A HOLE in the Milky Way Galaxy found; may reveal how stars are formed
A huge 500 light-year wide hole has been discovered in the Milky Way Galaxy by astronomers. Here’s everything you need to know about the latest discovery in the Milky Way that may well reveal much more about how stars are formed.
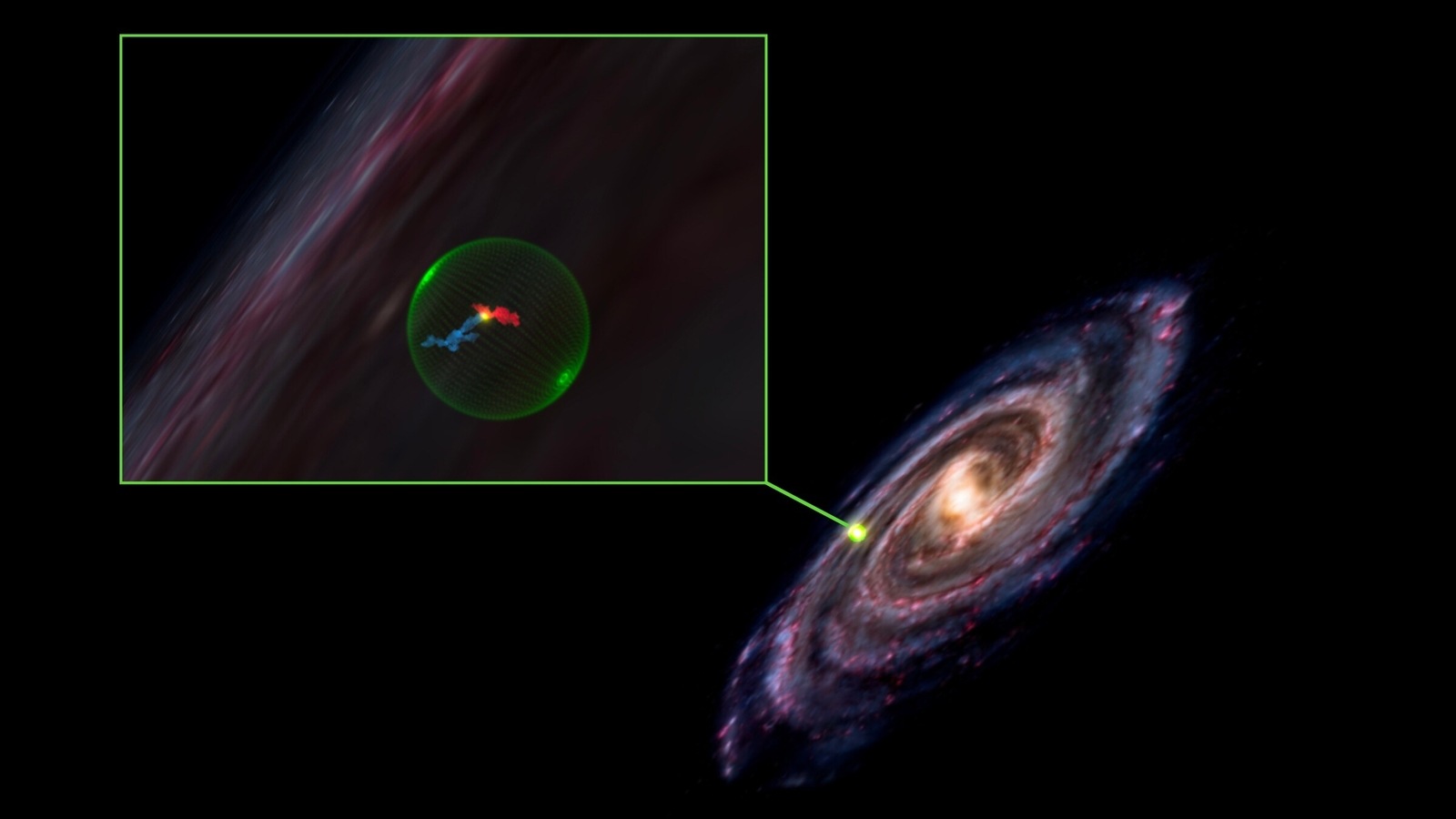

In another step taking humans closer to understanding the origins of the universe and how stars are formed, astronomers have discovered a massive void in the Milky Way Galaxy, between star-forming regions in the Perseus and Taurus constellations, according to a new study. The void, or space cavity, is a massive 500 light-years in width.
According to several reports, the void in the Milky Way Galaxy was spotted surrounded by molecular clouds, which could have been formed by the explosive death of a star around 10 million years ago, also known as a supernova. The researchers at the Institute for Theory and Computation (ITC) at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center For Astrophysics (CfA) believe the study's findings could help scientists understand how stars could be formed due to supernovas.
Also read: Looking for a smartphone? Check Mobile Finder here.
In a statement, the researchers stated that the European Space Agency's star-mapping Gaia spacecraft yielded data that was used to map molecular clouds located around the void, giving them a 3D view for the first time, a big upgrade over two-dimensional views of the Milky Way Galaxy region. The researchers say that they now know where they lie “with only 1 percent uncertainty” which will allow them to calculate the distance of the void from Earth.
In order to visualise the data, the researchers used software called Glue, which allowed them to create 3D molecular maps that could map the region where stars are formed. This new perspective will help them study how molecular clouds can be formed with gas and dust after a supernova explosion – to form new stars. "You can literally make the universe float over your kitchen table," says Harvard professor and CfA astronomer Alyssa Goodman.
The data from these 3D maps of the region showed the researchers that the previously mentioned clouds were not actually connected, but instead located on either side of a large, invisible cavity. The clouds could have been formed as a result of the same supernova explosion about 10 million or 20 million years ago, according to the researchers. The findings of the study were published on September 22 in The Astrophysical Journal.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.