NASA spots Earth-threatening asteroid; Clocked at 29808 kmph
Another day, another asteroid flyby. But is this asteroid any different from others? Here’s what NASA says about this dangerous space rock.






 View all Images
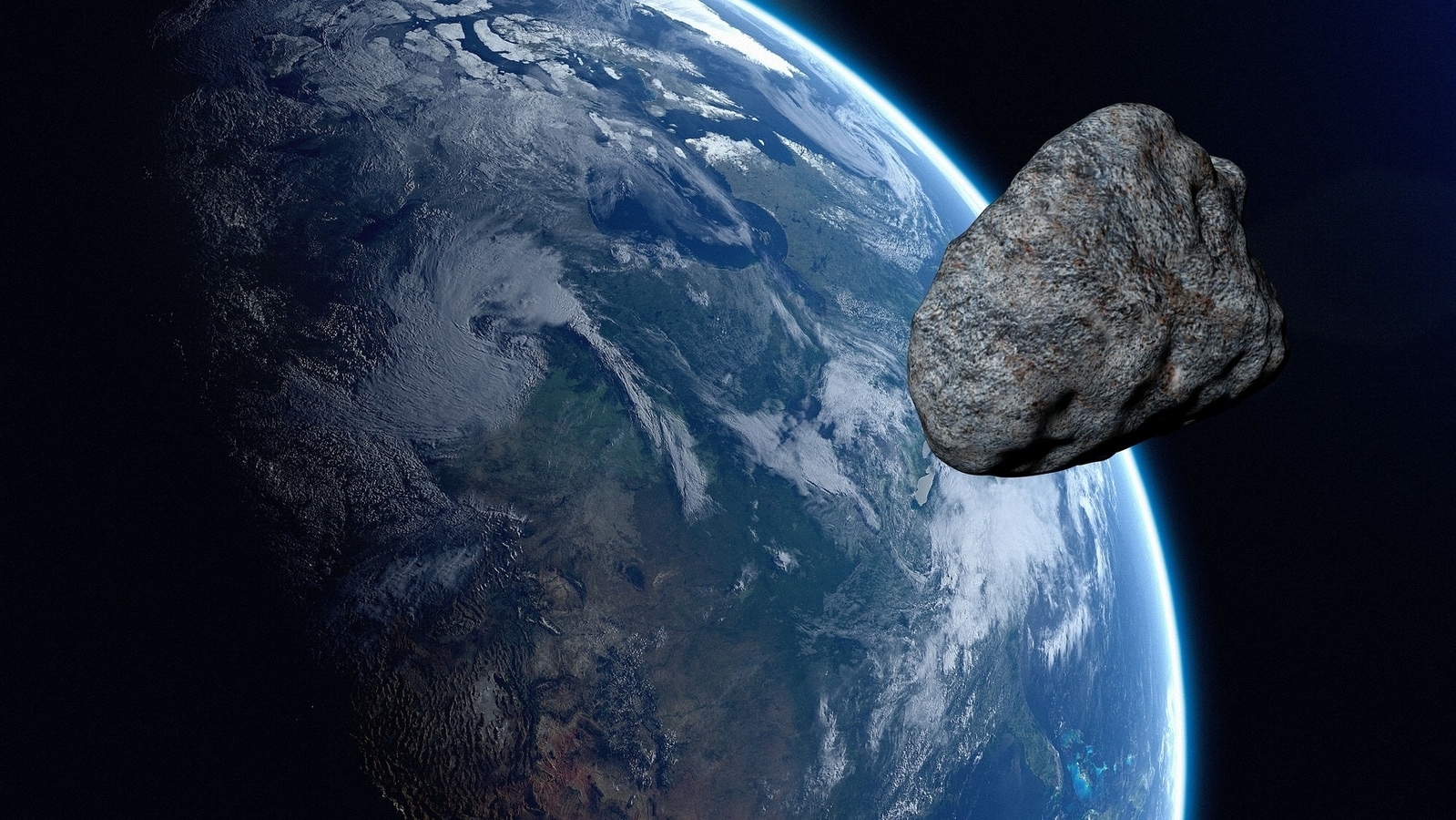
View all ImagesDid you know that almost 100 tons of dust-sized particles bombard Earth every single day. Once a year, a vehicle-sized asteroid hits Earth's atmosphere, creating a giant fireball although it burned up before reaching the surface. According to NASA, every 2000 years, an asteroid the size of a football field hits Earth and causes significant damage to the area. If you're wondering about planet-killing asteroids, they come along only once every few million years. NASA has warned that an asteroid is headed for Earth and although it might not be a planet-killer, it could still potentially cause damage if it impacts Earth.
Asteroid 2022 UQ20 details
NASA's Planetary Defense Coordination Office has issued an alert against an asteroid named Asteroid 2022 UQ20. The 38 feet wide asteroid is expected to fly past Earth today, November 4, at a distance of 1.1 million kilometers. The asteroid is already on its way towards Earth, travelling at a staggering speed of 29808 kilometers per hour!
Nasa has issued a warning, classifying the Asteroid 2022 UQ20 as a “Potentially Hazardous Object” due to the close proximity with which it will pass by Earth. Although it will not collide with Earth, a slight deviation in its trajectory due to the Earth's gravitational pull can send it towards the planet for an impact.
How is an Asteroid Orbit Calculated?
An asteroid's orbit is computed by finding the elliptical path about the sun that best fits the available observations of the object using various space and ground-based telescopes such as NASA's NEOWISE telescope and its brand-new Sentry II algorithm. That is, the object's computed path about the sun is adjusted until the predictions of where the asteroid should have appeared in the sky at several observed times match the positions where the object was actually observed to be at those same time.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.