Aditya-L1 mission update: First high-energy X-ray of solar flares captured by ISRO spacecraft!
In a recent update by ISRO about the Aditya-L1 mission, the X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS) captured a high-energy solar flare.




 View all Images
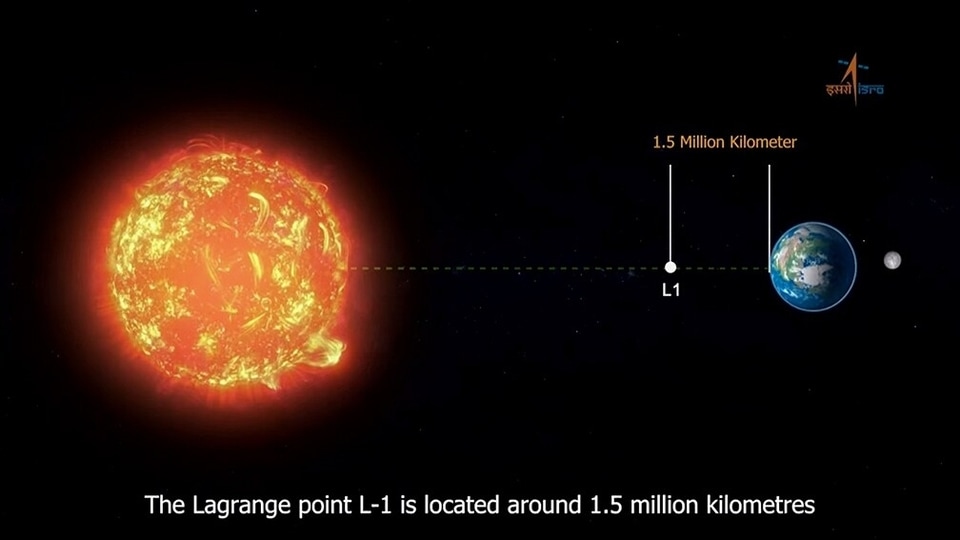
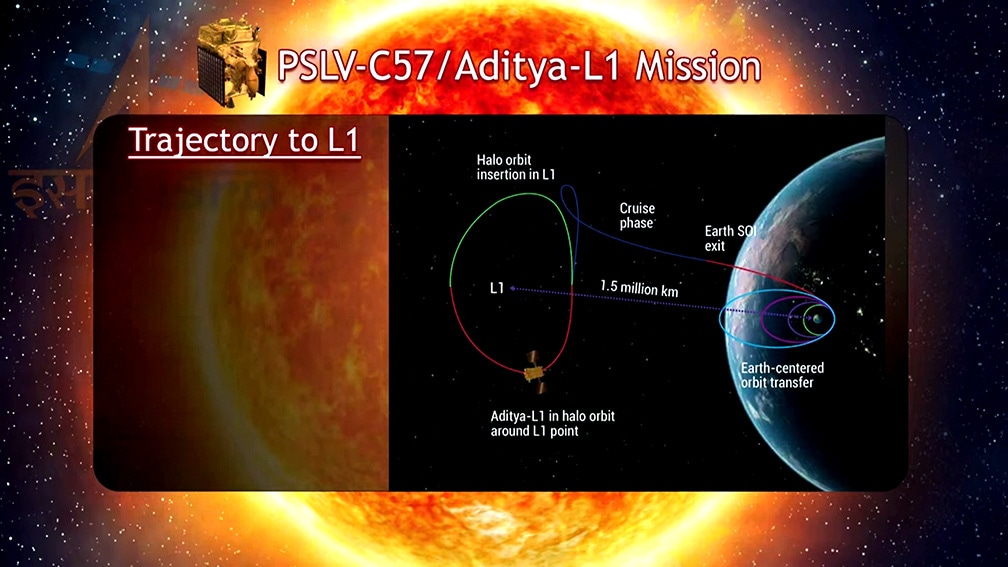
View all ImagesAditya-L1 mission spacecraft is now in its trajectory towards a point where the Sun-Earth system is at equilibrium to study various phenomena. In a recent update, the Aditya-L1 spacecraft has captured the first-ever high-energy X-ray of solar flares during its monitoring phase. Till now, the spacecraft has made successful manoeuvres including a Trans-Lagrangean Point 1 Insertion (TL1I) manoeuvre and now it will be placed at the halo orbit of Lagrange Point 1. Know what ISRO uncovered with the X-ray image of the Sun.
Aditya-L1 mission findings
ISRO shared an update about the Aditya-L1 mission through their official X (Formerly Twitter) handle saying that the HEL1OS spectrometer captured the first high-energy X-ray of solar flares along with GOES X-ray light curves. The Indian space agency further reported that the spectrometer attached to the spacecraft was responsible for recording the highest phase of the solar flare on October 29, during its first observation period.
We are now on WhatsApp. Click to join
ISRO reported that such solar flares are sudden occurrences of the Sun's outer layers. These flares emit harmful radiations across the electromagnetic spectrum – radio, optical, UV, soft X-rays, hard X-rays and gamma-rays. Right now the HEL1OS is in fine-tuning of thresholds and calibration operations phase and it will continue to study the Sun's high-energy X-ray activities. ISRO said, “HEL1OS data enables researchers to study explosive energy release and electron acceleration during impulsive phases of solar flares.”
About HEL1OS spectrometer
The High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS) is designed to study the Sun's explosive energy release, electron acceleration, and transport during solar flares with fast timing measurements and high resolution spectra. The instrument was developed by the Space Astronomy Group of the U. R. Rao Satellite Centre, ISRO, Bengaluru, in collaboration with different centre entities.
The HEL1OS spectrometer has been studying the Sun's solar flare activities since October 27, and it captured the highest energy of the flare on October 29, 2023, giving insights into the activities of the Sun. ISRO will be providing more information on the findings.
One more thing! HT Tech is now on WhatsApp Channels! Follow us by clicking the link so you never miss any updates from the world of technology. Click here to join now!
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.