Google researchers have performed a chemical simulation on a quantum computer for the first time ever
The Google AI Quantum team used a noise-robust variational quantum eigensolver (VQE) to directly simulate a chemical mechanism via a quantum algorithm.
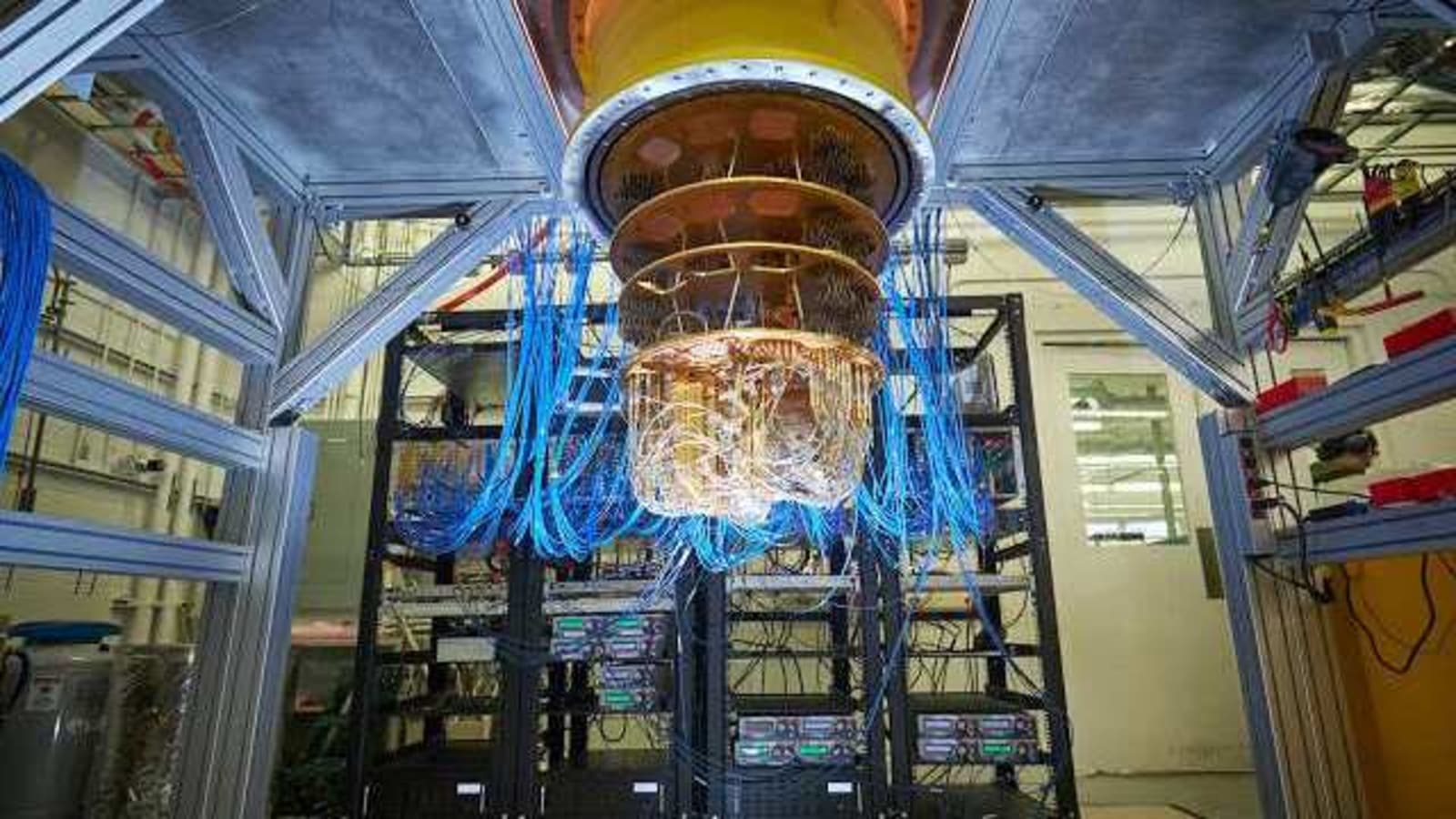

Google has successfully managed to perform the largest chemical simulation on a quantum computer ever. This feat can unlock new frontiers in chemistry and help many industries take the next big step. The Google AI Quantum team used a noise-robust variational quantum eigensolver (VQE) to directly simulate a chemical mechanism via a quantum algorithm.
The calculation focused on the "Hartree-Fock" approximation of a real chemical system, however, it was twice as large as any other previous chemistry calculations on a quantum computer and contained 10 times as many quantum gate operations. Hartree-Fock, in computational physics and chemistry, is a method of approximation for the determination of the wave function and the energy of a quantum many-body system in a stationary state.
"Importantly, we validate that algorithms being developed for currently available quantum computers can achieve the precision required for experimental predictions, revealing pathways towards realistic simulations of quantum chemical systems," the Google team wrote in a paper that appeared in the journal Science.
The experiment was run on the Sycamore processor that was recently used to demonstrate quantum supremacy.
Sycamore has 54-qubits and consists of over 140 individually tunable elements, each controlled with high-speed, analog electrical pulses. Achieving precise control over the whole device requires fine-tuning more than 2,000 control parameters, and even small errors in these parameters can quickly add up to large errors in the total computation, Google explained in the blog.
Marking the event Alphabet and Google CEO Sundar Pichai tweeted:
Proud to share @GoogleAI team's recent advances in quantum chemistry: the largest quantum computation of chemistry to date & the first time a quantum computer has been used to model a chemical reaction pathway -- results published in @ScienceMagazine today https://t.co/THmXRXYeFH
— Sundar Pichai (@sundarpichai) August 27, 2020
Researchers say that the exact solution of quantum chemical equations, for all but the smallest systems, remain out of reach for modern classical computers. And that is due to the exponential scaling in the number and statistics of quantum variables.
The researchers explained that by using a quantum computer, which by its very nature takes advantage of unique quantum mechanical properties to handle calculations intractable to its classical counterpart, simulations of complex chemical processes could be achieved.
Today's quantum computers are powerful enough for a clear computational advantage for some tasks, however, whether such devices can be used to accelerate current quantum chemistry simulation techniques remains to be seen.
Furthermore, the team has released the code for the experiment, which uses "OpenFermion", Google's open-source repository for quantum computations of chemistry.
"We hope that this experiment serves as a blueprint for how to run chemistry calculations on quantum processors, and as a jumping-off point on the path to physical simulation advantage," the researchers added.
(With agency inputs)
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.