In a first, IXPE telescope has revealed Supernova secrets, says NASA
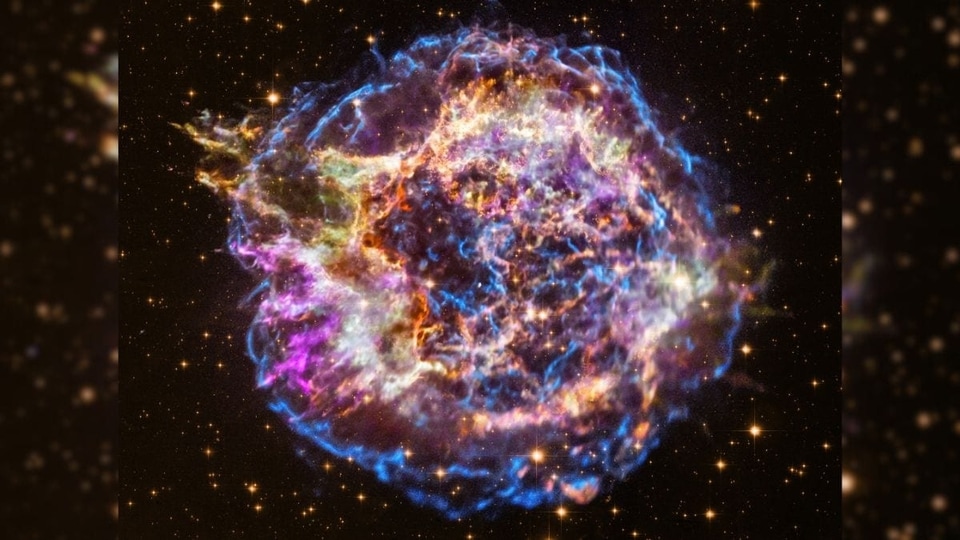
NASA's IXPE telescope has unveiled polarized X-ray images of SN 1006, a historic supernova remnant, revealing magnetic field secrets and cosmic acceleration.


_1639373804152_1639373815879.jpg)
_1650614444757_1650614518141.png)

 View all Images
View all ImagesSupernova's have been some of the most spectacular space events ever to happen in the Universe. They are massive in nature and even more amazing in terms of their gigantic nature. Now, in a groundbreaking discovery, NASA's Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) telescope has unveiled the mysteries shrouding the historic supernova remnant, SN 1006. The telescope's first-of-its-kind polarized X-ray images have illuminated the enigmatic connection between magnetic fields and the flow of high-energy particles from exploding stars.
Dr. Ping Zhou, an astrophysicist at Nanjing University in Jiangsu, China, and the lead author of a paper recently published in The Astrophysical Journal, expressed his excitement about the findings. He stated, “Magnetic fields are extremely difficult to measure, but IXPE provides an efficient way for us to probe them. Now we can see that SN 1006's magnetic fields are turbulent, but also present an organized direction.”
We are now on WhatsApp. Click to join.
SN 1006: A Celestial Time Capsule
Located 6,500 light-years away in the Lupus constellation, SN 1006 is the sole remnant of a colossal explosion that was first seen by humanity as long ago as 1006 CE. This explosion, theorized to have resulted from either the merger of two white dwarfs or a white dwarf siphoning mass from a companion star, was visible to observers across China, Japan, Europe, and the Arab world for years. To this day, modern astronomers consider it the brightest recorded stellar event.
While researchers have long puzzled over SN 1006's unusual double structure, distinct from other spherical supernova remnants, they have also identified bright "limbs" or edges detectable in the X-ray and gamma-ray spectra. Douglas Swartz, a researcher at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, explained, "Close-proximity, X-ray-bright supernova remnants such as SN 1006 are ideally suited to IXPE measurements, given IXPE's combination of X-ray polarization sensitivity with the capability to resolve the emission regions spatially."
IXPE's Vision Unravels Cosmic Mysteries
Previous X-ray observations of SN 1006 provided the first evidence that supernova remnants can significantly accelerate electrons. These findings identified rapidly expanding nebulae around exploded stars as the birthplaces of highly energetic cosmic rays, capable of traveling at nearly the speed of light.
Researchers had postulated that SN 1006's unique structure was linked to the orientation of its magnetic field, suggesting that supernova blast waves in the northeast and southwest aligned with the magnetic field direction could more efficiently accelerate high-energy particles. IXPE's recent revelations have now substantiated and clarified these theories, underlining the telescope's reliability and robust capabilities.
The data confirms a correlation between the magnetic fields and the remnant's high-energy particle outflow. Despite the somewhat disordered magnetic fields in SN 1006's shell, they still exhibit a preferred orientation. As the original explosion's shock wave traverses the surrounding gas, the magnetic fields align with its motion, trapping charged particles. These particles subsequently receive bursts of acceleration, maintaining the magnetic fields' strength and turbulence.
As researchers delve deeper into IXPE's data, their understanding of how particles accelerate in extreme celestial objects is evolving.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.



































