Man-in-the-disk: New vulnerability has put millions of Android phones at risk
Thanks to ‘careless’ usage of external storage by certain apps, millions of Android users are left vulnerable to cyber threats, said Checkpoint researchers. Here’s everything you need to know about Man-in-the-disk flaw.

Mobile handsets, especially the Android platform, have long been targeted by the cyber criminals. But most of the vulnerabilities or exploits have revolved around the software. Of late, the trend is changing with critical security flaws being found at the chipset levels. Now, security researchers have discovered a new flaw in the external storage that houses microSD cards.
The vulnerability, aptly dubbed as Man-in-the-disk, has put millions of Android phones at risk, reported security firm Checkpoint. Unfortunately, there's very little that users can do to protect themselves from this exploit. According to the researchers, the loophole is mainly because the Android applications have been "careless" about how they handle their data on these external storages.
"Through our research analysis we have witnessed cases where an app was downloaded, updated or received data from the app provider's server, which passed through the External Storage before being sent on to the app itself - as seen in the diagram on the left. Such practice offers an opportunity for an adversary to manipulate the data held in the External Storage before the app reads it again," wrote the researchers in their blog post.
Interesting enough, a lot of apps that were tested for this vulnerability are from Google itself. The list of Google apps includes Google Voice Typing and Google Translate among others. The researchers also discovered that Xiaomi's native browser was using external storage and that they were able to "carry out an attack by which the application's update code was replaced, resulting in the installation of an alternative, undesired application instead of the legitimate update."
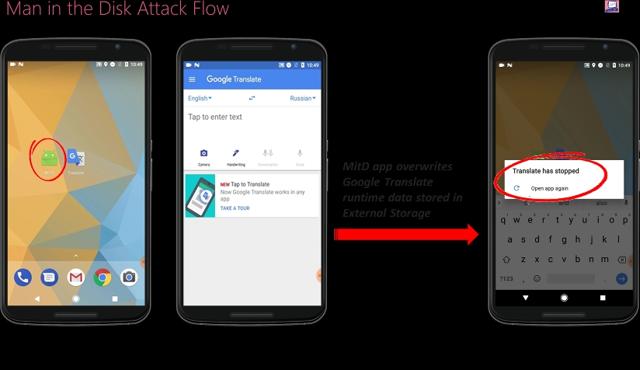

Researchers also stressed that they could not identify who is really at fault for the critical security flaw.
"On the one hand, although Android's developers have created guidelines to app developers on how to ensure their apps are safe, they must also be aware that it is well known for developers to not build their applications with security front of mind. On the other hand, and being aware of this foresaid knowledge, is there more Android could be doing to protect their operating system and the devices that use it?," they added.
Note that most of the applications use internal storage for their data. The external storage is mainly used for sharing and store files. But some Android developers may use external storage to for their apps as they may not want the app to take too much space on the phone or just not paying enough attention.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.

























