NASA's James Webb Telescope exceeds expectations again, snaps Pandora cluster in fine detail
NASA’s James Webb Telescope has managed to capture never-seen-before details of the Pandora cluster. Have a look.


_1661230453587.jpg)



 View all Images
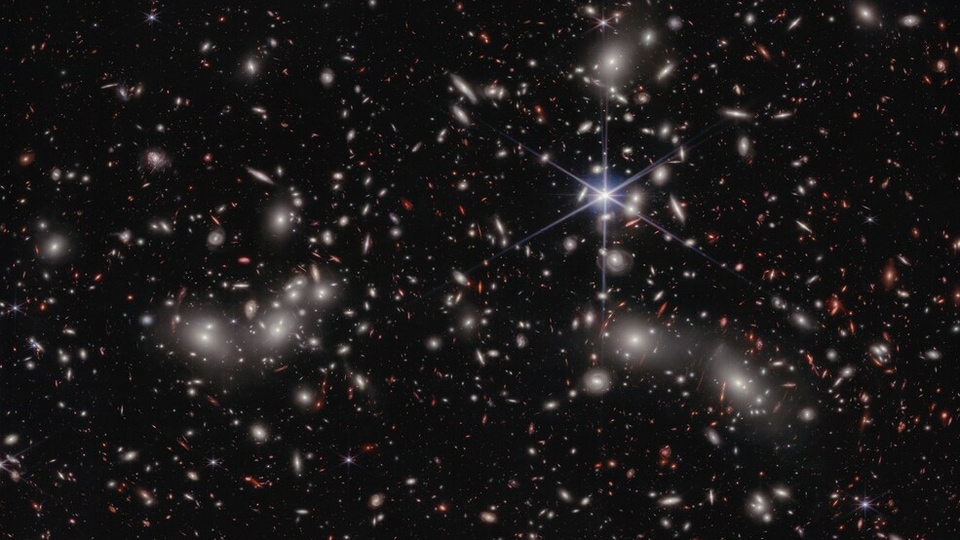
View all ImagesNASA's James Webb Space Telescope has shared another surprising view of a celestial object. The James Webb Telescope has captured the region in space identified as Pandora's Cluster (Abell 2744), which reveals three already enormous clusters of galaxies converging to create a mega-cluster. This combined mass generates a potent gravitational lens, a natural effect of gravity that amplifies the observation of galaxies in the early universe located far beyond the cluster by utilizing it like a magnifying glass.
Earlier, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope had captured only the central core of Pandora. Thanks to the great and powerful infrared instruments combined with a broad mosaic view of the region's multiple areas of lensing of the Webb telescope, astronomers could achieve a balance of breadth and depth to study cosmology and galaxy evolution.
“When the images of Pandora's Cluster first came in from Webb, we were honestly a little star struck. There was so much detail in the foreground cluster and so many distant lensed galaxies, I found myself getting lost in the image. Webb exceeded our expectations,” a NASA blog quoted astronomer Rachel Bezanson of the University of Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania.
Webb's new view of Pandora's Cluster stitches 4 snapshots together into a panorama, showing 3 separate galaxy clusters merging into a mega-cluster and some 50,000 sources of near-infrared.
Tech behind James Webb Space Telescope that captured Pandora image
Researchers utilized Webb's Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) to capture the cluster by taking exposures lasting between 4 to 6 hours, resulting in an overall observing time of approximately 30 hours. After that, the team analyzes the imaging data to select specific galaxies for further observation with the Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec), allowing for precise distance measurements and providing detailed information about the composition of the lensed galaxies. It offers new insights into the early stages of galaxy assembly and evolution.
"The imaging mosaics and catalog of sources on Pandora's Cluster (Abell 2744) provided by the UNCOVER team combine publicly available Hubble data with Webb photometry from three early observation programs: JWST-GO-2561, JWST-DD-ERS-1324, and JWST-DD-2756," NASA said in a blog.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.
































