NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day 6 February 2023: Heart of the Rosette Nebula
NASA’s Astronomy Picture of the Day is an amazing image revealing the heart of the Rosette Nebula.







 View all Images
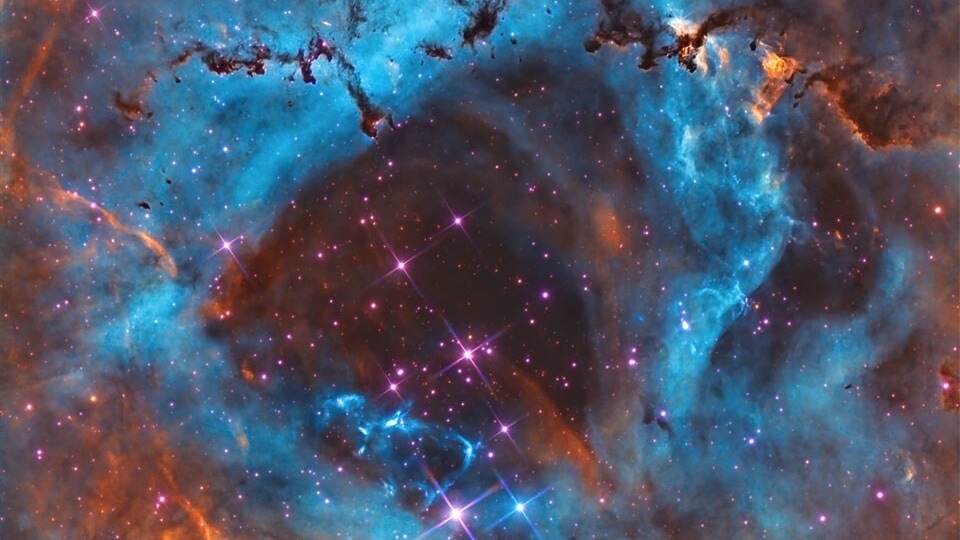
View all ImagesA breathtaking image of a nebula, which is around 5200 light-years away from Earth has been featured as the NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day. While explaining the image, NASA says in the heart of the Rosette Nebula, there lies a bright cluster of stars that light up the nebula. NGC 2244's stars only formed a few million years ago from the surrounding gas. The center of the Rosette Nebula, visible through binoculars in the Monoceros constellation, measures about 50 light-years in diameter.
NASA further mentioned that the featured image was captured in mid-January using multiple exposures and specific colours. Sulfur is shown in red, Hydrogen in green, and Oxygen in blue, providing a highly detailed view of the central region. A hot wind of particles from the cluster stars contributes to the intricate mix of gas and dust filaments, while also gradually clearing the cluster center.
How do scientists name Nebulae
Scientists have uncovered amazing information about the Rosette Nebula since the 1880s. Currently, they categorize different parts of the cloud of gas and dust as NGC 2237, NGC 2238, NGC 2239, NGC 2244, and NGC 2246, and have started mapping the nebula. The term "NGC" is short for "New General Catalog", an updated version of the nebulae catalog created by Danish astronomer Johan Ludvig Emil Dreyer, theplanets.org said.
How do nebulae forms
According to the report, scientists now think that nebulae form due to either the death of a star or the birth of stars. The gas and dust within a nebula typically contains Hydrogen and Helium. Sometimes, this material spreads throughout space as a result of a supernova, which is the explosive death of an old star.
While in some other scenarios, NASA suggests that space dust aggregates in "star nurseries". When dense clumps of gas and dust collapse, they heat up and may give rise to new stars. The central clear area of the Rosette Nebula is believed by many scientists to contain recently formed stars, while the red areas of the nebula are likely sites of star formation.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.
































