NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day 12 January 2023: Star Cluster and Flying Ghost Nebula captured
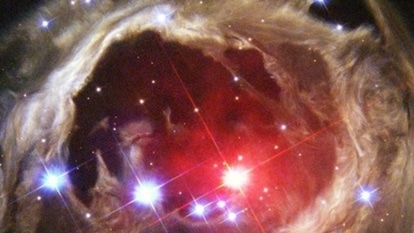
NASA’s Astronomy Picture of the Day is a stunning picture of the star cluster and the Flying Ghost Nebula surrounded by stardust.






 View all Images
View all ImagesStars are the most widely recognized astronomical objects, and represent the most fundamental building blocks of galaxies. They are celestial objects millions of years old floating in space. The older and bigger the star, the brighter it appears. They are formed in star-forming regions called Nebulae. The makeup of a Nebula consists of gases, mainly hydrogen and helium. Gravity within a molecular cloud causes the gas and dust to collapse, forming dense cores. As the cores grow denser and hotter, they begin to fuse hydrogen atoms into helium, which releases energy in the form of light and heat. Once a core reaches a certain temperature and density, a new star is born.
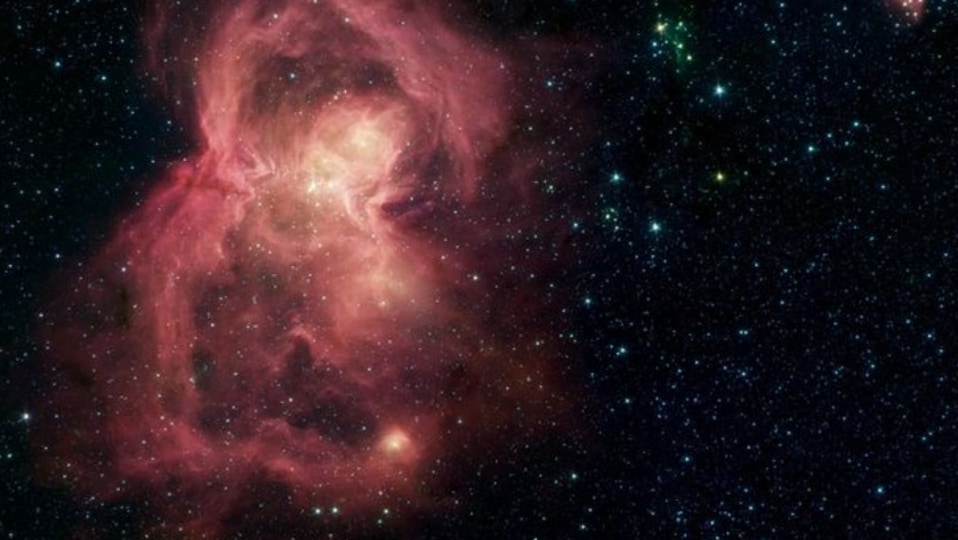
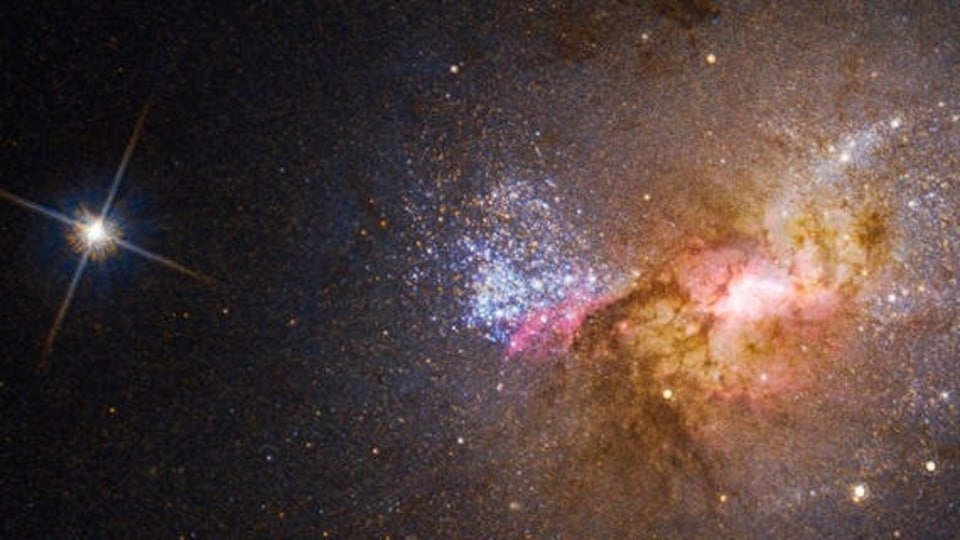
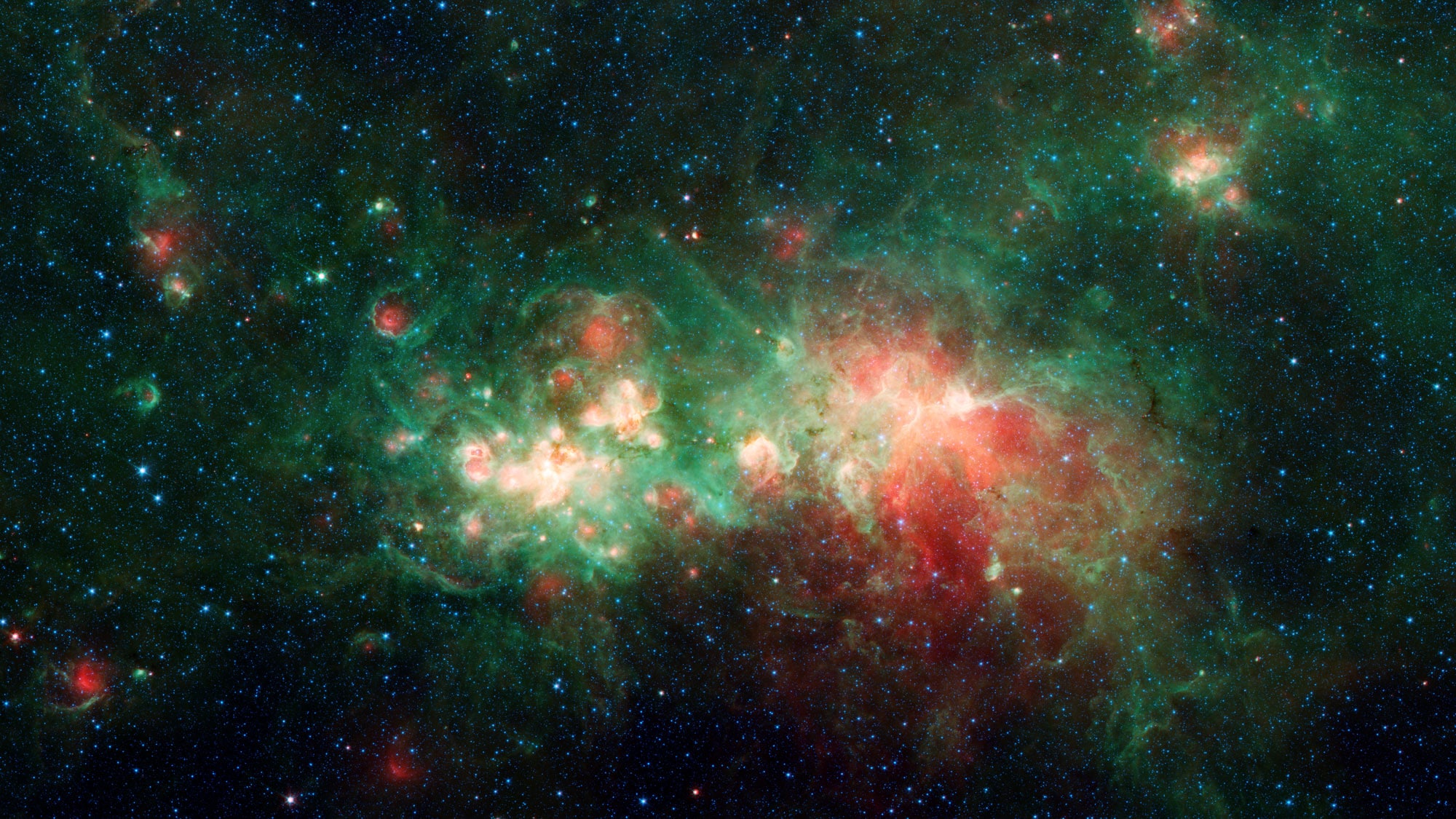
Grouped stars sometimes form patterns in the sky recognized by humans known as Constellations. As of now, there are nearly 88 recognized constellations in the sky. NASA's Astronomy Picture of the Day is a stunning picture of stars and their clusters in the vast expanse of space in the constellation Perseus. The star cluster IC348 can be seen alongside the Flying Ghost Nebula surrounded by interstellar dust termed as Barnard 3 and 4.
The image was captured by Jack Groves, an Amateur astrophotographer from Minnesota, USA.
NASA's explanation
This cosmic expanse of dust, gas, and stars covers some 6 degrees on the sky in the heroic constellation Perseus. At upper left in the gorgeous skyscape is the intriguing young star cluster IC 348 and neighboring Flying Ghost Nebula with clouds of obscuring interstellar dust cataloged as Barnard 3 and 4. At right, another active star forming region NGC 1333 is connected by dark and dusty tendrils on the outskirts of the giant Perseus Molecular Cloud, about 850 light-years away. Other dusty nebulae are scattered around the field of view, along with the faint reddish glow of hydrogen gas.
In fact, the cosmic dust tends to hide the newly formed stars and young stellar objects or protostars from prying optical telescopes. Collapsing due to self-gravity, the protostars form from the dense cores embedded in the molecular cloud. At the molecular cloud's estimated distance, this field of view would span over 90 light-years.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.