Gisat-1 satellite: ISRO blames launch failure on cryogenic engine; what it means and what India lost
Gisat-1 satellite: This was to be a game-changer eye-in-the-sky satellite for India, but all went wrong in seconds.
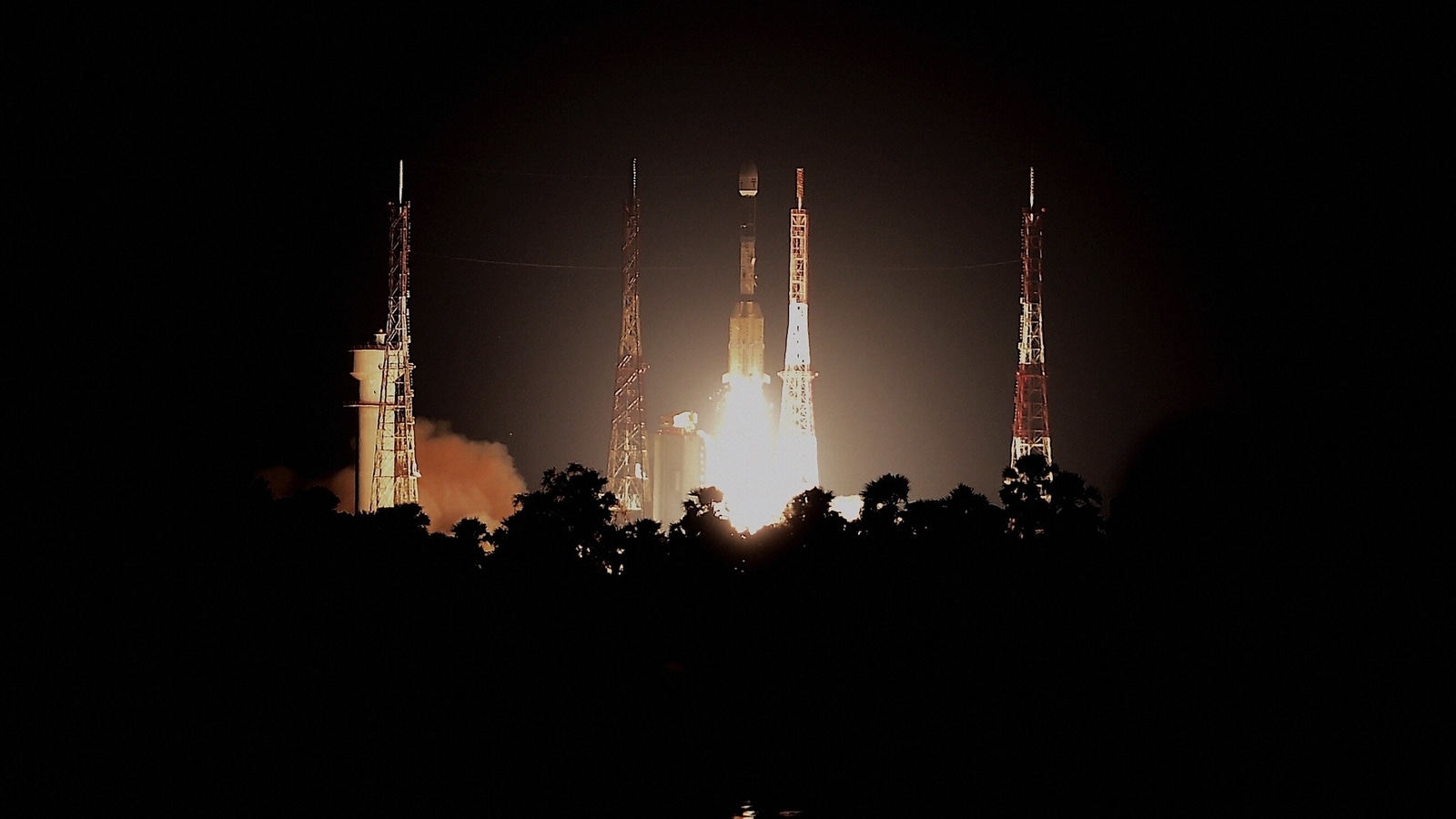

Gisat-1 satellite: In a disappointing turn of events, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) could not manage to park its EOS-3 earth observation satellite in its proper orbit due to failure of the cryogenic engine. The satellite was supposed to be India's eye in the sky to keep a watch on the borders, the oceans and much more.
Gisat-1 flight: Blow-by-blow account
However, it all started perfectly smothly and there was no inkling that things were going to take a turn for the worse very soon afterwards.
1. The lift-off was perfect as the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle-F10 (GSLV-F10) rocketted into the sky from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota.
2. The first stage of the rocket fired perfectly
3. The second stage fired perfectly too
4. ISRO managed the separation very smoothly too.
5. Just seconds later the cryogenic engine developed a snag and that is when all the trouble started.
6. The module lost attitude control and speed as was recorded by ISRO during flight.
7. ISRO scientists fought desperately to regain control but it could not be re-established.
With the mission gone wrong, ISRO issued this explanation, "GSLV-F10 launch took place on August 12, 2021 at 0543 Hrs IST as scheduled. Performance of first and second stages was normal. However, Cryogenic Upper Stage ignition did not happen due to technical anomaly. The mission couldn't be accomplished as intended."
ISRO Chairman, K. Sivan blamed a "technical anomaly observed in the cryogenic stage” for the launch mission not be fully accomplished mainly.
What is the cryogenic engine that has been blamed for the loss of the non-accompishment of the mission?
ISRO says, "A Cryogenic rocket stage is more efficient and provides more thrust for every kilogram of propellant it burns compared to solid and earth-storable liquid propellant rocket stages. Greater efficiency is achievable with cryogenic propellants (liquid Hydrogen and liquid Oxygen) compared to earth storable liquid and solid propellants, giving it a substantial payload advantage."
While this my be very efficient, it is also a very difficult thing to carry out as it carries a huge amount of risk.
ISRO adds, "Cryogenic stage is technically a very complex system compared to solid or earth-storable liquid propellant stages due to its use of propellants at extremely low temperatures and the associated thermal and structural problems."
The temperatures are extremely low. The propellants, at these low temperatures are to be pumped at -183 deg C and Hydrogen at -253 deg C. using turbo pumps running at around 40,000 rpm.
What was the loss caused?
The satellite was dubbed as a “game changer" for India due to its ability to keep a watch on the country's land mass as well as its ocean. The most important aspect was to keep a close watch on India's borders.
Apart from defence, there was civil-use loss too. The satellite was expected to provide the latest information on monitoring and warning on natural disasters. It was also expected to make big contributions to "agriculture, forestry, mineralogy, cloud properties, snow and glaciers and oceanography".
The mission suffered from bad luck the start. The first launch was supposed to happen on March 5, 2020. However, the launch was postponed then and on a number of occasions thereafter for reasons that included technical glitches and Covid-19 pandemic lockdowns.
Notably, in 2021, ISRO has only 1 launch to its credit and that was back in February when it launched 18 small satellites successfully. Today's launch was the 2nd one of the year.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.