Powerful M-class solar flare sparks blackout over Atlantic Ocean! NOAA shares details
An unstable sunspot, AR3335 has exploded producing a solar flare that triggered blackouts over the Atlantic Ocean.





 View all Images
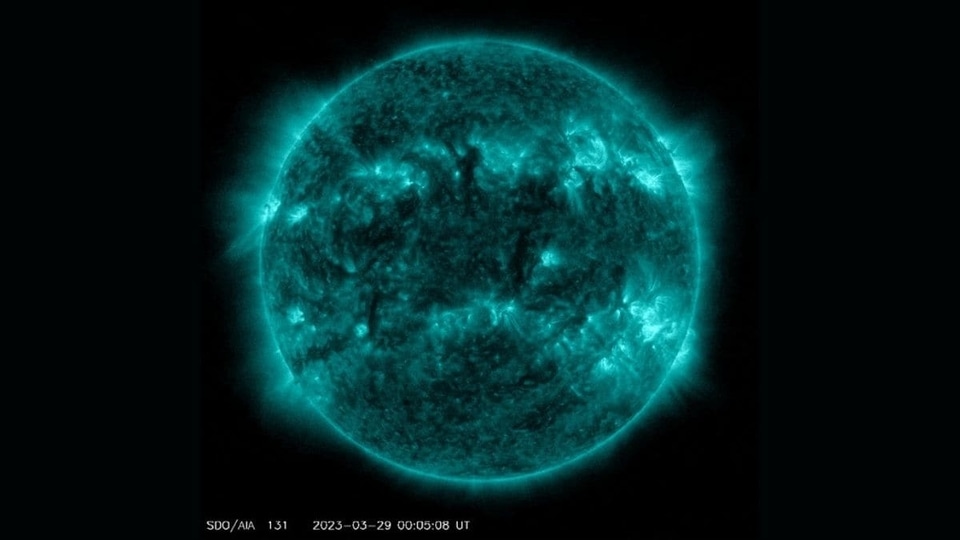
View all ImagesOver the recent weeks, the Sun has emitted massive amounts of energy in the form of solar flares. While some of these flares unleashed from the Sun pass harmlessly into space, others hit Earth, resulting in geomagnetic storms. Over the past few days, an unstable sunspot named AR3335 has caused concerns due to the possibility of it releasing hazardous solar flares. For those unfamiliar, a sunspot is a dark area on the Sun's surface that appears due to intense magnetic activity.
As per a SpaceWeather.com report, this unstable Sunspot AR3335 exploded on June 18th. Resultantly, it produced an M2.5-class solar flare. “The explosion lasted long enough to lift a CME out of the sun's atmosphere since confirmed by SOHO coronagraphs,” the report added.
How strong it is? According to NASA, solar flares are classified based on their intensity using a scale that starts with A-class flares, which are the smallest and near background levels. It then advances through B, C, M, and X classes, with each subsequent class indicating a tenfold increase in strength. Consequently, an X-class flare is ten times more potent than an M-class flare and a hundred times more intense than a C-class flare.
Solar Flare Impact on Earth
This strong M2.5-class solar flare has also caused a shortwave radio blackout over the Atlantic Ocean, a SpaceWeather.com report mentioned. NOAA forecasters have also confirmed that Radio blackouts reached the R1 levels over the past 24, while the largest was on Jun 18, 2023. For the next three days, there is a chance for R1-R2 (Minor-Moderate) radio blackouts and a slight chance for R3 (Strong) or greater blackouts. However, NOAA analysts are currently modelling the coronal mass ejection (CME) to determine whether it possesses a component that is directed towards Earth.
Tech to detect solar flares
The joint operation between NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) oversees the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-16 (GOES-16). This satellite plays a crucial role in various functions such as sensing, solar imaging, and measuring the space environment. In addition to GOES-16, NASA operates several other spacecraft dedicated to monitoring the Sun, including SOHO, ACE, IRIS, WIND, Hinode, the Solar Dynamics Observatory, and STEREO.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.




































