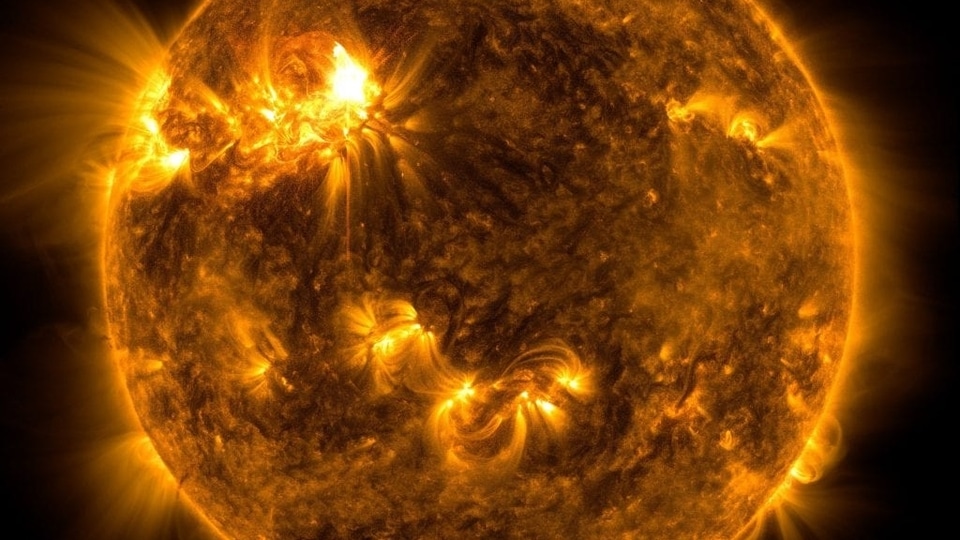
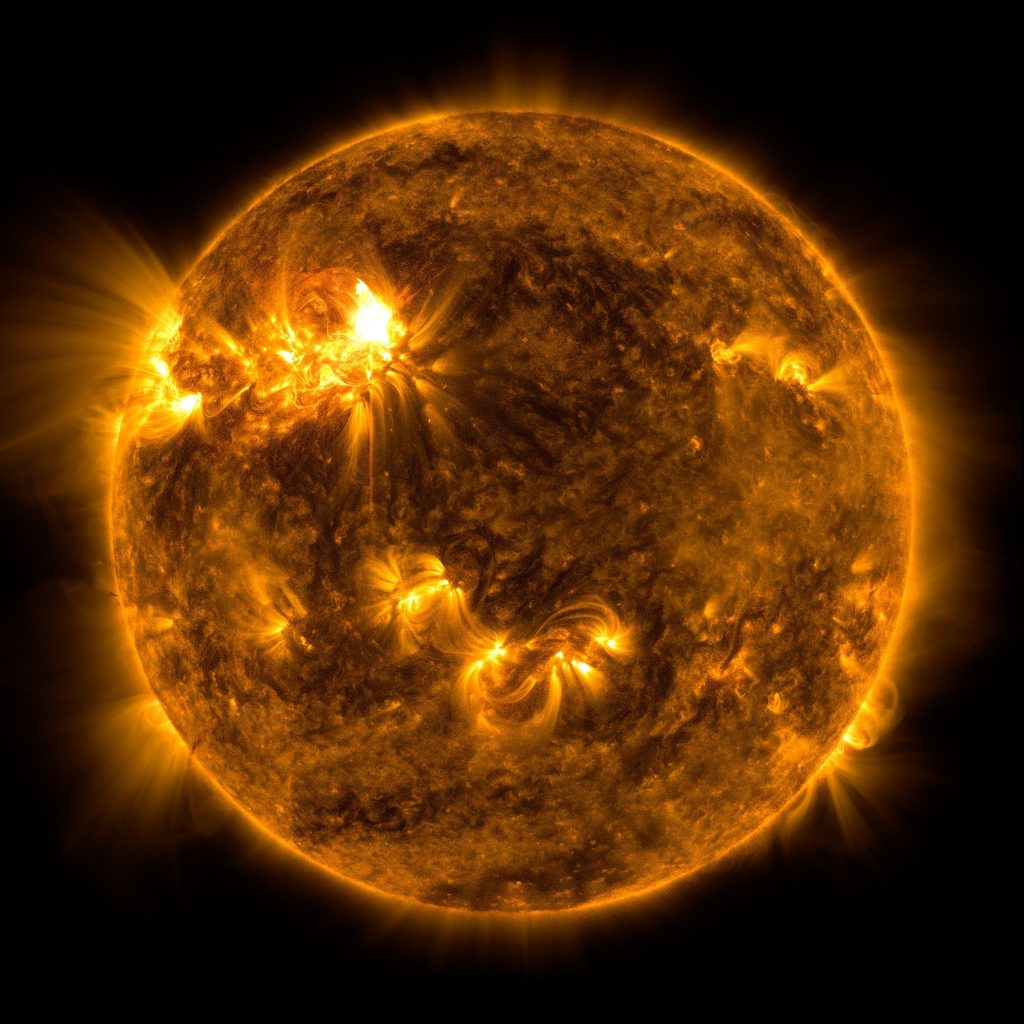
India's Aditya L1 mission to study the Sun, CME, solar flares and more
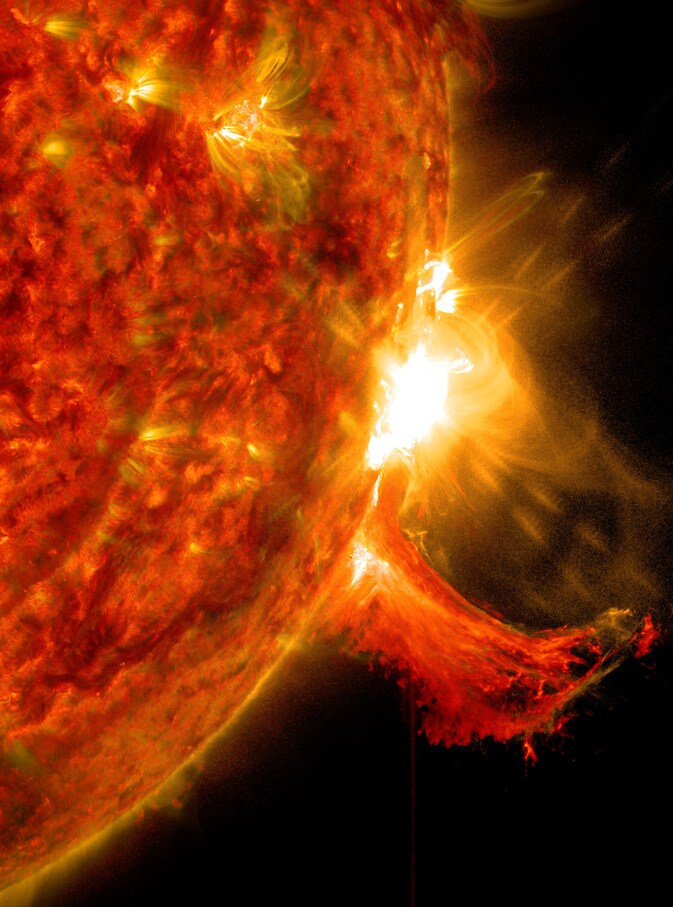
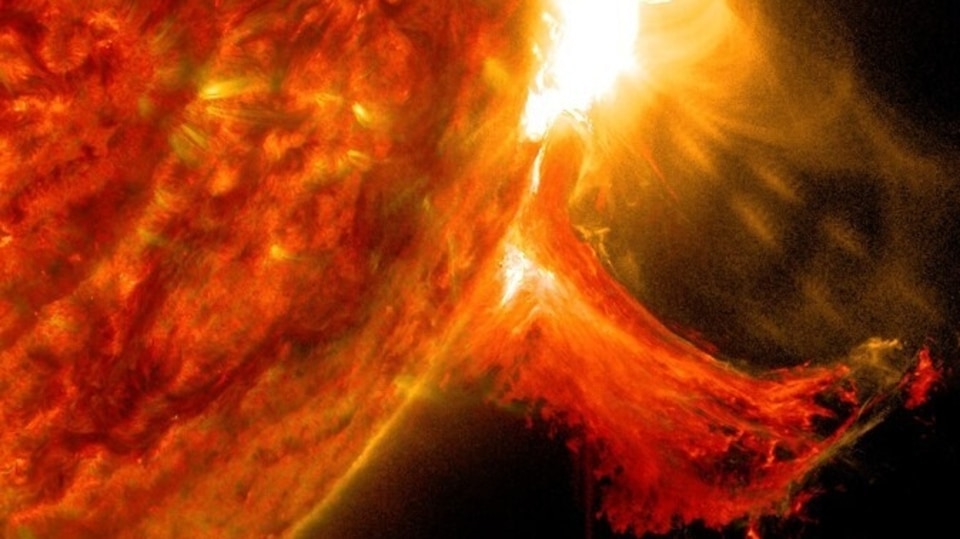
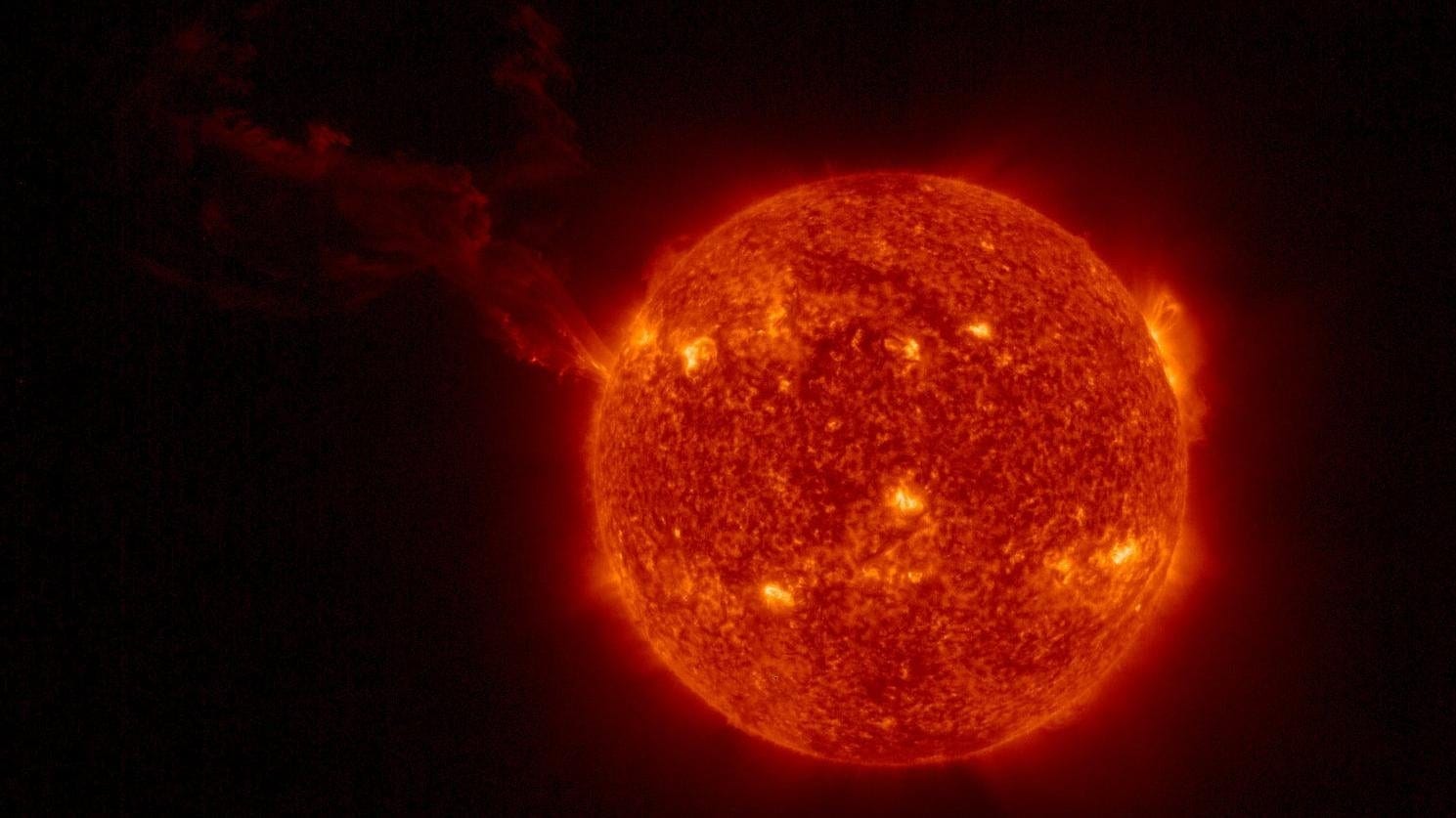
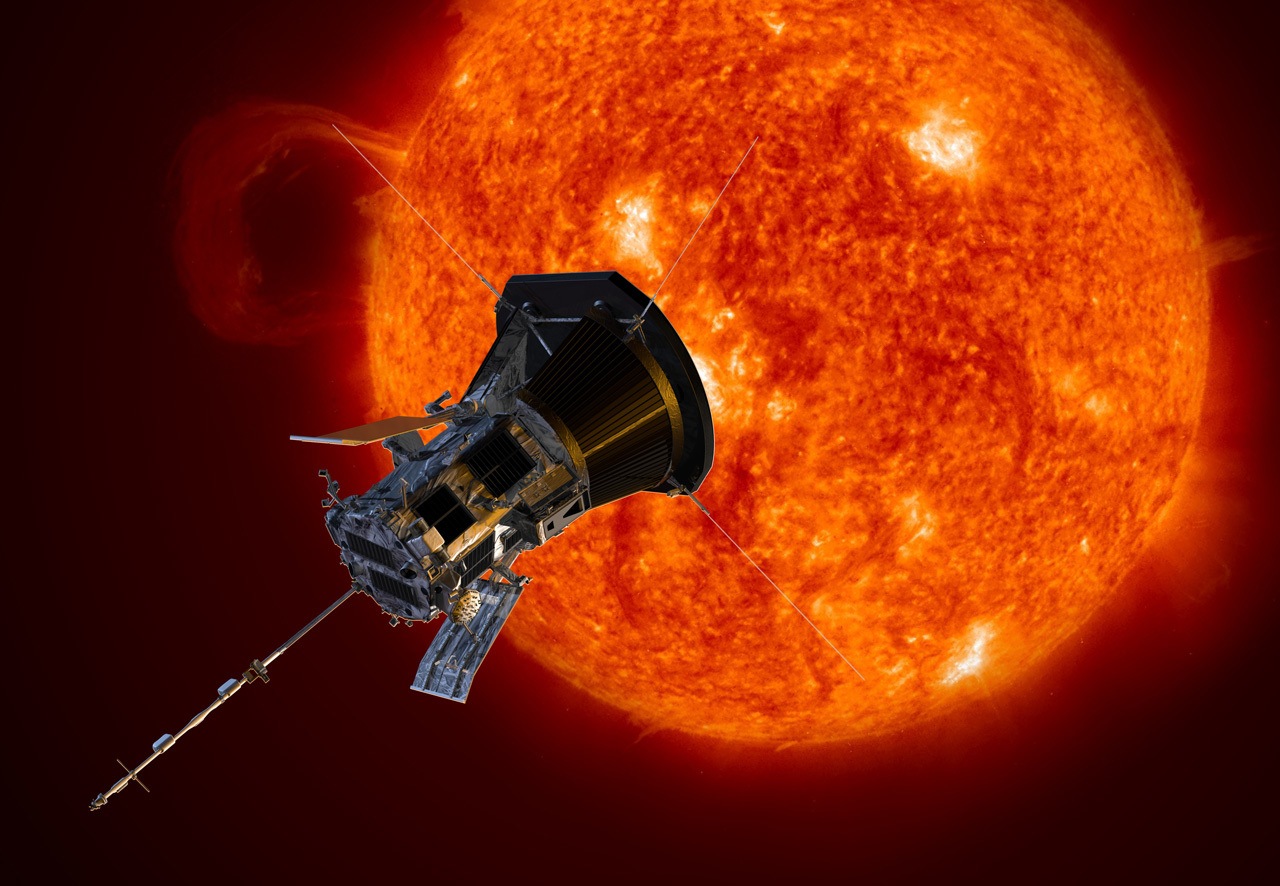
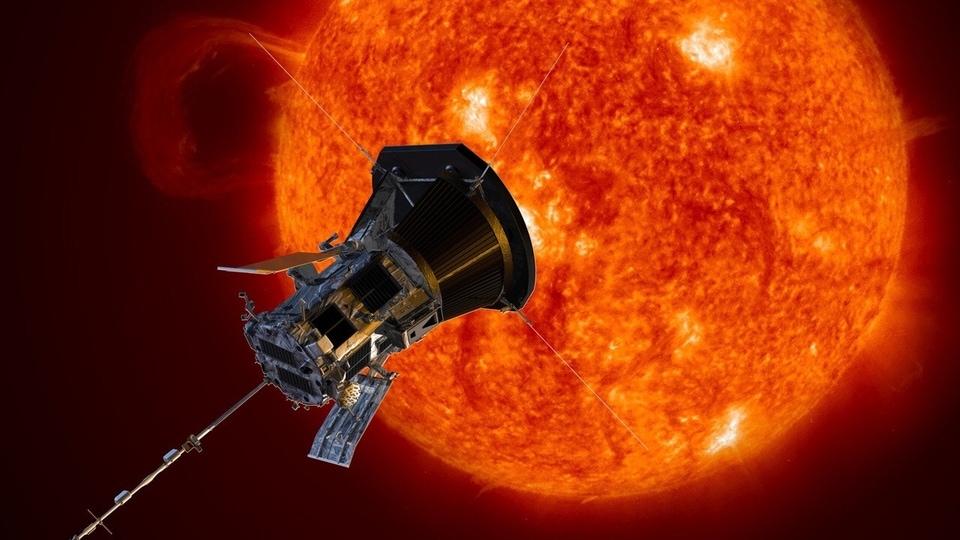
Know all about India’s first space-based solar mission called Aditya L1. The PSLV-C57 is getting ready to launch soon, says ISRO. It will give insights into thw working of the Sun, what generates solar storms like coronal heating, coronal mass ejections, solar flares, and more.











First Published Date: 17 Aug, 09:17 IST
NEXT ARTICLE BEGINS