NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day 28 April 2023: Runaway star Alpha Camelopardalis
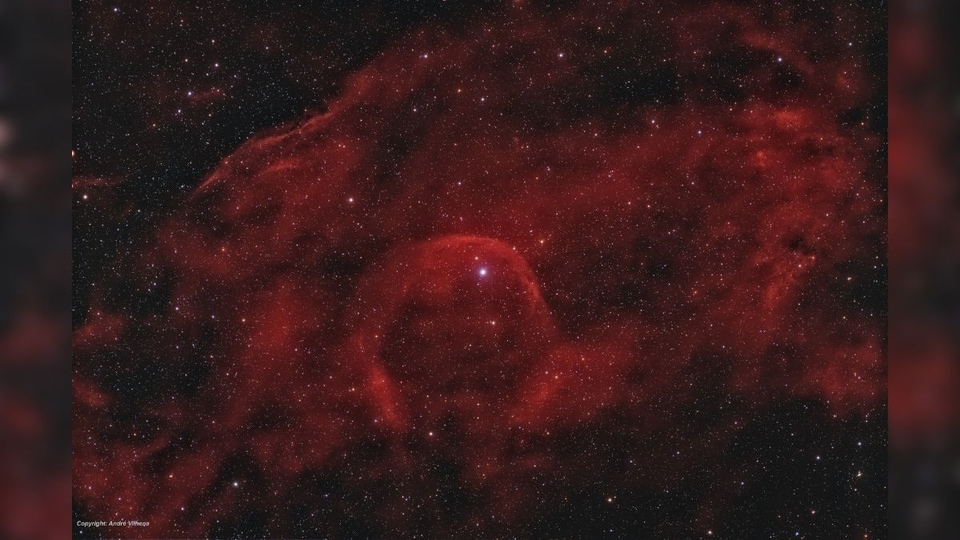
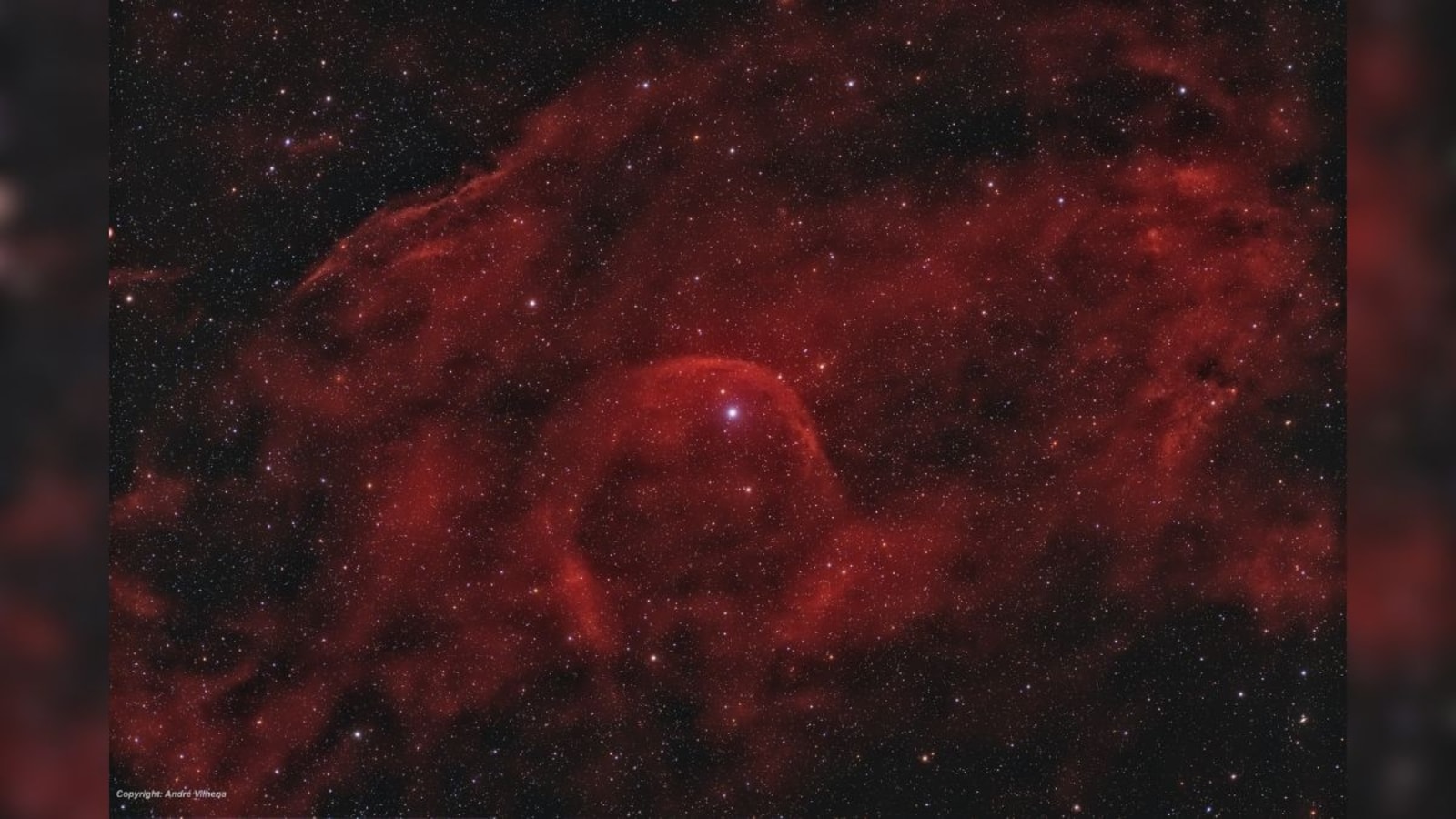
Today’s NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day is a snapshot of Alpha Camelopardalis, a runaway star located about 4,000 light-years away in the long-necked constellation Camelopardalis.






 View all Images
View all ImagesAs many as 200 sextillion (200 billion trillion) stars illuminate our universe. Our Milky Way Galaxy itself has at least 100 billion stars, and there are over 100 billion galaxies in the universe. According to NASA, some stars move through space faster than others. These celestial objects are known as Runaway Stars. Astronomers believe runaway stars are set into motion either through the supernova explosion of a companion star or through gravitational interactions with other stars in a cluster.
Today's NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day is a snapshot of Alpha Camelopardalis, a runaway star located about 4,000 light-years away in the long-necked constellation Camelopardalis. According to NASA, this star is moving through space at a rapid speed of about 60 kilometers per second.
In fact, this star is about 25-30 times the size of our Sun and over 500,000 times brighter! NASA has also revealed that Alpha Camelopardalis is 5 times hotter than our Sun, with a temperature of about 30,000 Kelvin.
The picture was captured by astrophotographer Andre Vilhena.
NASA's description of the picture
Like a ship plowing through cosmic seas, runaway star Alpha Camelopardalis has produced this graceful arcing bow wave or bow shock. The massive supergiant star moves at over 60 kilometers per second through space, compressing the interstellar material in its path. At the center of this nearly 6-degree wide view, Alpha Cam is about 25-30 times as massive as the Sun, 5 times hotter (30,000 kelvins), and over 500,000 times brighter. About 4,000 light-years away in the long-necked constellation Camelopardalis, the star also produces a strong stellar wind. Alpha Cam's bow shock stands off about 10 light-years from the star itself.
What set this star in motion? Astronomers have long thought that Alpha Cam was flung out of a nearby cluster of young hot stars due to gravitational interactions with other cluster members or perhaps by the supernova explosion of a massive companion star.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.