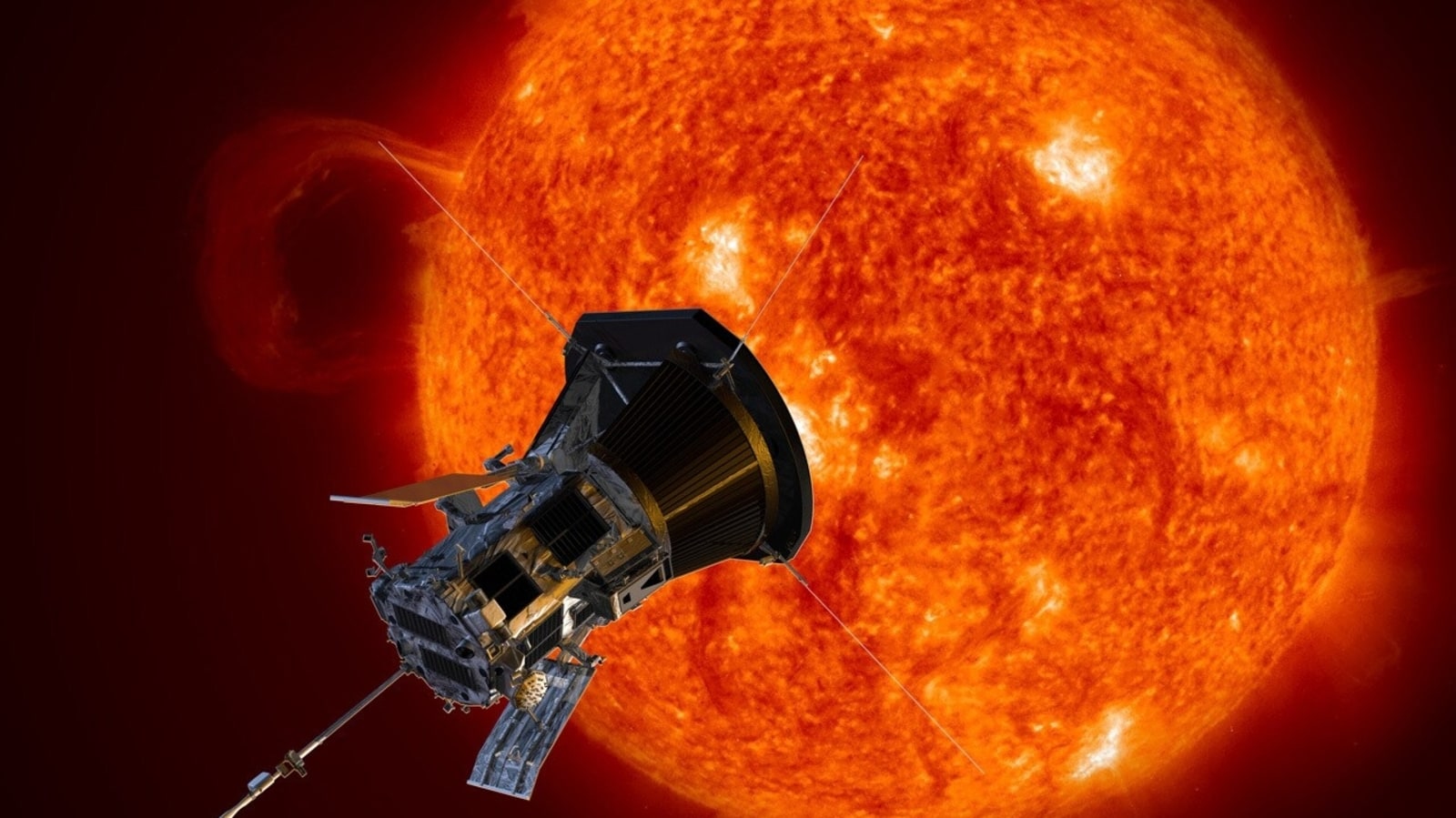
Parker Solar Probe reveals secrets of the solar wind, which sparks geomagnetic storms on Earth
The data obtained from Parker Solar Probe has helped scientists to better understand Solar wind speed and this may help in predicting solar eruptions and understanding geomagnetic storms.





 View all Images
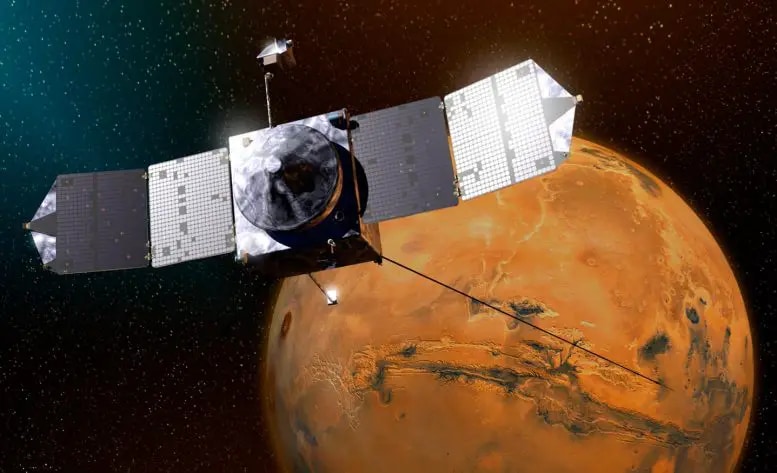
View all ImagesScientists have made a groundbreaking discovery about the solar wind, revealing how it reaches extraordinary speeds exceeding 1 million miles per hour. The findings, published in the journal Nature, draw on data collected by NASA's Parker Solar Probe. The researchers found that the magnetic field's energy near the sun's surface pushes the solar wind to achieve such terrifying speeds.
Co-led by James Drake from the University of Maryland and Stuart Bale from UC Berkeley, the study sheds light on a long-standing mystery regarding the drivers of solar wind, reports SciTech Daily. Understanding the implications for Earth is crucial. The solar wind creates a massive magnetic bubble called the heliosphere, shielding our solar system's planets from cosmic rays. However, it also carries plasma and a portion of the sun's magnetic field, which can interact with Earth's magnetosphere and cause disruptions, including the dangerous geomagnetic storms.
Geomagnetic storms occur during periods of heightened solar activity, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections. While these storms result in the magnificent Auroras Borealis in the North and Aurora Australis in the South, they can also have severe consequences, including power grid failures and disruptions to global communications. In extreme cases, they pose risks to astronauts in space.
Previous studies indicated that the sun's magnetic field played a role in driving the solar wind, but the process was unknown. Earlier this year, Drake co-authored a paper proposing that magnetic reconnection is responsible for heating and accelerating the solar wind.
The researchers found that the sun's surface is covered in small "jetlets" of hot plasma propelled upward by magnetic reconnection. By analyzing plasma data from the Parker Solar Probe, the scientists gained new insights into bursts of magnetic energy occurring in coronal holes. These are openings in the sun's magnetic field and the source of the solar wind.
The team demonstrated that the interchange connection between open and closed magnetic fields, a form of magnetic reconnection, is a continuous process rather than isolated events. They concluded that the rate of magnetic energy release, which propels the outward flow of heated plasma, overcomes gravity and produces the sun's fast wind.
By studying these frequent releases of energy on the sun's surface, researchers aim to comprehend and potentially predict larger and more hazardous eruptions that expel plasma into space.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.