3D printed human tissue and organs now possible
A group of US scientists have successfully transplanted living tissue constructed by a sophisticated and improved 3D printer, according to a study released on Monday by British scientific journal Nature.
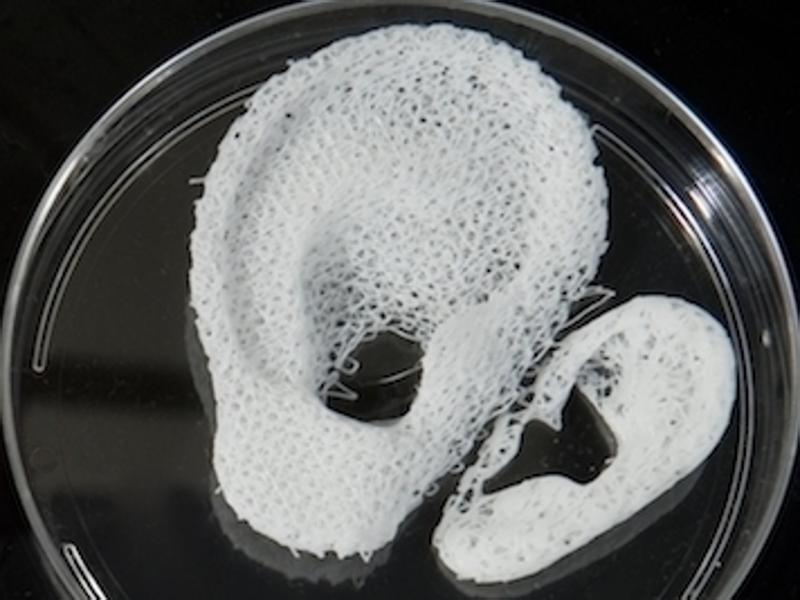
A group of US scientists have successfully transplanted living tissue constructed by a sophisticated and improved 3D printer, according to a study released on Monday by British scientific journal Nature.
This research, developed by the Wake Forest Baptist Medical Centre in North Carolina, represents a breakthrough for regenerative medicine, as it suggests that these tissues could be transplanted in patients in the future, and thus overcoming a number of technical obstacles that currently hinder the process, the study noted.
The scientists managed to print "stable" cartilage, bone and muscle structures and after their transplant into rodents, they matured into functional tissue while developing a system of blood vessels.
Although the new printed tissues are not yet ready to be used in human patients, experts assert that the first results of the study suggest that they have the size, strength and functionality suitable to be used in humans.
The accuracy of this new 3D printer means that in the near future, it could perfectly replicate more complex tissues and organs of the human body.
"This novel tissue and organ printer is an important advance in our quest to make replacement tissue for patients," said Anthony Atala, M.D., director of the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) and senior author on the study. "It can fabricate stable, human-scale tissue of any shape. With further development, this technology could potentially be used to print living tissue and organ structures for surgical implantation."
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.