NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day 13 March 2023: A mesmerising Rainbow
NASA's Astronomy Picture of the Day is that of a rainbow hiding behind a tree captured in California, USA.





 View all Images
View all ImagesNearly everyone has witnessed the stunning phenomenon in the sky we call a rainbow. But why does this spectrum of colours form in the sky? A rainbow forms due to the interaction between sunlight and the atmosphere. Sunlight enters a water droplet, slowing down and changing direction as it passes from air to water, which is denser. This causes the light to refract and separate into its different colours.
As the light reflects off the inside of the droplet, it creates a recognizable spectrum of colours – Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red. When the light exits the droplet, it produces the Rainbow.
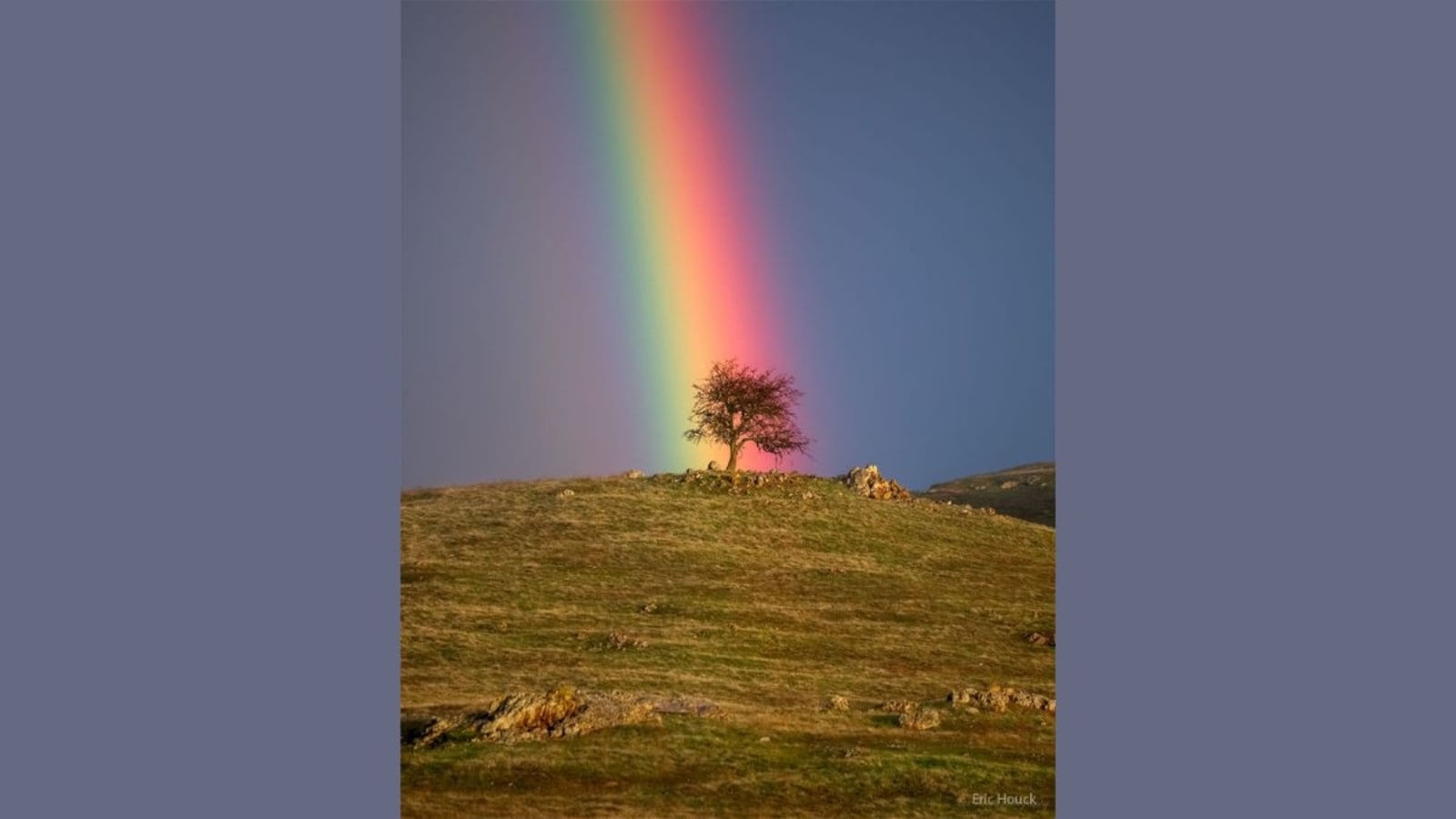
NASA's Astronomy Picture of the Day today is an image of a rainbow backdropping a tree. The reason the rainbow can be seen behind the tree is because its position depends on the observer. The midpoint of a rainbow is consistently visible in the direction that is directly opposite the location of the Sun. However, the precise alignment of this direction in relation to the horizon can vary depending on the observer's location.
The picture was captured by published landscape and wildlife photographer Eric Houck in early January near Knight's Ferry, California, USA.
NASA's description of the picture
What lies at the end of a rainbow? Something different for everyone. For the photographer taking this picture, for example, one end of the rainbow ended at a tree. Others nearby, though, would likely see the rainbow end somewhere else. The reason is because a rainbow's position depends on the observer. The center of a rainbow always appears in the direction opposite the Sun, but that direction lines up differently on the horizon from different locations.
This rainbow's arc indicates that its center is about 40 degrees to the left and slightly below the horizon, while the Sun is well behind the camera and just above the horizon. Reflections and refractions of sunlight from raindrops in a distant storm in the direction of the rainbow are what causes the colorful bands of light. This single exposure image was captured in early January near Knight's Ferry, California, USA.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.




























