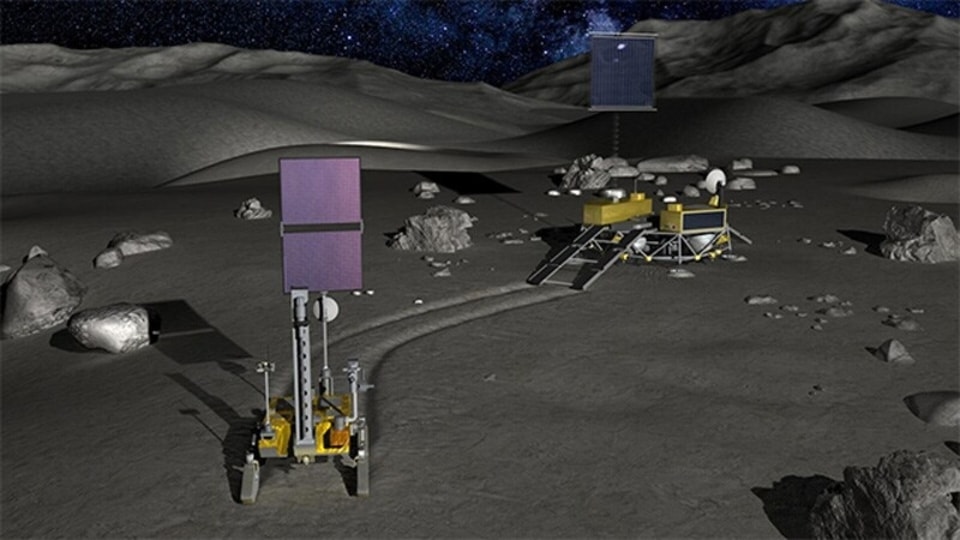
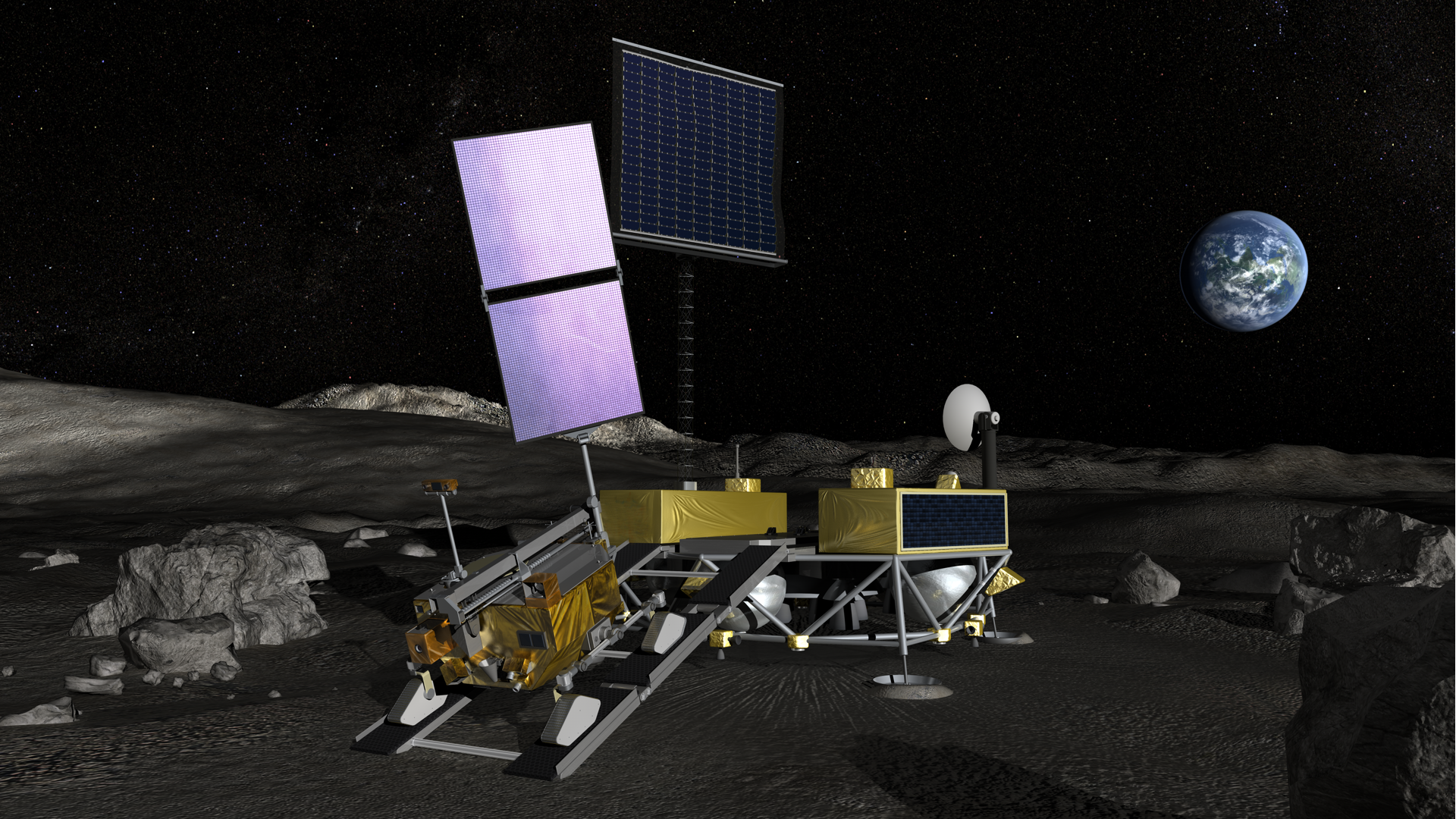
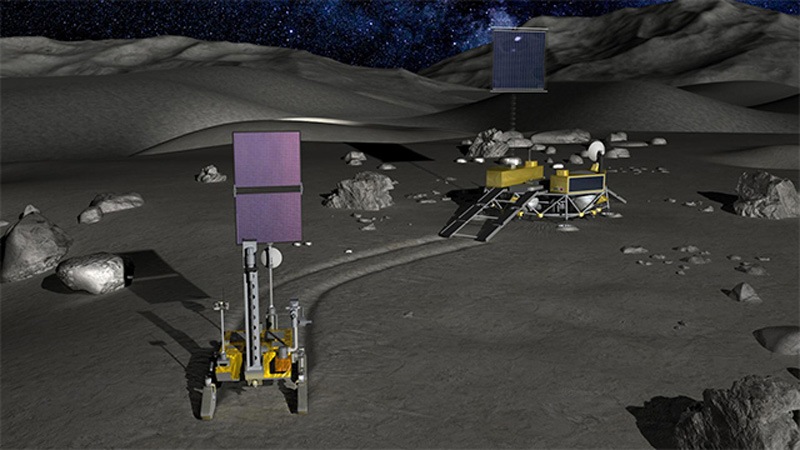
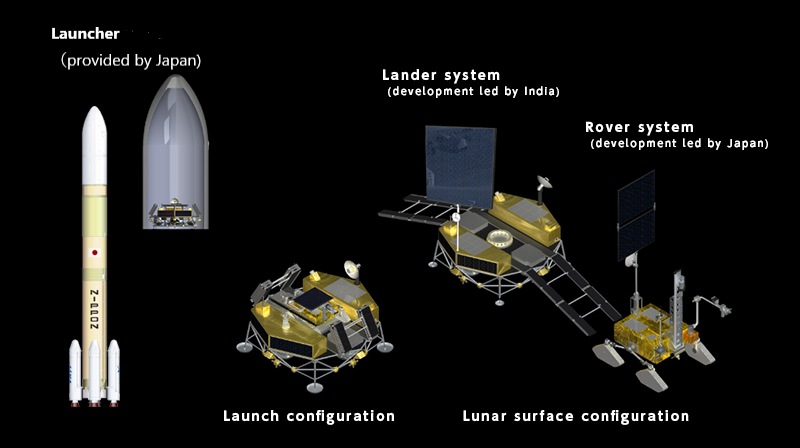
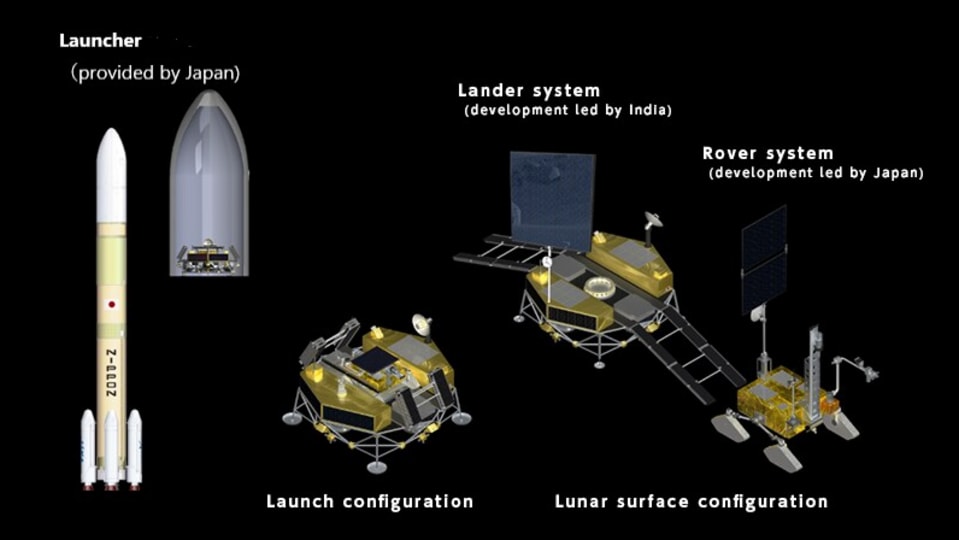
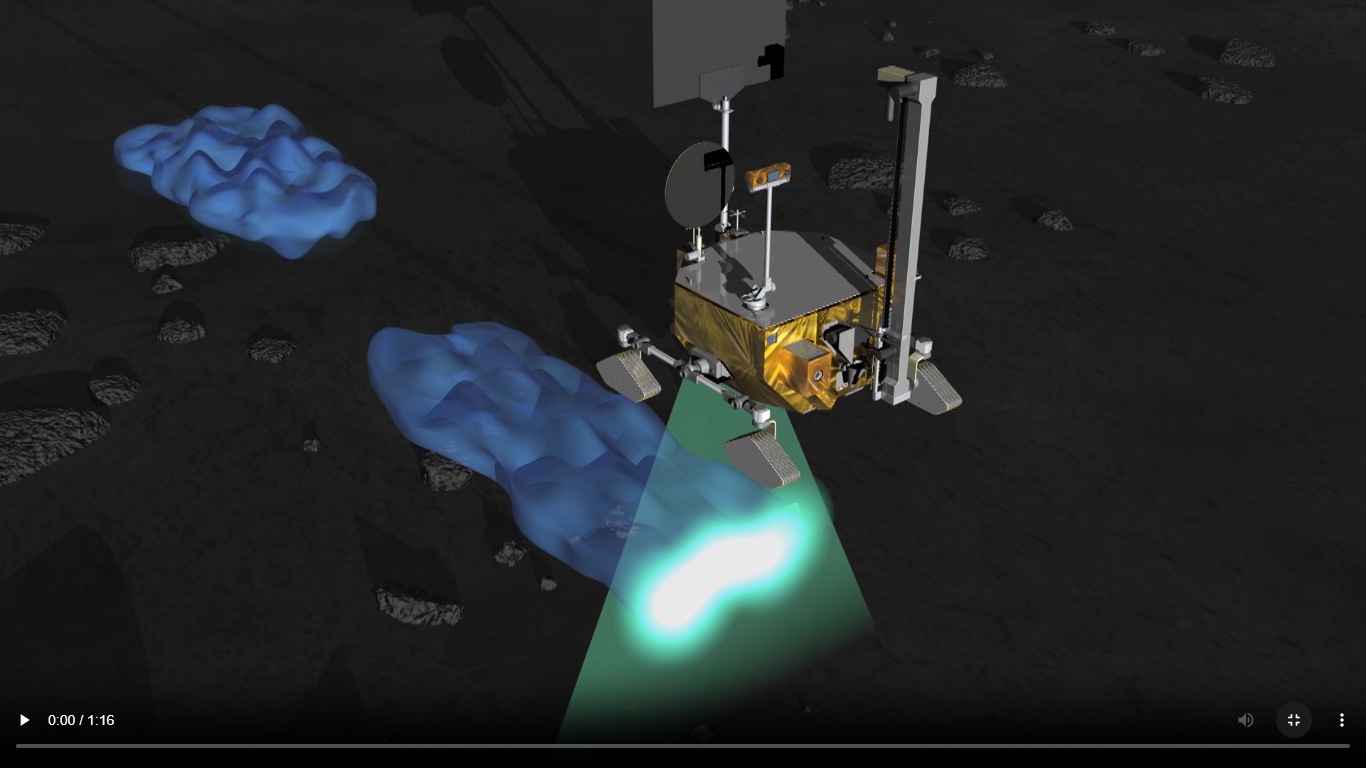
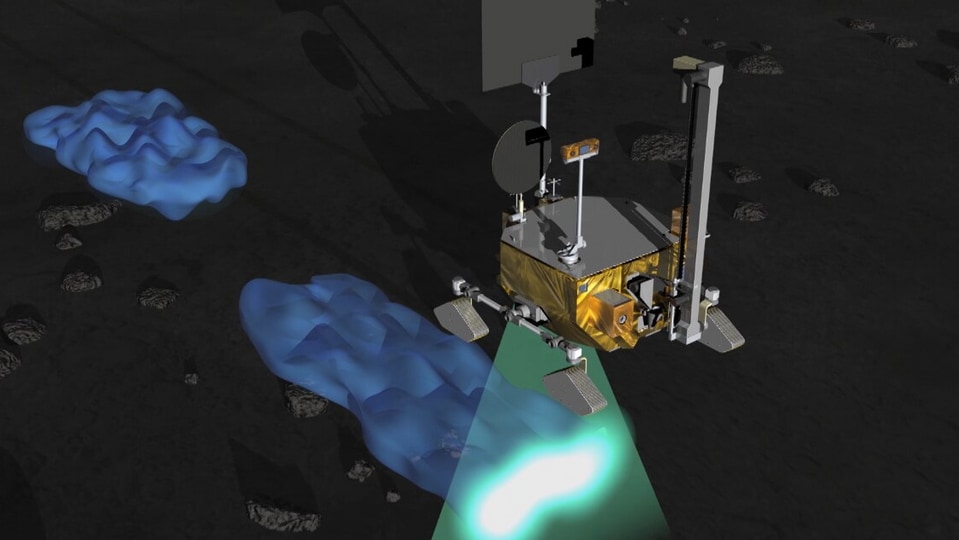
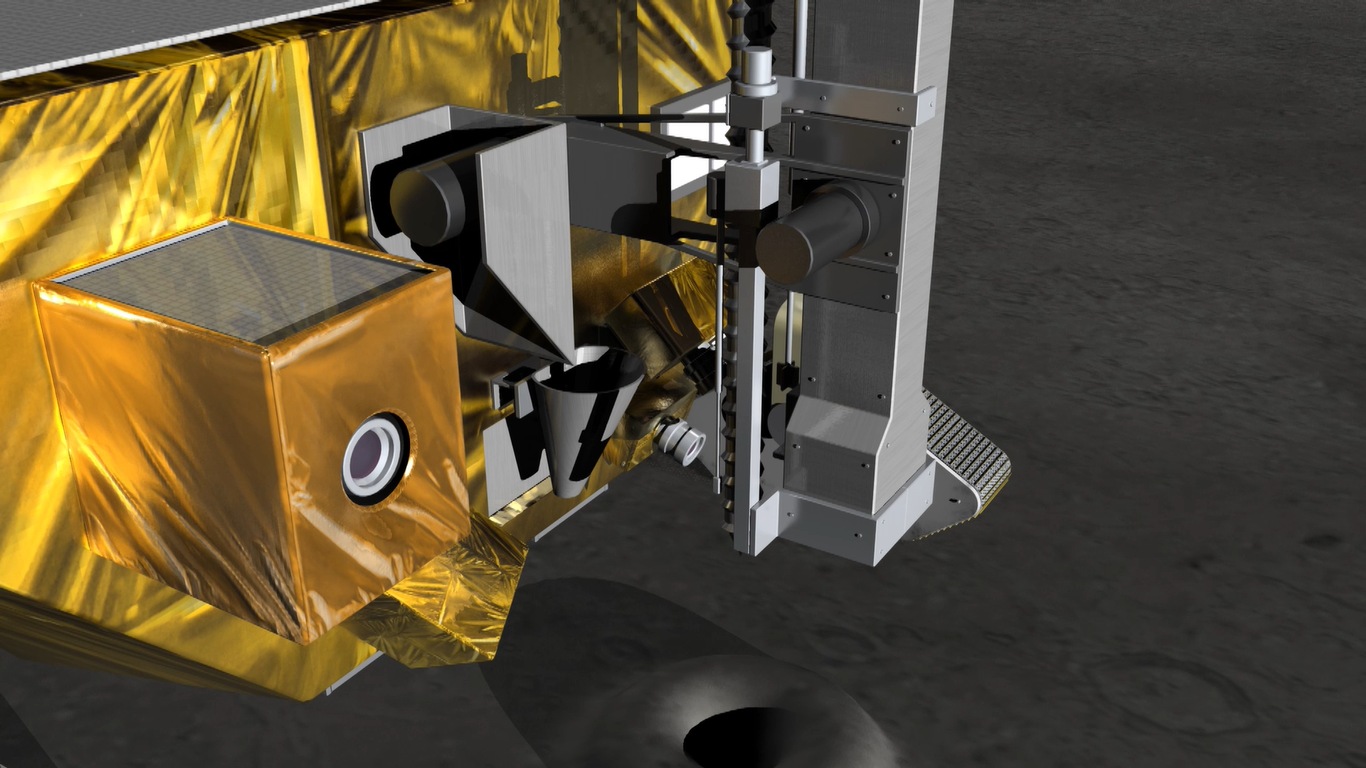
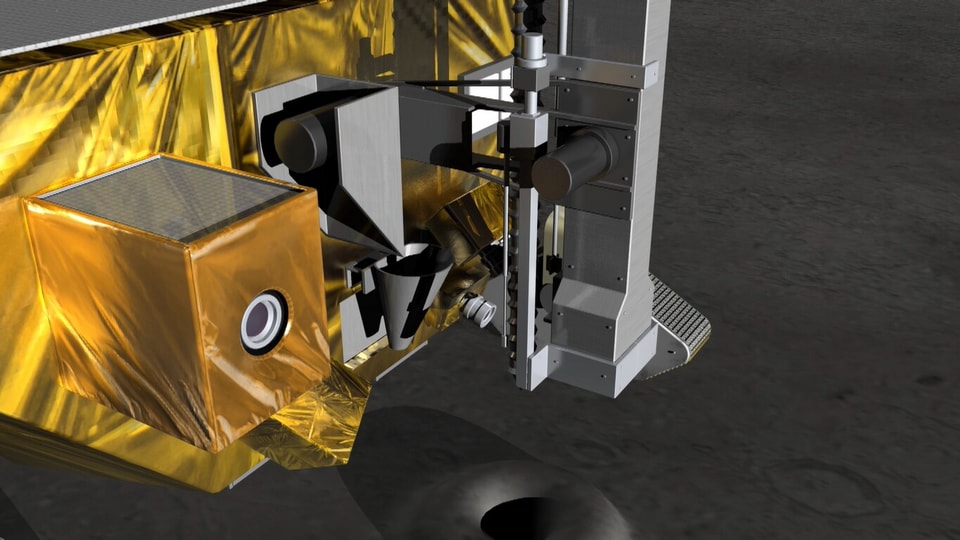
Chandrayaan-4 mission: How ISRO will carry out the lunar mission
All eyes are on ISRO and JAXA as they prepare for the Chandrayaan-4 mission. Know the mission sequence and how it will be carried out.


First Published Date: 03 Nov, 09:25 IST
NEXT ARTICLE BEGINS