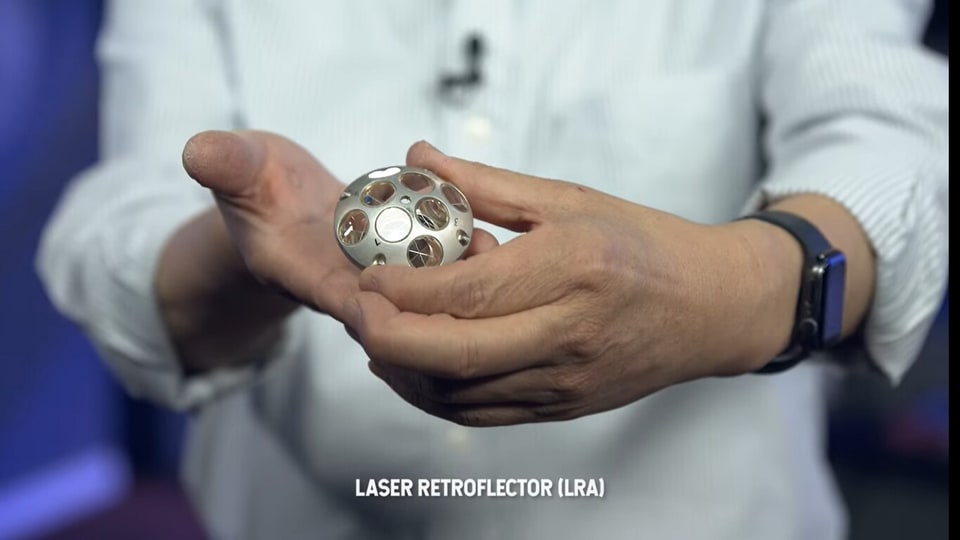
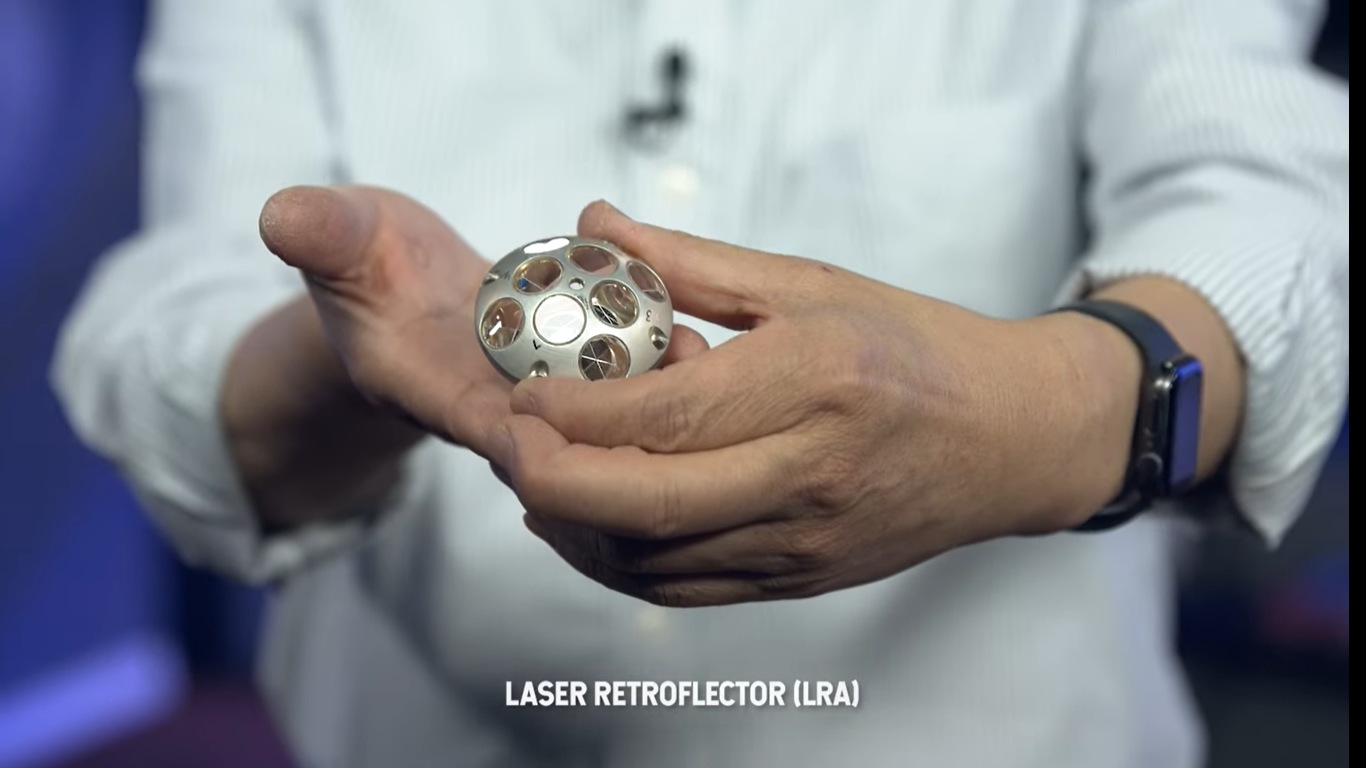
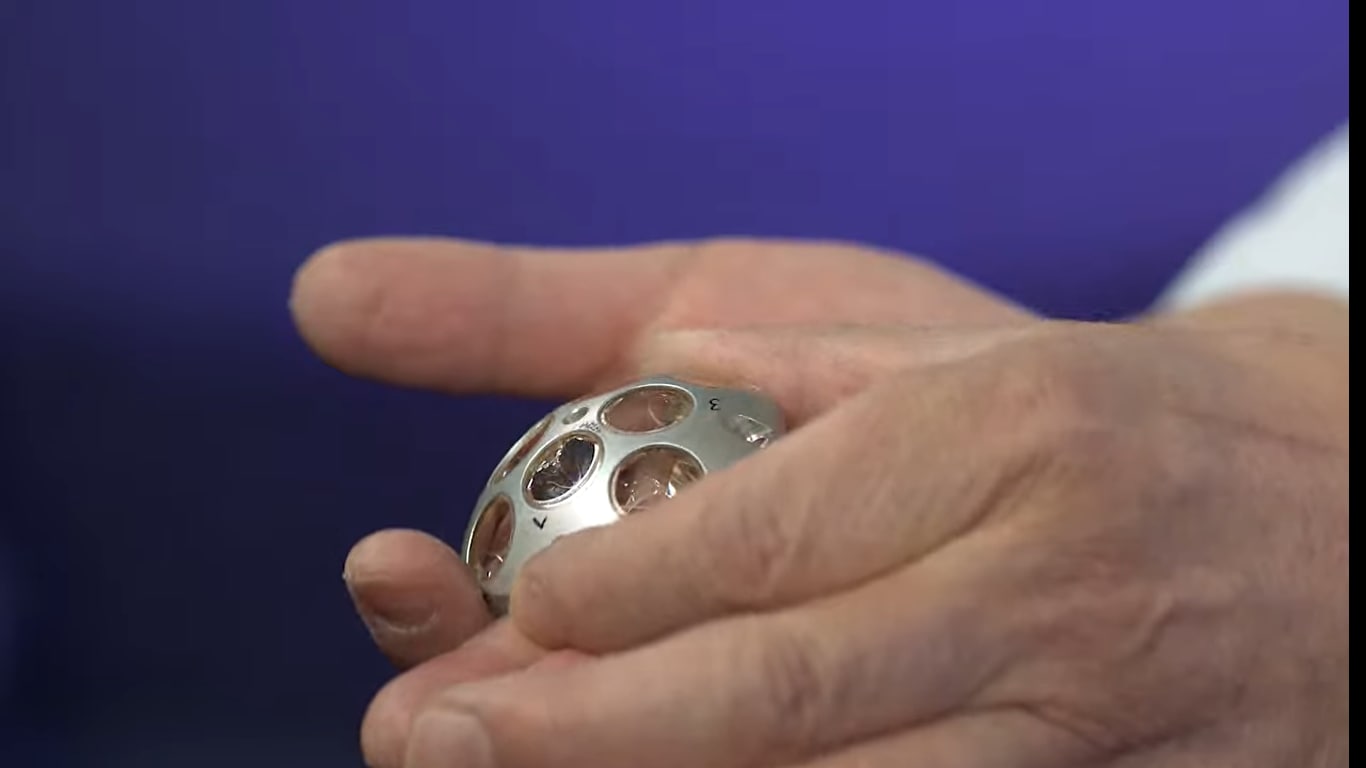
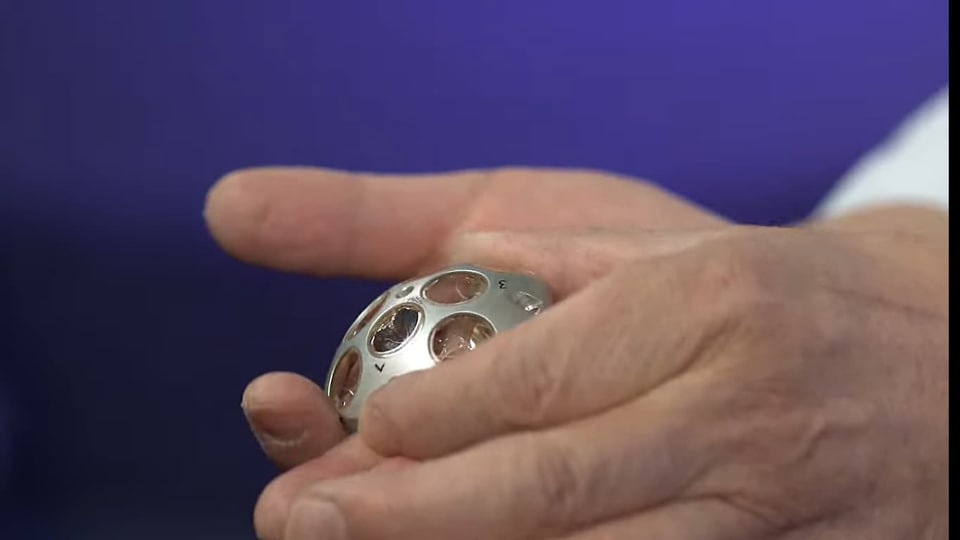
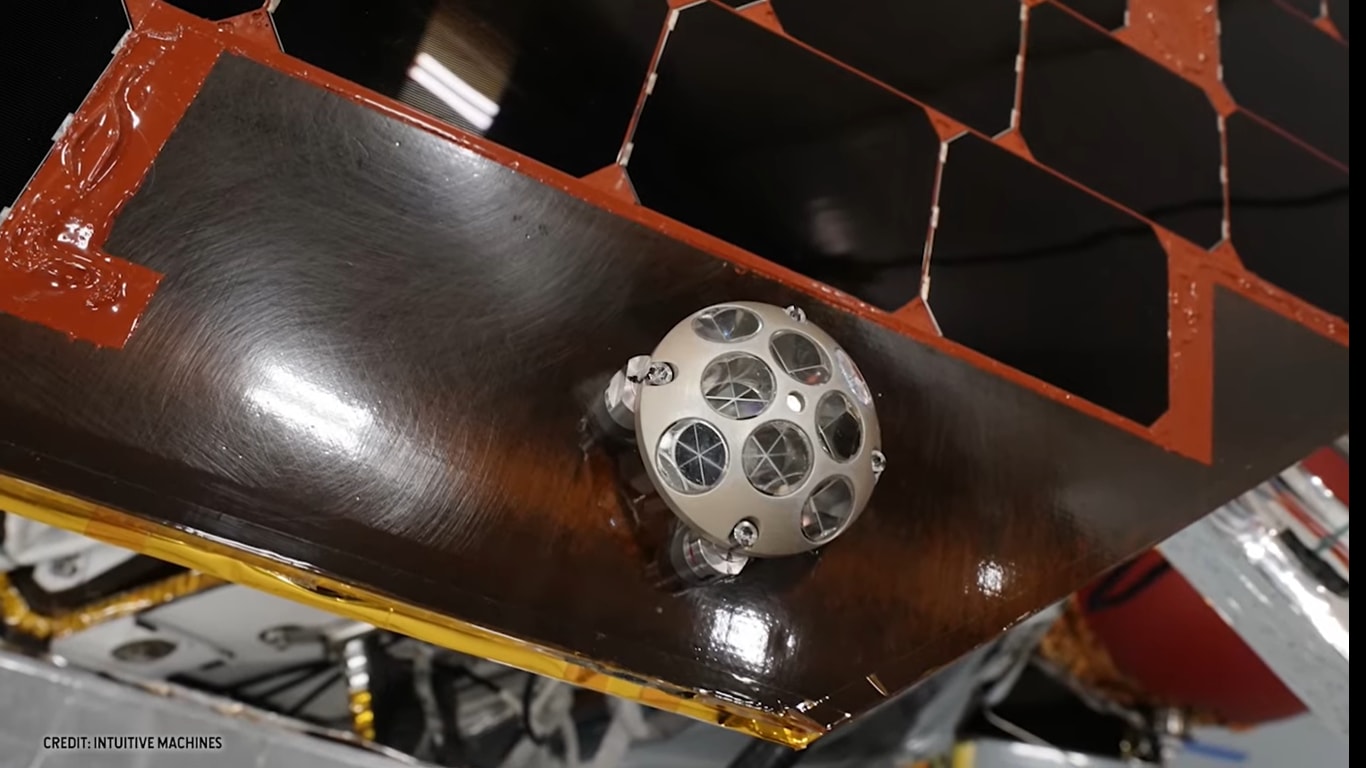
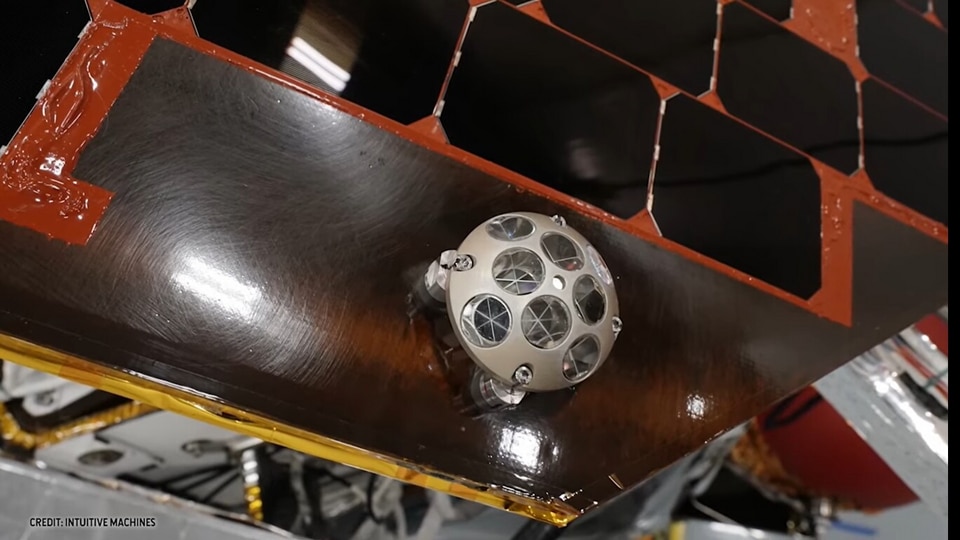
NASA's lunar mission tracking device: Know all about Laser Retroreflective Arrays
Know all about NASA’s lunar mission tracking device called Laser Retroreflective Arrays.
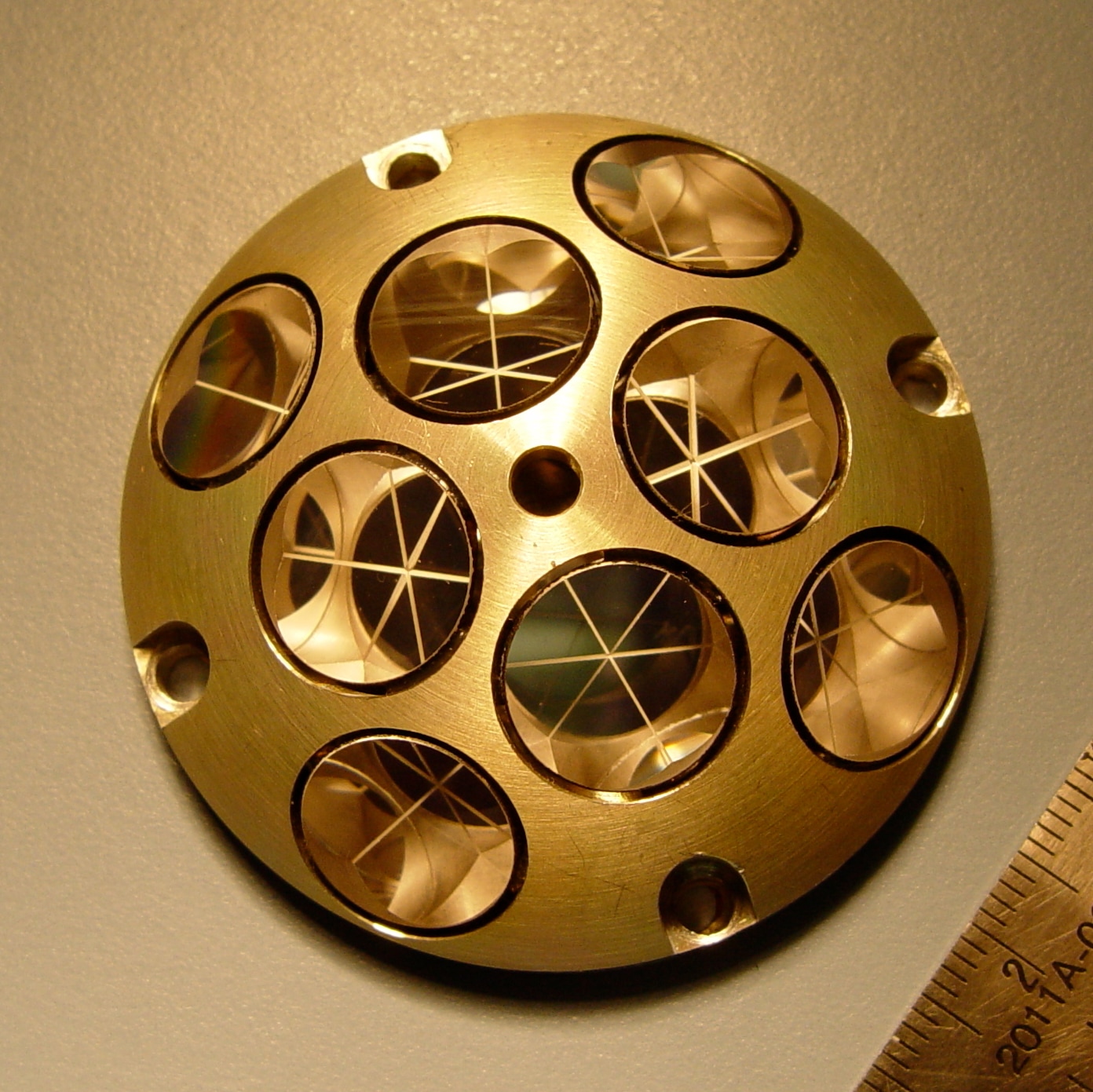
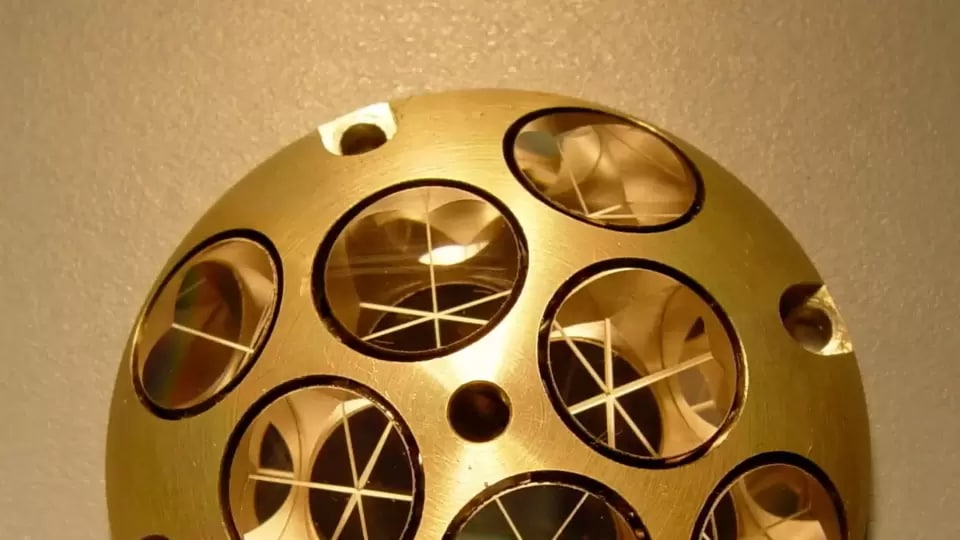
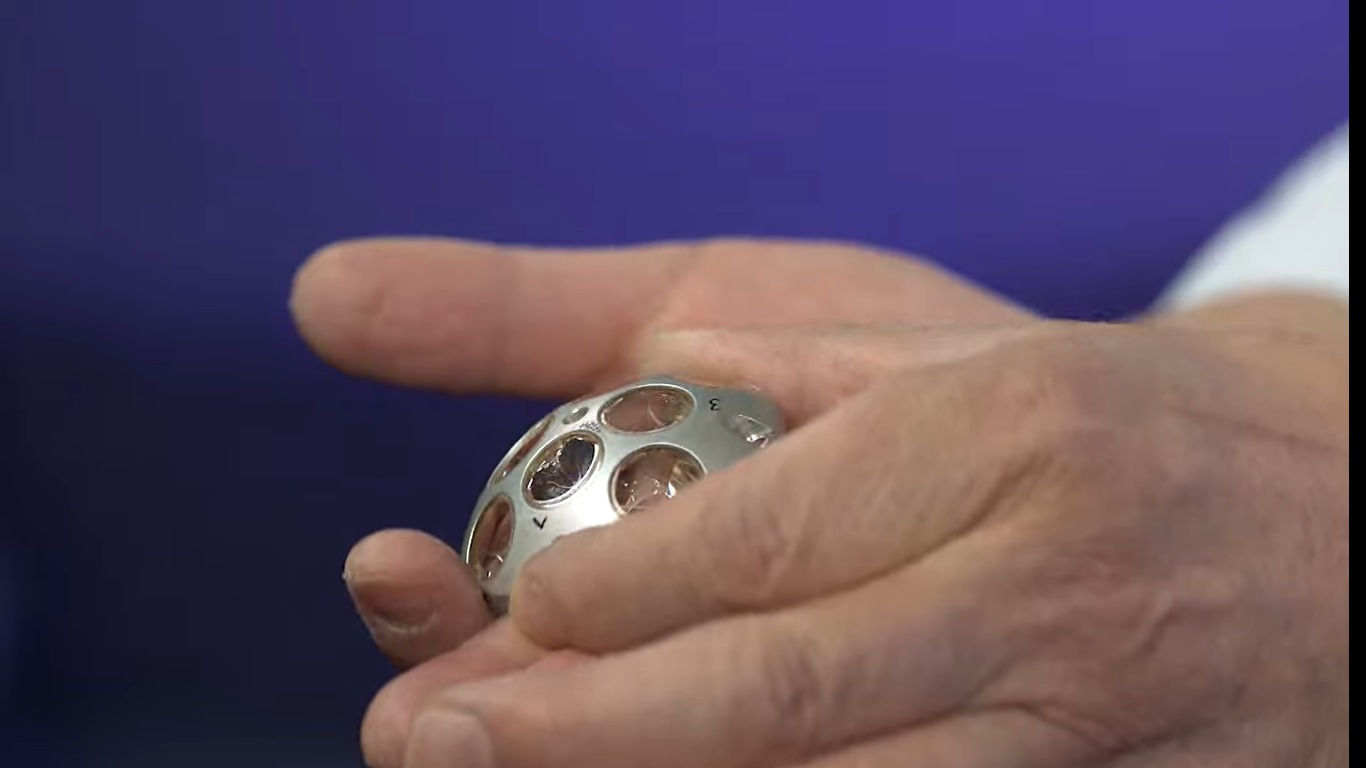
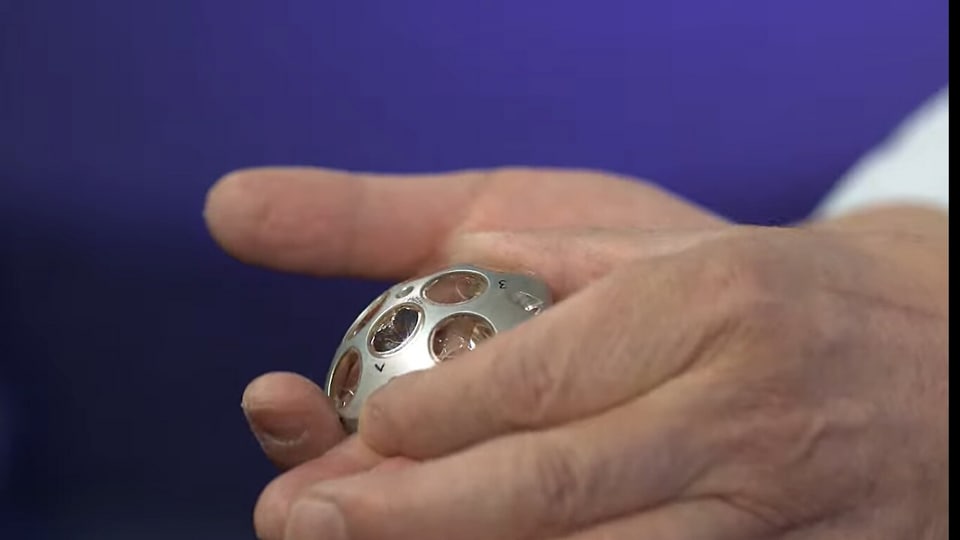







First Published Date: 15 Feb, 17:34 IST
Tags:
nasa
NEXT ARTICLE BEGINS