Discovery of galaxy born soon after Big Bang shows James Webb Space Telescope's amazing power
The detection of a galaxy that formed soon after Big Bang is the latest example of how the James Webb Space Telescope is reshaping our understanding of the early universe.


_1661230453587.jpg)


 View all Images
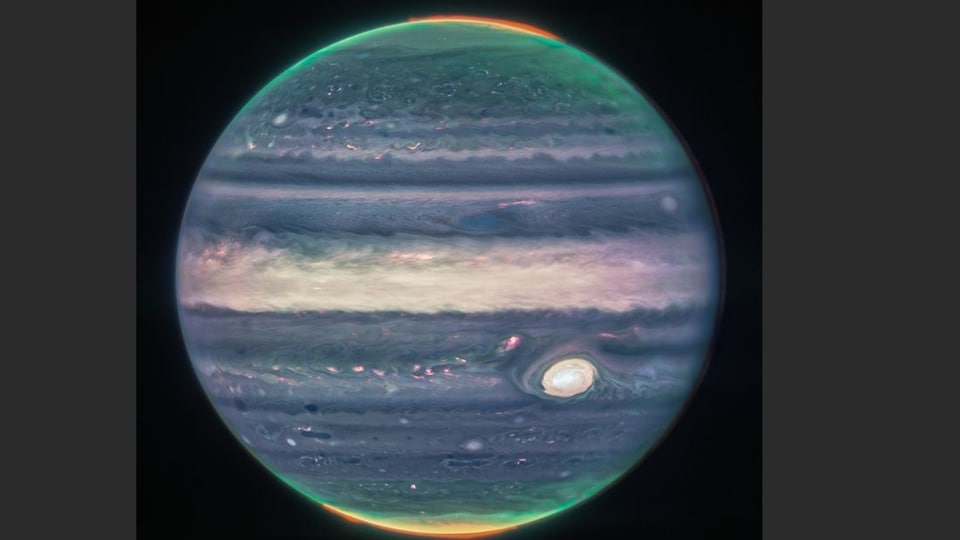
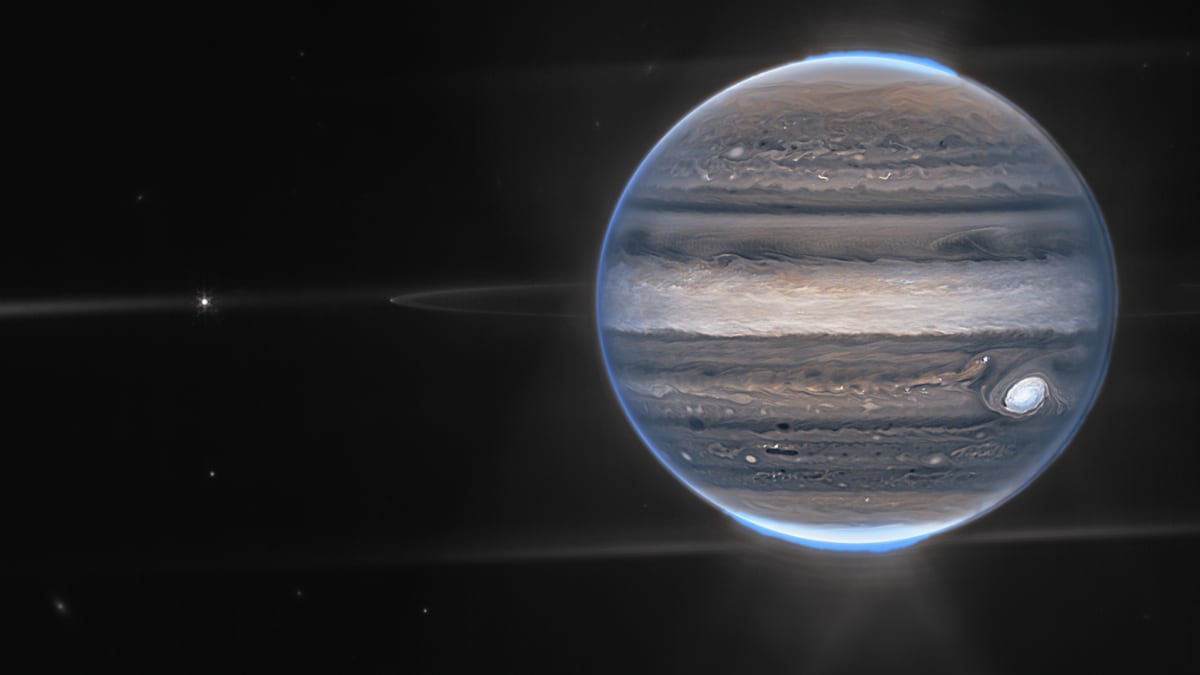
View all ImagesThe detection of a highly compact galaxy that formed relatively soon after the Big Bang and displayed an impressive rate of star formation is the latest example of how the James Webb Space Telescope is reshaping our understanding of the early universe.
Scientists said the galaxy, dating to 13.3 billion years ago, has a diameter of approximately 100 light-years - about 1,000 times smaller than the Milky Way - but forms new stars at a rate very similar to that of our much-larger present-day galaxy. A light-year is the distance light travels in a year, 5.9 trillion miles (9.5 trillion km).
It existed about 510 million years after the Big Bang event marking the universe's origin. The universe at the time was less than 4% of its current age.
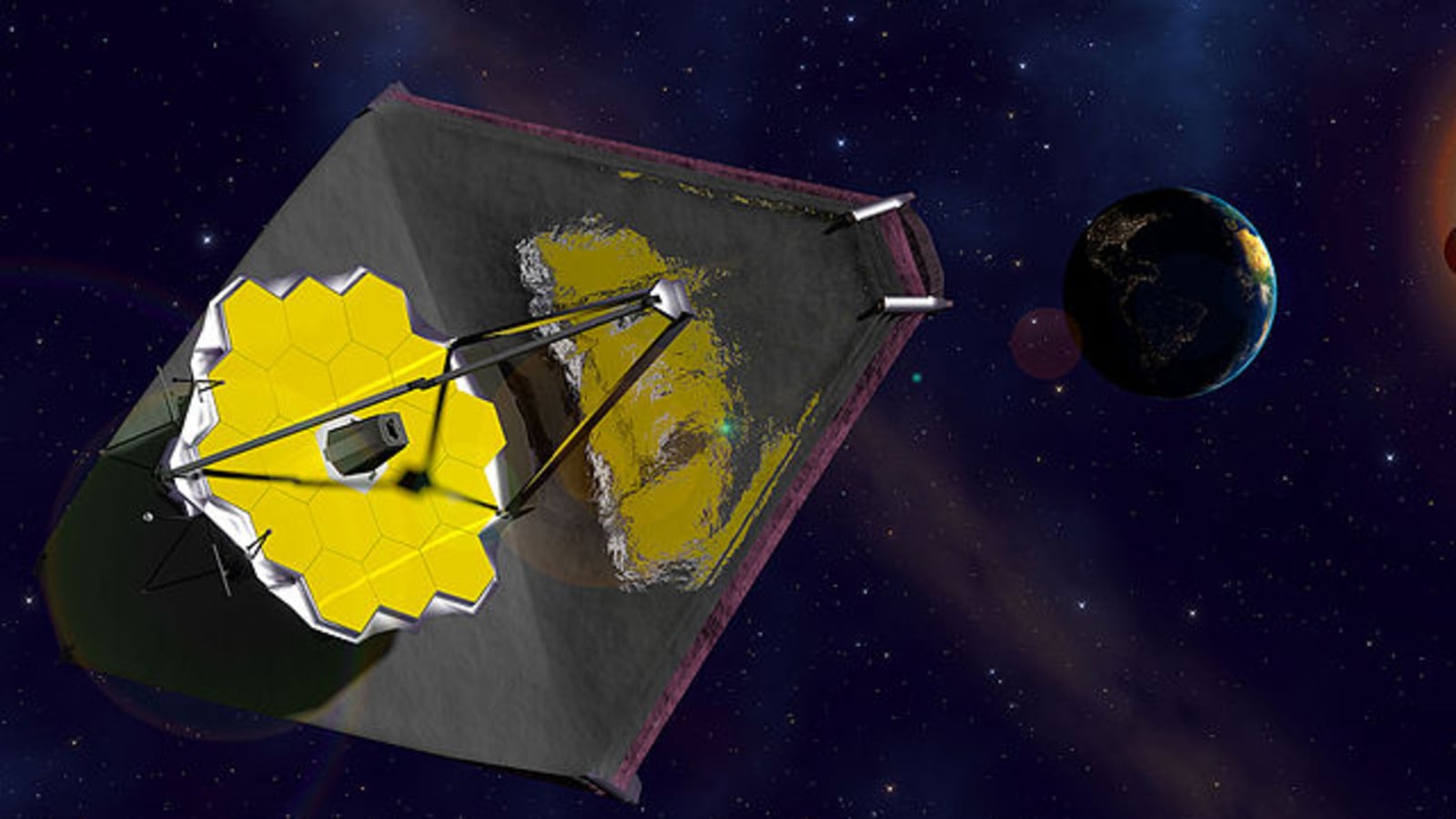
The discovery is another example of how observations by Webb, which was launched in 2021 and began collecting data last year, are transforming our knowledge of the nature of the early universe. The orbiting infrared observatory was designed to be far more sensitive than its Hubble Space Telescope predecessor.
"Our current understanding of galaxy formation in the early universe doesn't predict that we would see this many galaxies at such early times in the universe's life, so this is really exciting," said Hayley Williams, a University of Minnesota doctoral student in astrophysics and lead author of the study published this week in the journal Science.
"As we observe more and more of these distant galaxies, we'll be able to put together a more complete picture of how the first galaxies in our universe came to be," Williams added. "We are seeing that the galaxies that existed in the early universe are very different from the galaxies that exist today and that our usual assumptions about galaxy properties may not apply in the early universe."
Webb looks at the universe mainly in the infrared, while Hubble has examined it primarily at optical and ultraviolet wavelengths. Webb possesses a much bigger light-collecting area, letting it look at greater distances, thus farther back into time, than Hubble.
"JWST's (James Webb Space Telescope's) reach into the first billion years of the universe has been amazing, and has given astronomers a lot to consider and try to understand about when and how many galaxies formed," University of Minnesota astronomy professor and study co-author Patrick Kelly said.
What is being observed in the newly described galaxy, Kelly said, might be a "globular cluster" - a tightly bound collection of tens of thousands to millions of stars - in the process of forming.
This galaxy, Kelly said, is "absolutely tiny" in relative terms.
"Nonetheless, we found that it was forming about two stars each year, which is similar to the rate at which the Milky Way is forming stars," Kelly added.
The researchers examined this galaxy's chemical composition, finding, for example, an oxygen abundance much lower than typically found in present-day galaxies - and for good reason. Oxygen and other elements heavier than hydrogen and helium are forged in the thermonuclear furnaces at the interior of stars and then blown into space when stars explode at the end of their life cycles.
Because so many fewer stars had lived and died at that time in the universe, such heavier elements were more scarce.
Observing this galaxy was aided by a phenomenon called "gravitational lensing" that occurs when an immense amount of matter, like a grouping of galaxies, creates a gravitational field that distorts and magnifies light traveling from distant galaxies located behind it but in the same line of sight.
"The combined power of the James Webb Space Telescope and the galaxy's magnification due to gravitational lensing allows us to study this galaxy in detail," Williams said.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.