Asteroid Ryugu is older than the Sun, Earth, even solar system, says this shocking new discovery
Asteroid Ryugu’s collected samples revealed that they are aged even before the solar system was made. Know all details here.



_1639115875543_1639115887157.jpg)


 View all Images
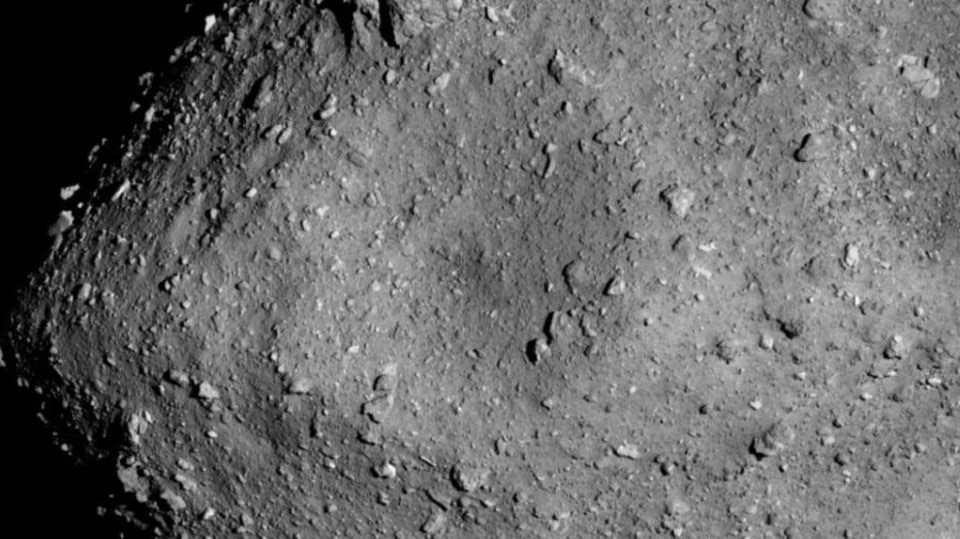
View all ImagesThe small fragments of the giant space rock named Asteroid Ryugu brought to Erth have led to a shocking discovery. Scientists have analyzed the samples of asteroid Ryugu that have revealed the presence of microscopic grains of ancient materials that are even older than the Sun, Earth or even the Solar System. The presence of some these grains of the asteroid indicate that parts of Ryugu may have remained unchanged since the formation of the asteroid, the researchers revealed in the paper titled "Presolar Stardust in Asteroid Ryugu" published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
The Hayabusa2 spacecraft of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) was designed to reeach and explore Asteroid Ryugu from June 2018 to November 2019 in order to reveal some scerets of the creation of life and the birth of the Solar System. The Hayabusa2 spacecraft arrived at asteroid Ryugu on June 27, 2018, collected samples during two touchdowns in 2019, and delivered it back to the Earth on December 6, 2020. Astonishingly, the study revealed that the returned samples of Asteroid Ryugu contain presolar stardust grains. What does it mean? Know in detail here.
Asteroid Ryugu samples have a secret
The researchers mentioned in the research paper that the abundances and compositions of the presolar stardust grains are similar to the presolar material found in CI chondrites. "Thus, our results provide further evidence that asteroid Ryugu is closely related to CI chondrites. However, small regions of Ryugu escaped extensive alteration and allowed their preservation," the researchers explained in their paper.
Presolar grains are finished goods as snapshots of processes occurring in distant stars; as such, they are a direct record of those stars and their chemistry. This is due to the preservation of the isotope ratios in presolar grains. They can be studied to understand the evolution of stars other than the Sun and the rocks that make up the Solar System.
More interestingly, these presolar grains are rare. They are frequently discovered in carbonaceous chondrites, which account for a relatively minor portion of all meteorites that strike the Earth. Furthermore, presolar grains have been discovered in only around 5 percent of carbonaceous chondrites.
"They also reveal intriguing hints of small-scale heterogeneities in the Ryugu samples, such as locally distinct degrees of alteration that allowed the preservation of delicate presolar material," researchers mentioned.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.