NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day 5 February 2023: Saturn moon shining bright
NASA’s Astronomy Picture of the Day for 5 February, 2023 is of Saturn's moon Enceladus. Here’s what’s special about the moon.







 View all Images
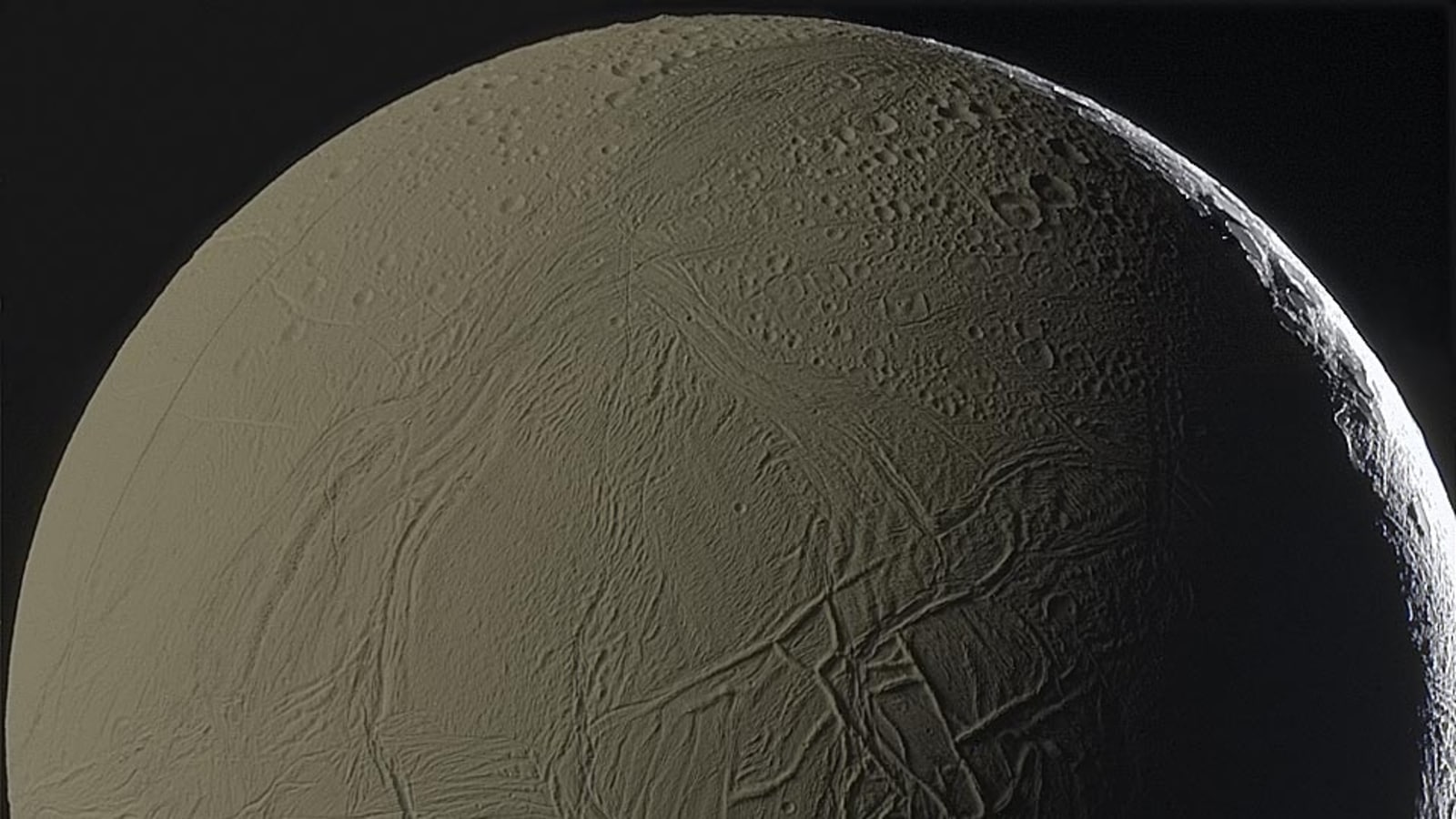
View all ImagesRecently, Jupiter took the crown of the planet with the most moons in our solar system away from Saturn. Saturn used to be on top with a total of as many as 83 moons. Now, Jupiter has been crowned with a whopping 92! However, if scientists are right, then Saturn will regain the title as they have found more moons circling the planet! Among the moons of Saturn, and one of the brightest, is Enceladus. And it has been featured in the NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day today. In fact, this moon is shining bright by the light of its planet. NASA explains that a large portion of Enceladus pictured here is illuminated primarily by sunlight first reflected from the planet Saturn. Resultantly, it shows the normally snow-white moon appearing in the gold colour of Saturn's cloud tops.
NASA's explanation of the image
While explaining the settings of the image, NASA says, “As most of the illumination comes from the image left, a labyrinth of ridges throws notable shadows just to the right of the image center, while the kilometre-deep canyon Labtayt Sulci is visible just below. While the bright thin crescent on the far right is the only part of Enceladus directly lit by the Sun. ”
The image was taken back in 2011 by the robotic Cassini spacecraft during its close approach towards the moon. While exploring the bottom left of this digitally enhanced image shows ice crystal plumes believed to come from a subterranean ocean.
More about Enceladus
Enceladus was discovered by English astronomer William Herschel in 1789 and named after a Giant from Greek mythology. It has a diameter of approximately 500 km and orbits Saturn in a nearly circular, prograde path at a mean distance of 238,020 km. Its surface is mostly composed of water ice, with small amounts of carbon dioxide, ammonia, and light hydrocarbons.
Enceladus reflects a high amount of sunlight, causing its surface temperature to be extremely low, at approximately -330°F (-201°C). However, it is not as inactive as it appears.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.