Simply fantastic! Cities on Asteroids out in space! Check out what NASA did
A study claims that in future, humans could live on asteroids by building megacities on these rocks and go ambling around in space. NASA commissioned designs for such megacities.



_1639115875543_1639115887157.jpg)
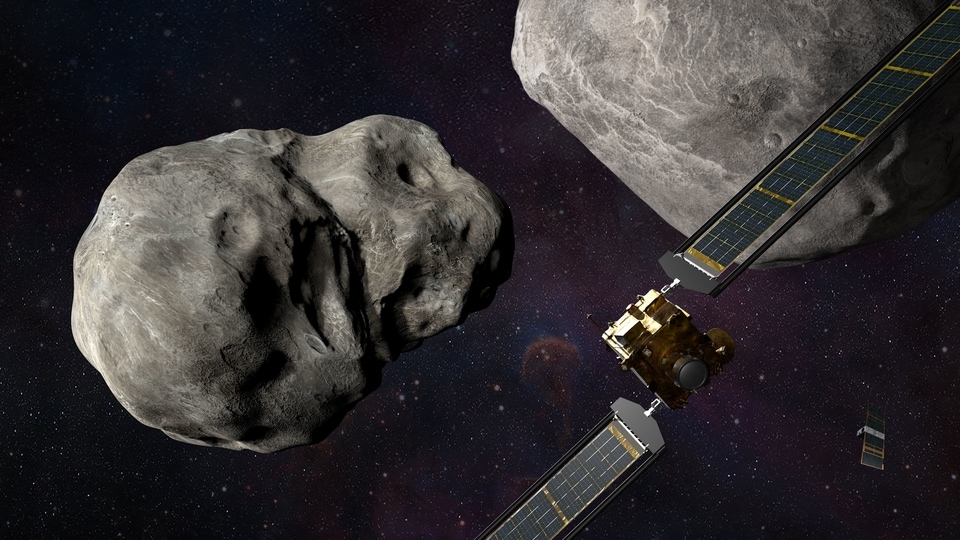


 View all Images
View all ImagesAsteroids have always terrified humans. After all, they were the reason behind one of the biggest known mass extinctions on the planet. And scientists realize that what happened to the dinosaurs at the end of the Cretaceous period could one day also happen to humans. That is why NASA recently conducted its Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) in order to build a defense system against asteroid strikes. But what if, instead of being afraid, we could live on these asteroids out in space and go where no man, or woman, has gone before? While it may seem preposterous to even imagine it, but that is what a new study is claiming. And to make it interesting, NASA appears to have commissioned designs for such habitats way back in the 1970s. Read on.
The study was published in the journal Frontiers in Astronomy and Space and was done as a thought experiment. It is essentially a theoretical hypothesis and the paper recognizes that we do not have the necessary technology to make it possible at present or in the near future. However, one thing the research paper highlights is that the concept might actually be possible.
“Obviously, no one will be building asteroid cities anytime soon, but the technologies required to accomplish this kind of engineering don't break any laws of physics,” physics professor Adam Frank, who worked on the project, said in a press conference.
In fact, even NASA believes in it. In 1972, physicist Gerard O'Neill drew up the schematics of a space habitat that would let humans live in space. This study is actually a twist on that design and it adds some modifications to it.
Humans could one day live in asteroid megacities
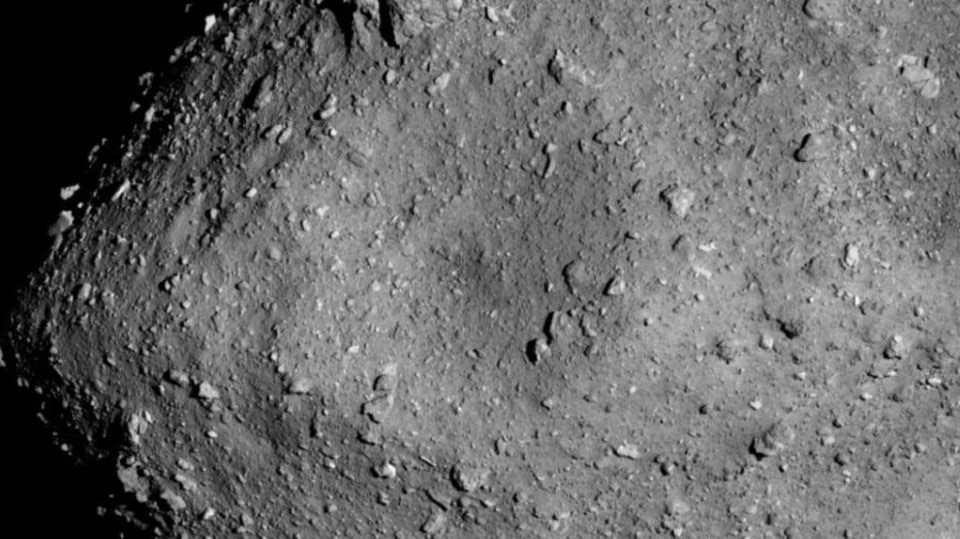
Primarily where the study modifies O'Neill's design is by reducing the amount of material needed to be flung into space and replacing it with an already existing structure of an asteroid. The researchers suggest that an asteroid of the size of Bennu (roughly 300 meters) can be used for this. By using mesh bags made up of carbon nanofiber, the entire asteroid could be covered. Then the mesh bag would be rotated to the point that the asteroid breaks apart. The rubble on the mesh would then serve as a hollowed outer layer to protect humans from radiation and cosmic waves.
After that, the hollowed asteroid rubble would be kept in the shape of a cylinder which would be spun fast enough to create artificial gravity but not enough to cause motion sickness. This habitat could, in theory, allow humans to live.
“The idea of asteroid cities might seem too distant until you realize that in 1900 no one had ever flown in an airplane, yet right this minute thousands of people are sitting comfortably in chairs as they hurtle at hundreds of miles an hour, miles above the ground. Space cities might seem like a fantasy now, but history shows that a century or so of technological progress can make impossible things possible,” said Frank.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.