NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day 8 February 2023: Wind-shaped Nebula RCW 58
NASA’s Astronomy Picture of the Day is a mesmerizing snapshot of the Stellar-wind shaped Nebula located in the constellation of Carina.
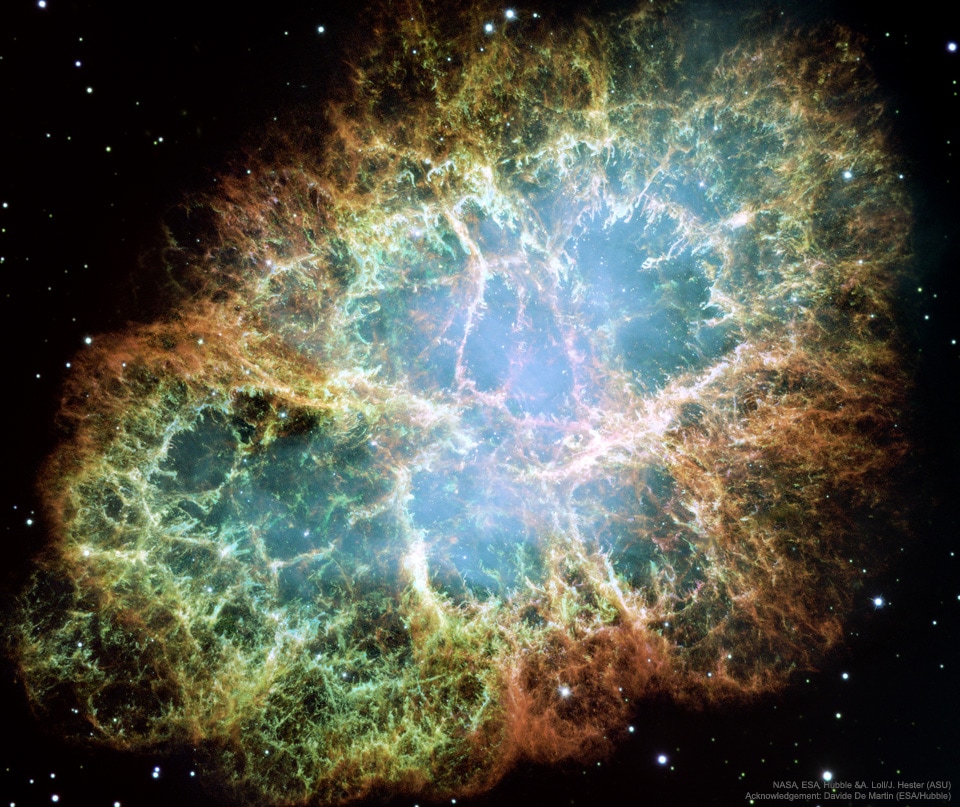







 View all Images
View all ImagesA nebula is a giant cloud of dust and gas in space, according to NASA. These celestial objects exist in the space between stars, known as the Interstellar space. Some nebulae originate from the gas and dust thrown out by the explosion of a dying star while other nebulae are star-forming regions. Although most of the Nebulae are located millions of light-years away, NASA is able to capture them with the help of its Spitzer Space Telescope, Hubble Space Telescope and the new James Webb Space Telescope.
NASA's Astronomy Picture of the Day is a mesmerizing snapshot of the Stellar Wind-Shaped Nebula RCW 58. It is located nearly 13000 light-years away in the constellation of Carina. The Nebula has a wolf star located in the center, a star which is 100 times as massive as our Sun, a million times more luminous, and with 30 times the surface temperature. When these stars expand, they eject high-speed stellar winds through their outer layer. These winds sculpt the material surrounding the Nebula, creating its peculiar shape, such as the oval shape of the Nebula in this case.
The Image was captured by astronomers Mike Selby and Mark Hanson.
NASA's description of the picture
Imagine traveling to a star about 100 times as massive as our Sun, a million times more luminous, and with 30 times the surface temperature. Such stars exist, and some are known as Wolf Rayet (WR) stars, named after French astronomers Charles Wolf and Georges Rayet. The central star in this image is WR 40 which is located toward the constellation of Carina. Stars like WR 40 live fast and die young in comparison with the Sun. They quickly exhaust their core hydrogen supply, move on to fusing heavier core elements, and expand while ejecting their outer layers via high stellar winds.
In this case, the central star WR 40 ejects the atmosphere at a speed of nearly 100 kilometers per second, and these outer layers have become the expanding oval-shaped nebula RCW 58.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.