NASA found this 4x MASSIVE Super Earth with the possibility of life
Another planet with a possibility of life has been detected by NASA behind the Milky Way Galaxy. Know all details here.





 View all Images
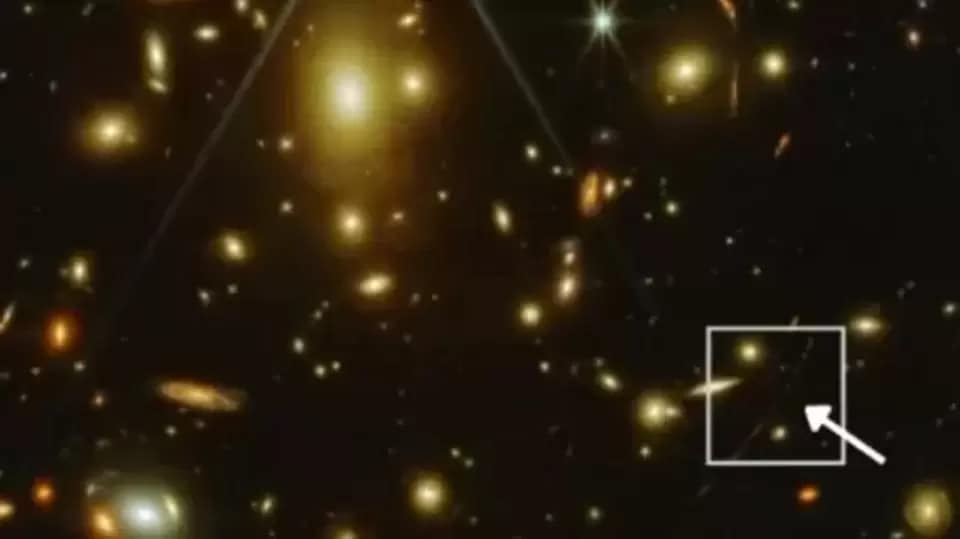
View all ImagesAnother world with life! NASA has found a new Earth-like planet which is quite far and on the outskirts of the Milky Way galaxy. This newly found Super Earth named Ross 508 b has raised expectations of the astronomers as it is in the habitable zone of its Red Dwarf star. This Earth-like planet was discovered by the Subaru Strategic Program using the infrared spectrograph on the Subaru Telescope.
The only concern is that this Earth-like planet, which is a potentially rocky world larger than Earth, is moving in and out of its habitable zone. Still, there it offers hope that it retains water on its surface, which means the possibility of life! According to NASA, Ross 508 b is a super Earth exoplanet that orbits an M-type star, located about 37 light-years away from the Earth. Its mass is 4 Earths, it takes 10.8 days to complete one orbit of its star, and is 0.05366 AU from its star.
Also read: India's AstroSat telescope makes awesome discovery in space
But how do scientists decide about the habitable zone for exo-planets? To detect the habitable conditions, scientists find Goldilocks zones which is basically described as the distance from a star at which liquid water could exist on the surface of the orbiting planets. This indicated the conditions which might be appropriate for life. According to NASA, this Super Earth Ross 508 b moves through this Goldilocks zone.
“Its orbit takes it in, and out, of its star's habitable zone. Such a planet may be able to retain water on its surface and will be an important target for future observations to study the possibility of life around low-mass stars like the M dwarf it orbits. Red dwarfs, which constitute three-quarters of the stars in our galaxy and exist in large numbers in the vicinity of our solar system, are excellent targets to find exoplanets in our neighborhood,” NASA said in a statement. So far, the only other planet with a habitable planet is Proxima Centauri b.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.