NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day 17 March 2023: Mythological Medusa Nebula; meet Abell 21
NASA's Astronomy Picture of the Day is a picture of the Medusa Nebula located in the Gemini constellation.





 View all Images
View all ImagesNebulae are one of the most spectacular sights to see in space. These celestial objects are a giant cloud of dust and gas in space, according to NASA. Nebulae exist in interstellar space, which is the space between stars. Some nebulae originate from the gas and dust thrown out by the explosion of a dying star while other nebulae are star-forming regions. Due to the star-forming nature of Nebulae, they are also known as Star Nurseries. A Nebula can contain as few as ten stars or as many as millions of stars.
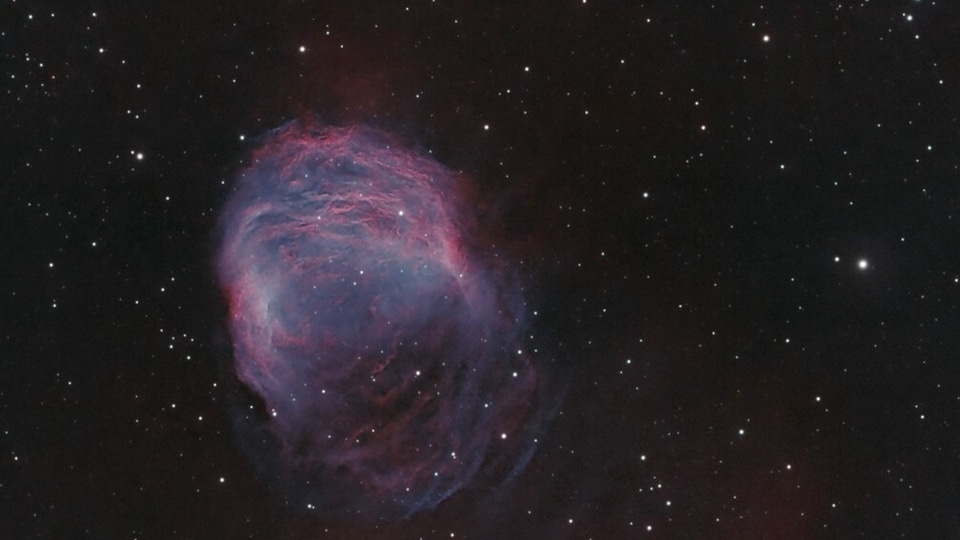
Today's NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day is a picture of Abell 21, which is also known as the Medusa Nebula due to the serpentine filaments of gas in the cloud. According to NASA, the Medusa Nebula is an old planetary nebula located in the Gemini constellation about 1500 light-years away and spans nearly 4 light-years across.
The picture was captured by astronomer Martin Bradley of the Chesterfield Astronomical Society.
How is a Nebula captured?
In order to see and capture pictures of nebulae, astronomers use very powerful telescopes. Space telescopes such as NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and Hubble Space Telescope are used for the same.
NASA's description of the picture
Braided and serpentine filaments of glowing gas suggest this nebula's popular name, The Medusa Nebula. Also known as Abell 21, this Medusa is an old planetary nebula some 1,500 light-years away in the constellation Gemini. Like its mythological namesake, the nebula is associated with a dramatic transformation.
The planetary nebula phase represents a final stage in the evolution of low mass stars like the sun as they transform themselves from red giants to hot white dwarf stars and in the process shrug off their outer layers. Ultraviolet radiation from the hot star powers the nebular glow. The Medusa's transforming star is the faint one near the center of the overall bright crescent shape. In this deep telescopic view, fainter filaments clearly extend below and right of the bright crescent region. The Medusa Nebula is estimated to be over 4 light-years across.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.
































