NASA reveals 5 asteroids zooming towards Earth! Check speed, size and more
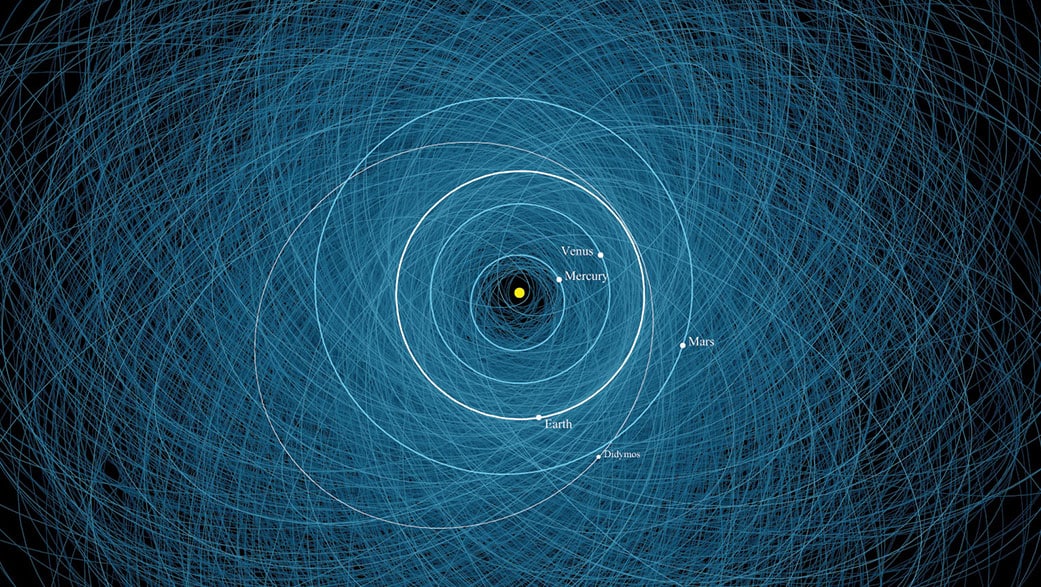
NASA has revealed details such as speed, distance of approach, and size of 5 asteroids that have been tracked approaching Earth at a close distance over the next few days.









First Published Date: 16 Jun, 13:36 IST
NEXT ARTICLE BEGINS