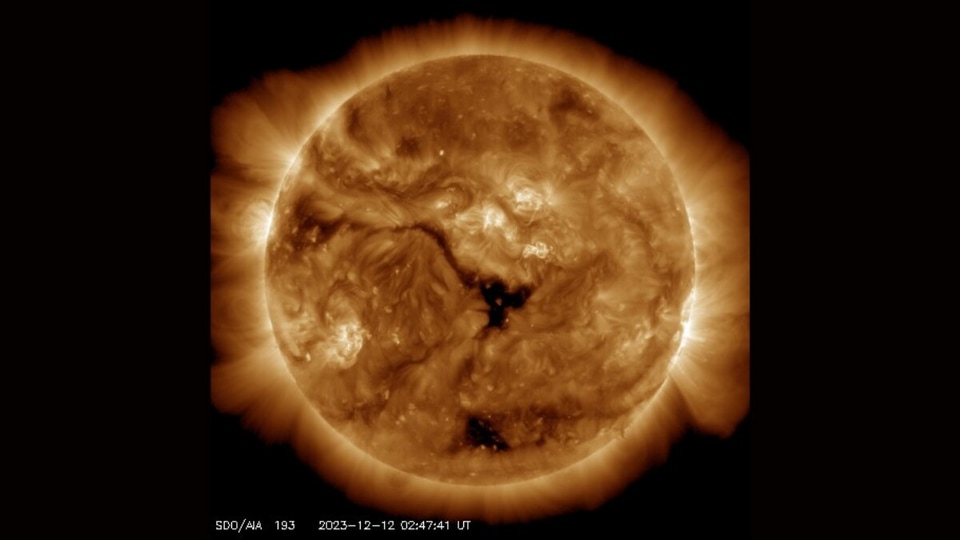
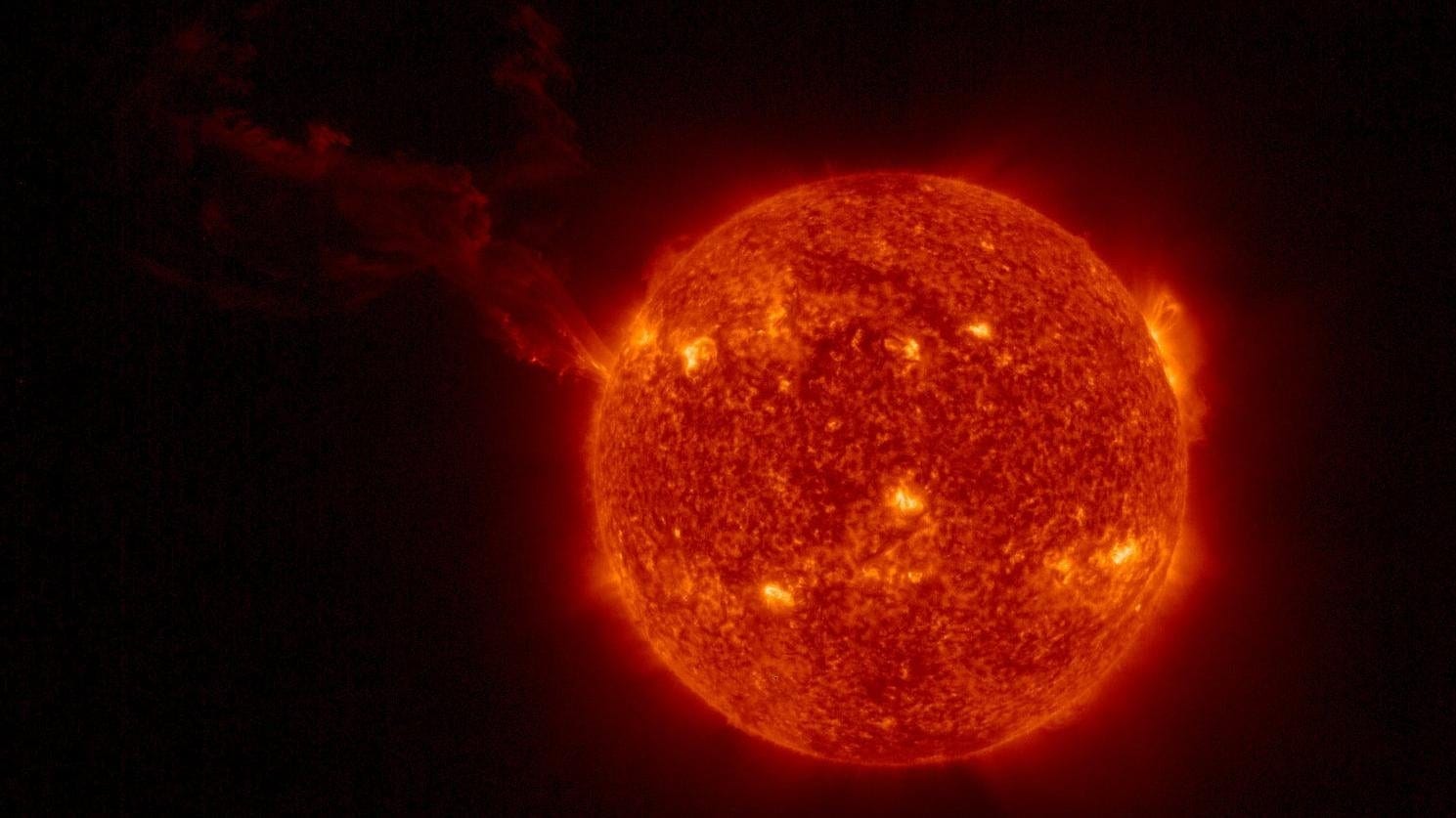
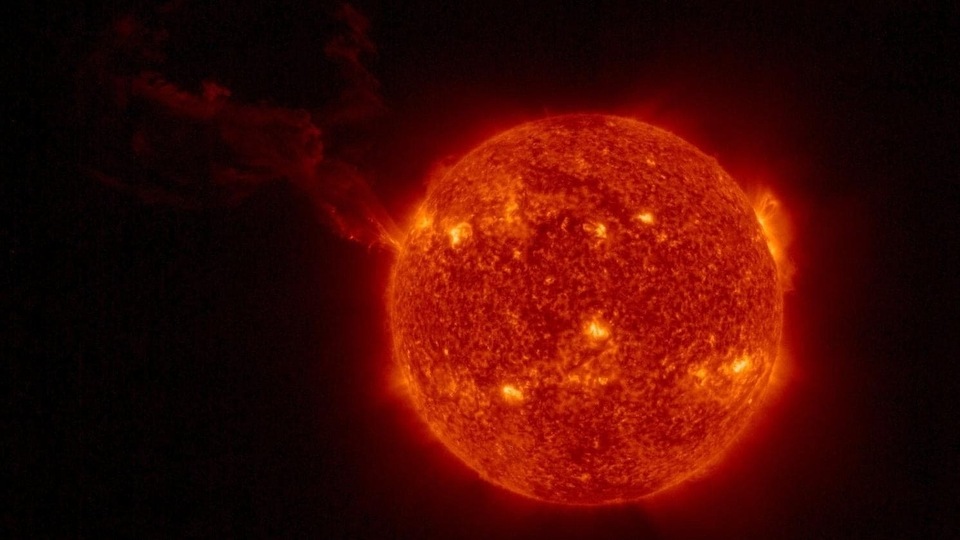
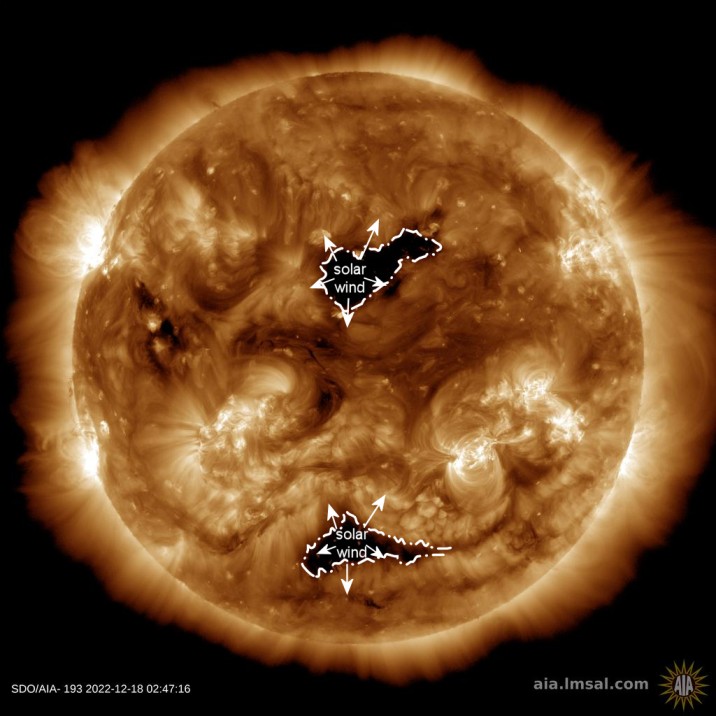
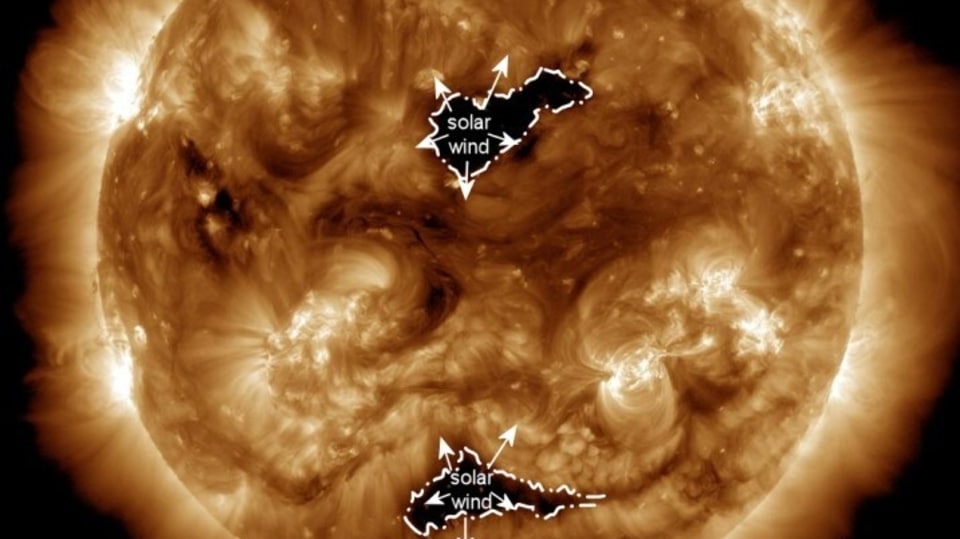
Massive hole opens on the Sun, hurls solar winds towards Earth, says NASA; Solar storm may strike soon
A gigantic hole has ripped open on the surface of the Sun. The solar winds expelled from the hole can reach the Earth in three days, revealed NASA. It is likely to result in a solar storm event.






First Published Date: 12 Dec, 14:26 IST
NEXT ARTICLE BEGINS