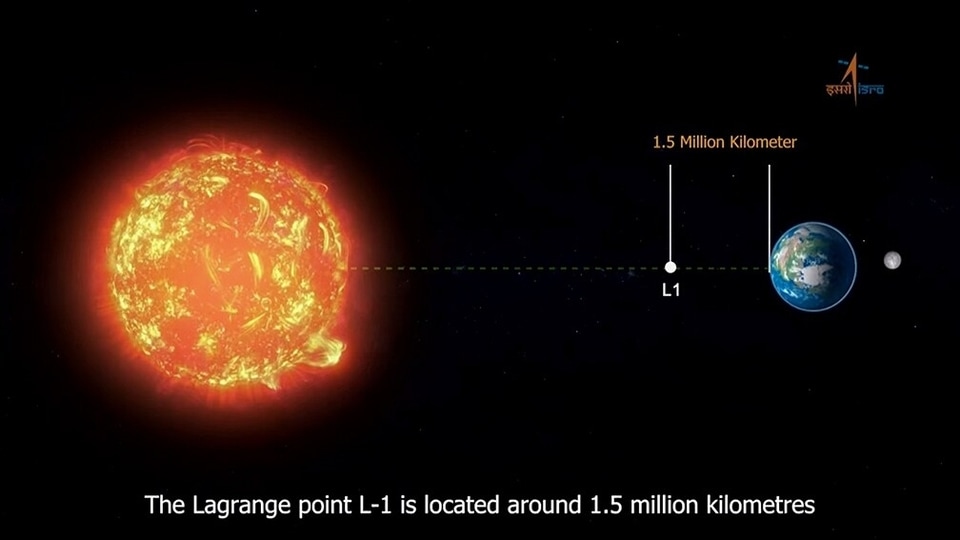
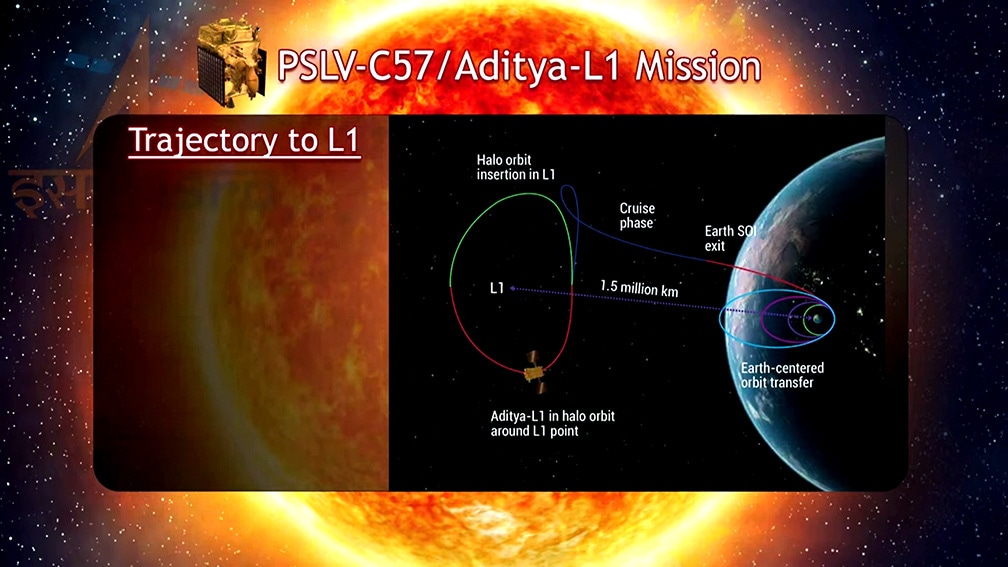
Aditya -L1 Mission: ISRO’s maiden solar mission heading toward the Sun
India is on a journey to achieve yet another milestone with Aditya-L1 mission. Know all about it in brief:








First Published Date: 25 Oct, 13:55 IST
NEXT ARTICLE BEGINS