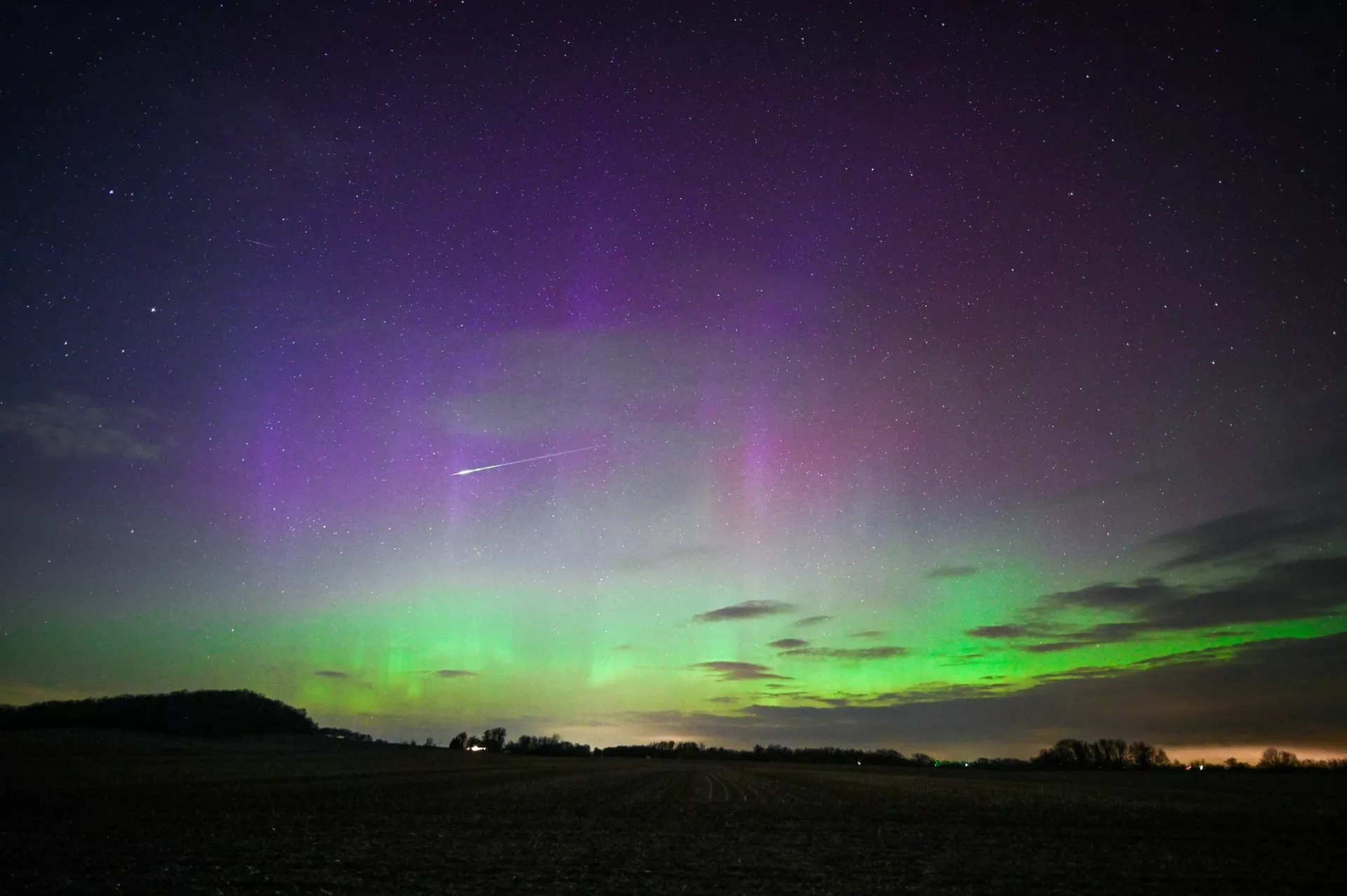
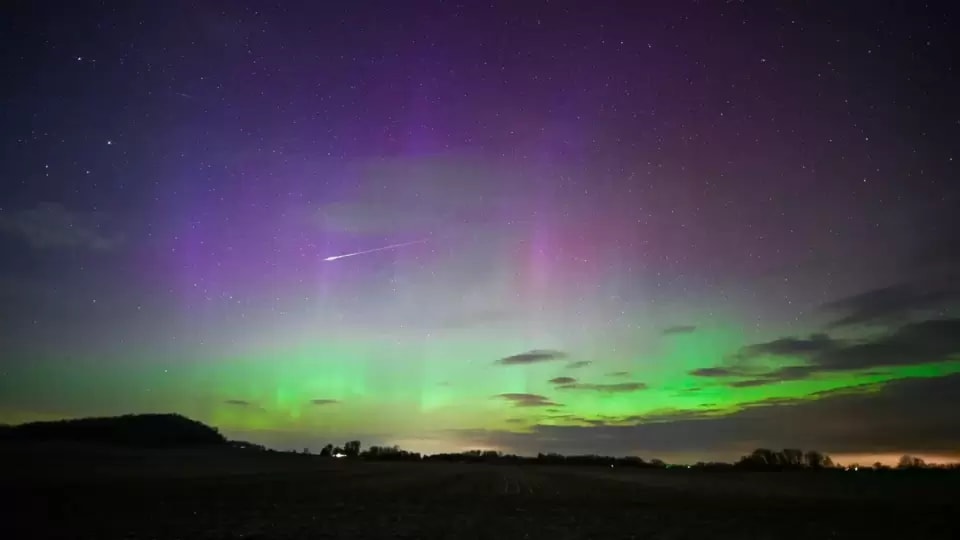
Best NASA Astronomy Pictures of the Week: Geomagnetic storms, Tarantula Nebula and more
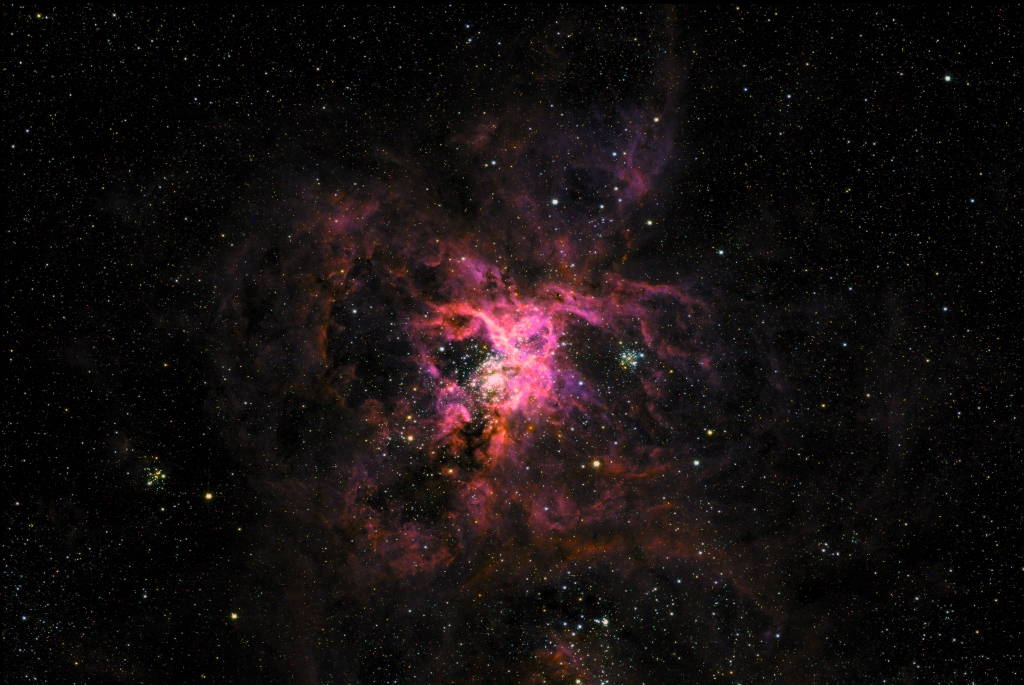
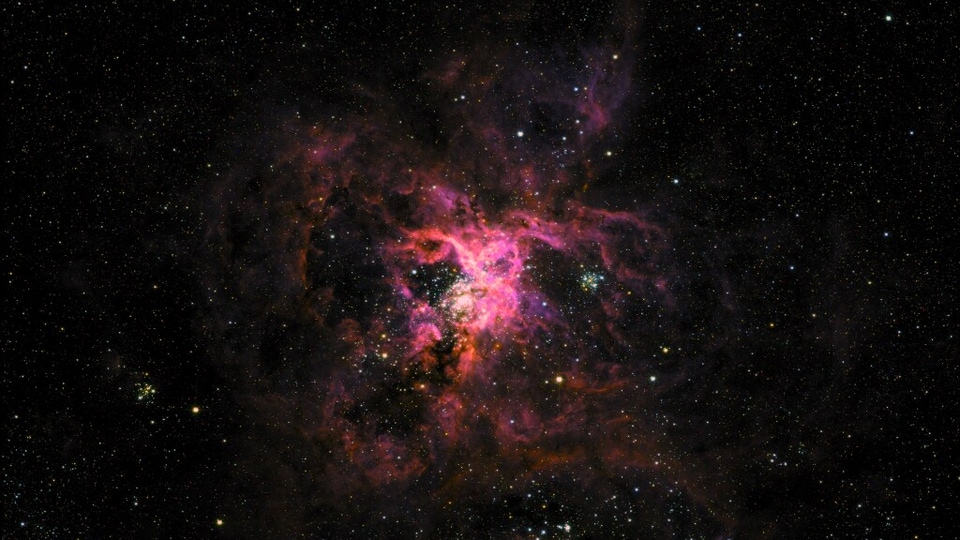
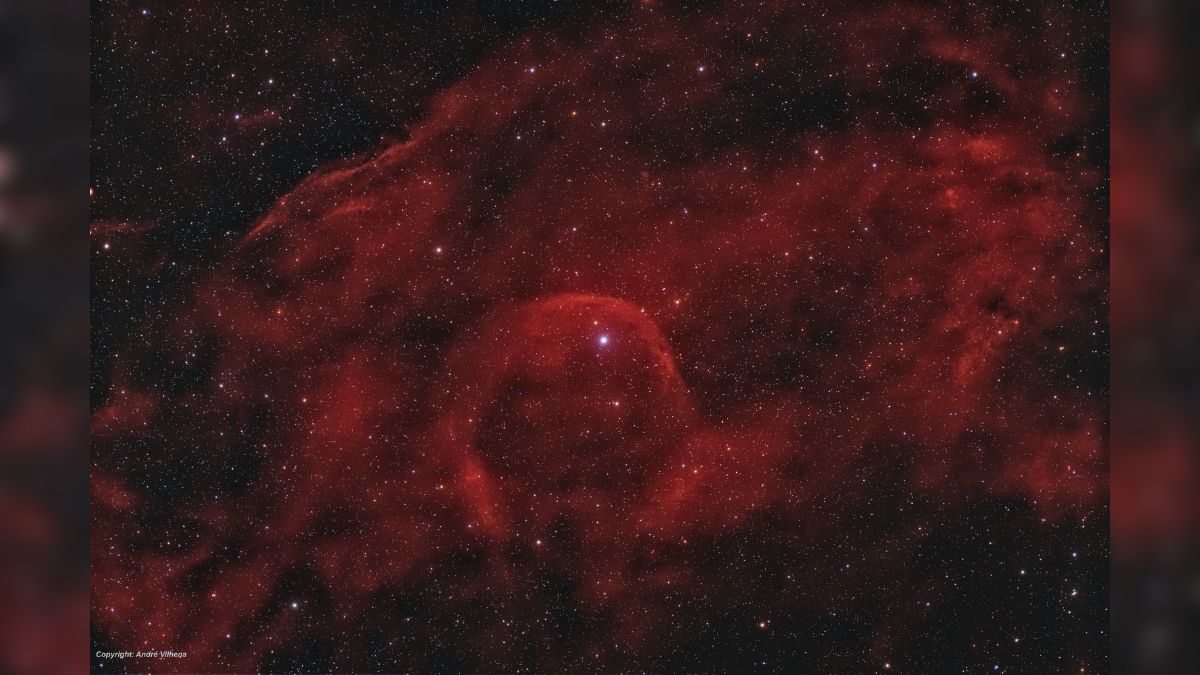
Astrophotographers from all over the world are featured in NASA's Astronomy Picture of the Day, which is published daily. This week's pictures include Auroras sparked by geomagnetic storm, the Tarantula Nebula and more.









First Published Date: 28 Apr, 13:23 IST
NEXT ARTICLE BEGINS