NASA and ISRO satellite to watch the Earth gets one step closer to launch
NISAR which is a NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar – an Earth science satellite - is all set to ship out to its last stop, which is southern India, before launching into orbit.







 View all Images
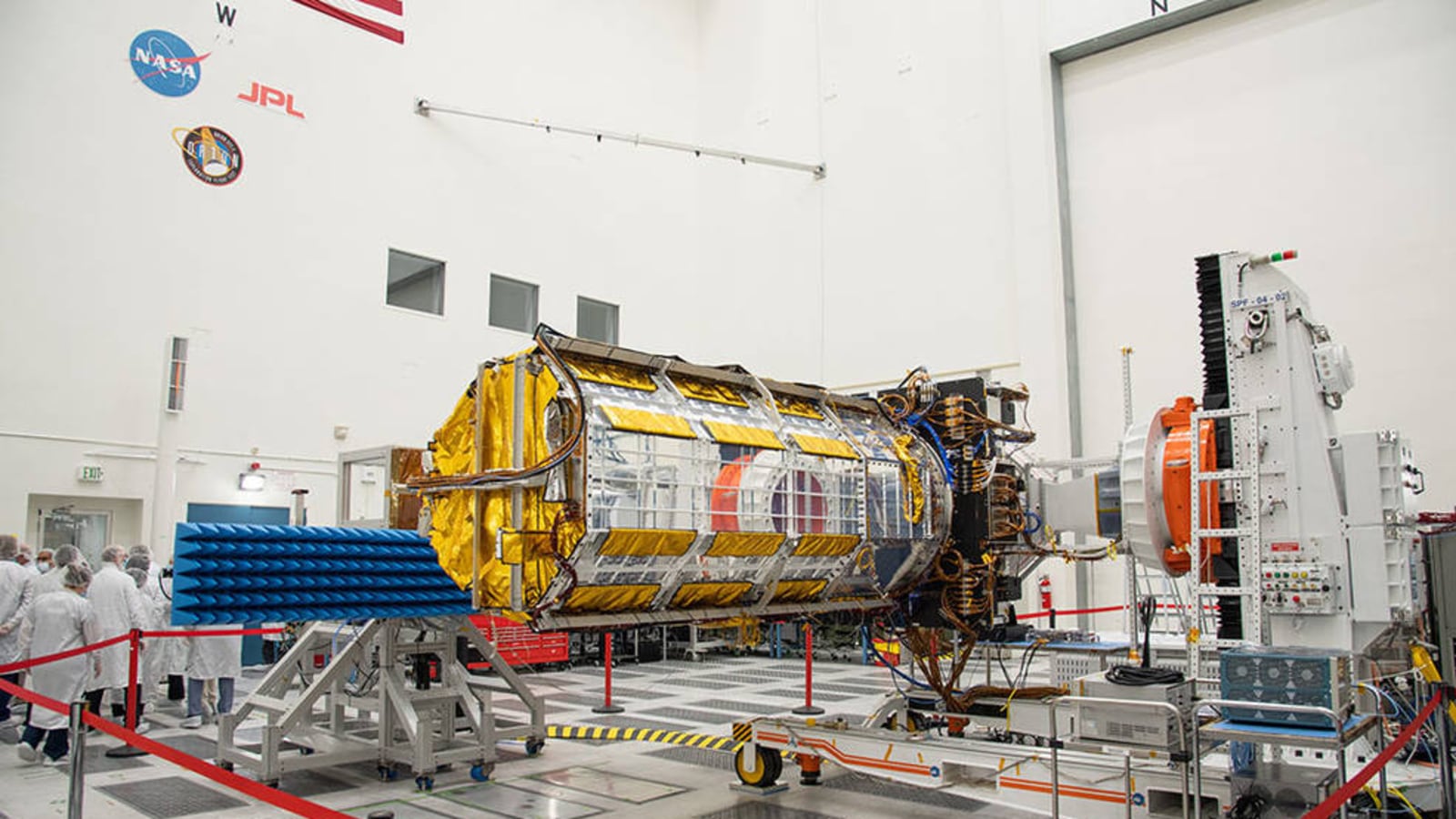
View all ImagesNISAR, short for NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar, is all set to ship out to its last stop before launching into orbit. Before its departure, members of the media got a chance to see NISAR's advanced radar instruments up close on February 3 in a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Southern California. "It's nearly time for the scientific heart of NISAR – short for NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar – an Earth science satellite being jointly built by NASA and the Indian Space Research Organisation, to ship out to its last stop before launching into orbit: southern India," NASA said in a report.
“This marks an important milestone in our shared journey to better understand planet Earth and our changing climate,” JPL Director Laurie Leshin said. “NISAR will provide critical information on Earth's crust, ice sheets, and ecosystems. By delivering measurements at unprecedented precision, NISAR's promise is new understanding and positive impact in communities. Our collaboration with ISRO exemplifies what's possible when we tackle complex challenges together,” he added.
NISAR will gather radar data with a drum-shaped reflector antenna almost 40 feet (12 meters) in diameter. It will use a signal-processing technique called interferometric synthetic aperture radar, or InSAR, to observe changes in Earth's land and ice surfaces down to fractions of an inch.
Since early 2021, engineers and technicians at JPL have been integrating and testing NISAR's two radar systems – the L-band SAR provided by JPL and the S-band SAR built by ISRO. Later this month, they will move the SUV-size payload into a special cargo container for a 9,000-mile (14,000-kilometer) flight to India's U R Rao Satellite Centre in the city of Bengaluru. There it will be merged with the spacecraft bus in preparation for a 2024 launch from Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Andhra Pradesh state.
The observations NISAR makes will help researchers measure the ways in which Earth is constantly changing by detecting both subtle and dramatic movements. Slow-moving variations of a land surface can precede earthquakes, landslides, and volcanic eruptions, and data about such movement could help communities prepare for natural hazards.
Measurements of melting sea ice and ice sheets will improve understanding of the pace and impacts of climate change, including sea level rise. And observations of the planet's forest and agricultural regions will improve our knowledge of carbon exchange between the atmosphere and plant communities, reducing uncertainties in models used to project future climate. Over the course of its three-year prime mission, the satellite will observe nearly the entire planet every 12 days, making observations day and night, in all weather conditions.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.