XPoSat Mission launched! After Chandrayaan-3 mission, Aditya-L1 mission triumphs, ISRO takes another big step
ISRO successfully launched the XPoSat Mission today and logged yet another historic success after Chandrayaan-3 mission, Aditya-L1 mission.


 View all Images
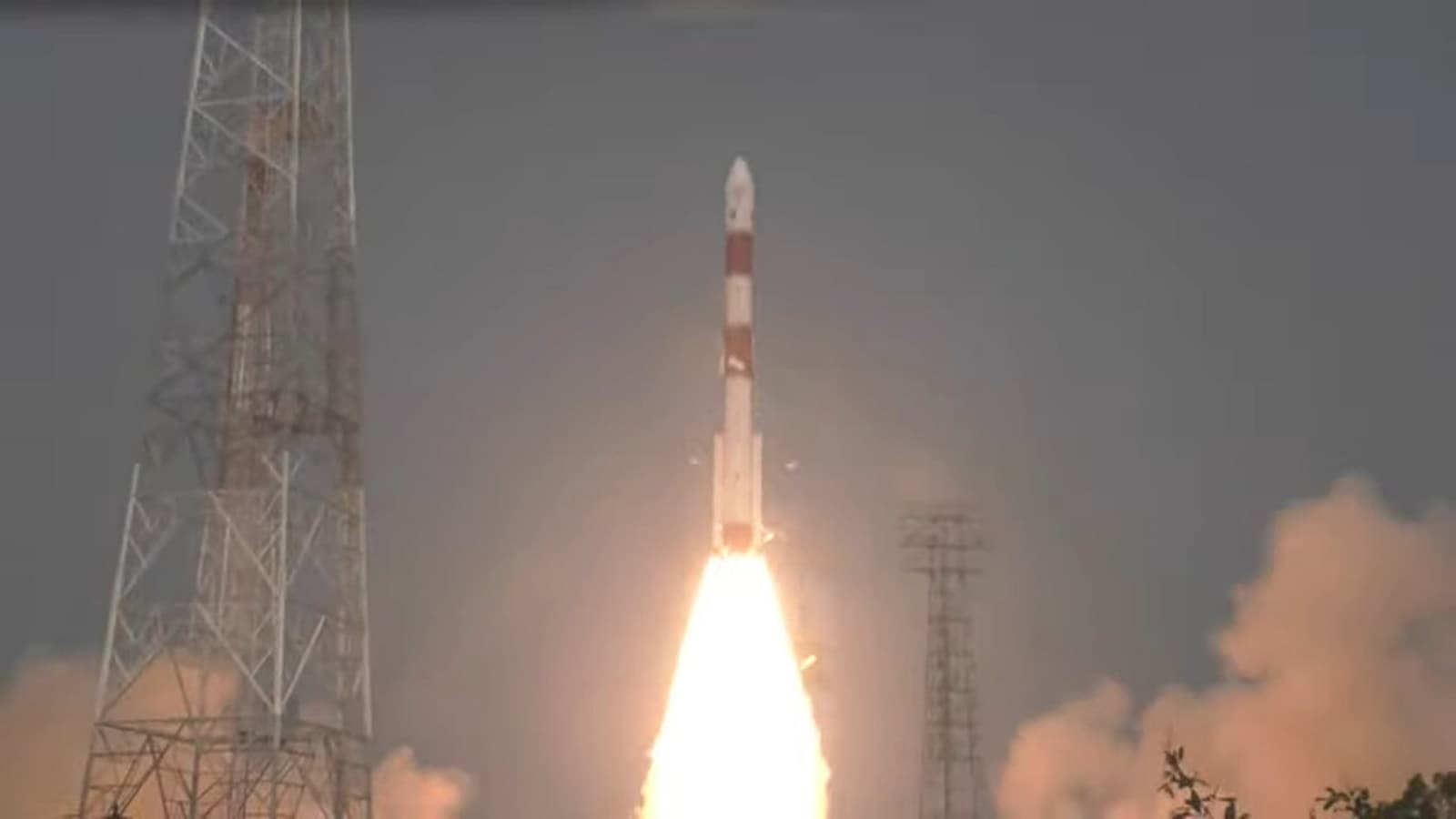
View all ImagesXPoSat Mission launch: In yet another proud moment created by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), a new satellite has been launched successfully. This project, dubbed as the XPoSat Mission was launched successfully today, the first day of 2024. And, even as ISRO ended 2023 with a huge number of successes, the most notable of them being the Chandrayaan-3 mission and the Aditya-L1 mission, the space agency registered yet another historic triumph by launching this critically important satellite. The satellite was hoisted into orbit aboard the PSLV-C58 rocket. The planned lifetime of XPoSat mission is about 5 years, according to ISRO. Among various other objectives, it will also study X-ray pulsars, black hole binaries, neutron stars, and Magnetars.
The launch came after an exhaustive 25-hour countdown that had commenced on Sunday at 8.10 am. ISRO had scheduled the lift-off at 9.10 am from the first launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, located about 135 kms east of Chennai, on January 1.
Significantly, this was the 60th mission for the PSLV-C58 rocket. It carried as many as 10 other satellites that were to be deployed in low earth orbits.
The spacecraft carried two scientific payloads:
1.POLIX: This is an X-ray Polarimeter for astronomical observations in the energy band of 8-30 keV. The instrument is made of a collimator, a scatterer and four X-ray proportional counter detectors that surrounds the scatterer. This is the first payload in the medium X-ray energy band dedicated for polarimetry measurements.
2. XSPECT: It is an X-ray SPECtroscopy and Timing payload onboard XPoSat, which can provide fast timing and good spectroscopic resolution in soft X-rays. XSPECT would observe several types of sources viz X-ray pulsars, black hole binaries, low-magnetic field neutron star (NS) in LMXBs, AGNs and Magnetars.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.