NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day 8 March 2023: LIGHT pollution
NASA's Astronomy Picture of the Day is an image highlighting the problem of Light pollution at night around the world. Yes, there is such a thing as light pollution.





 View all Images
View all ImagesTrillions of stars illuminate our Universe. According to NASA, they are the most widely recognized astronomical objects. Although stars are easily visible in the night sky even with the naked eye, it is becoming increasingly difficult to observe the celestial objects in the night sky due to one phenomenon caused by human activity – Light Pollution. In recent times, the impact of human-created light pollution has far exceeded the luminescence produced even by a full Moon. The consequences of this pollution are now evident to a vast number of individuals beyond astronomical society.
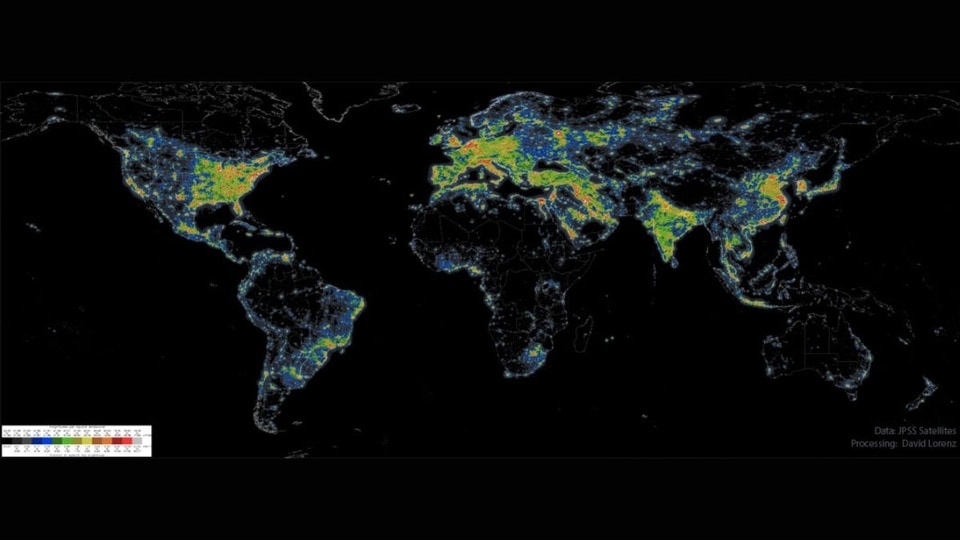
NASA's Astronomy Picture of the Day is a picture showing the artificial brightness present in the night sky, which makes observing celestial objects such as stars, planets and others, increasingly difficult. Parts of the US and Western Europe have artificial night sky glow which is nearly 10 times the natural light in the night sky. In the areas marked red or orange, the central band of the Milky Way Galaxy can no longer be seen.
The picture was generated using data collected by JPSS Satellites and processed by David J. Lorenz.
NASA's description of the picture
Where have all the dim stars gone? From many places on the Earth including major cities, the night sky has been reduced from a fascinating display of thousands of stars to a diffuse glow through which only a few stars are visible. The featured map indicates the relative amount of light pollution that occurs across the Earth. The cause of the pollution is artificial light reflecting off molecules and aerosols in the atmosphere.
Parts of the Eastern United States and Western Europe colored red, for example, have an artificial night sky glow over ten times that of the natural sky. In any area marked orange or red, the central band of our Milky Way Galaxy is no longer visible. The International Dark Sky Association suggests common types of fixtures that provide relatively little amounts of light pollution.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.