1600-foot, oddly shaped asteroid as big as Empire State Building tracked down by NASA
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory has captured a detailed view of an elongated asteroid over a couple of days. Here's what has been revealed.




 View all Images
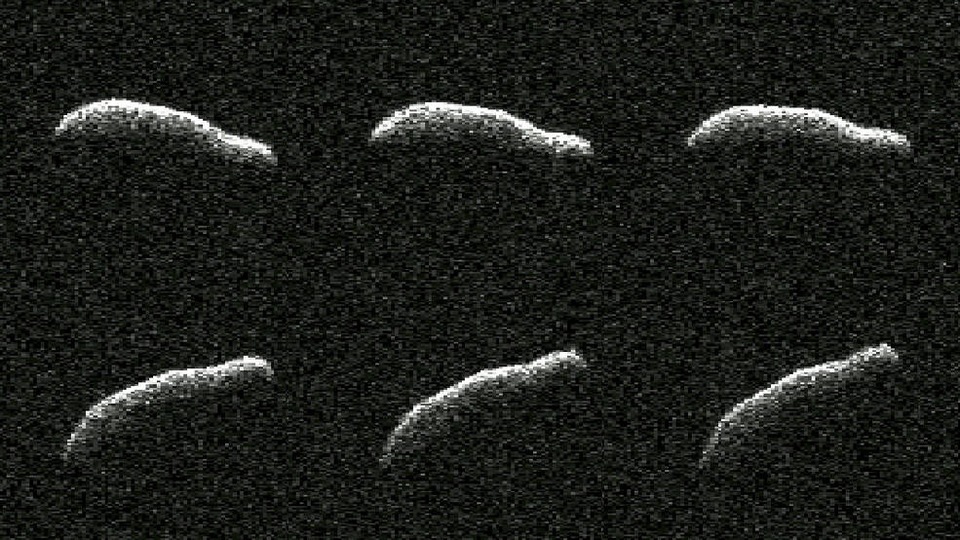
View all ImagesNASA and other space agencies keep an active eye on asteroids. Now, NASA has found one of the most elongated asteroids amongst the 1040 near-Earth objects observed by planetary radar to date. February 3 witnessed the passage of a sizable asteroid that was over three times longer than its width and safely flew past Earth at a distance of around 1.1 million miles, which is slightly under five times the distance between the Moon and our planet. Despite the fact that there was no possibility of the asteroid, named 2011 AG5, colliding with Earth, scientists at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory kept a close eye on it, collecting precious data to determine its size, surface features, rotational speed, and, significantly, its shape.
NASA says that this close approach provided the first opportunity to take a detailed look at the asteroid which is as big as the Empire State Building. The asteroid discovered in 2011 is about 1600 feet long and about 500 feet wide. The study of the asteroid took place from January 29 to February 4, 2023 which shared several other details such as asteroid 2011 AG5 showcases a large, broad concavity in one of the asteroid's two hemispheres, along with faint areas of both darker and lighter shades. This suggests the existence of small, surface-level attributes measuring a few dozen meters in diameter.
In terms of appearance, it would seem as dark as charcoal to the naked eye. Further observations confirmed that 2011 AG5 rotates slowly, completing a full revolution every nine hours. The asteroid 2011 AG5 has an orbit around the Sun that takes around 621 days to complete, and it won't come close to Earth until 2040. At that time, it will pass by Earth at a safe distance of roughly 670,000 miles or 1.1 million kilometres, which is almost three times the distance between the Earth and the Moon. Know that the average distance between Earth and the moon is about 239,000 miles.
Tech behind the asteroid observation
The powerful 230-foot (70-meter) Goldstone Solar System Radar antenna dish at the Deep Space Network's facility near Barstow, California, revealed the dimensions and solar orbit of this elongated asteroid.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.































