Solar wind shockwave sparks Dangerous solar storm on Earth; Know the consequences
A dangerous solar storm struck Earth yesterday, December 19 after a solar wind shockwave opened a crack in our planet’s magnetosphere. Check details.




 View all Images
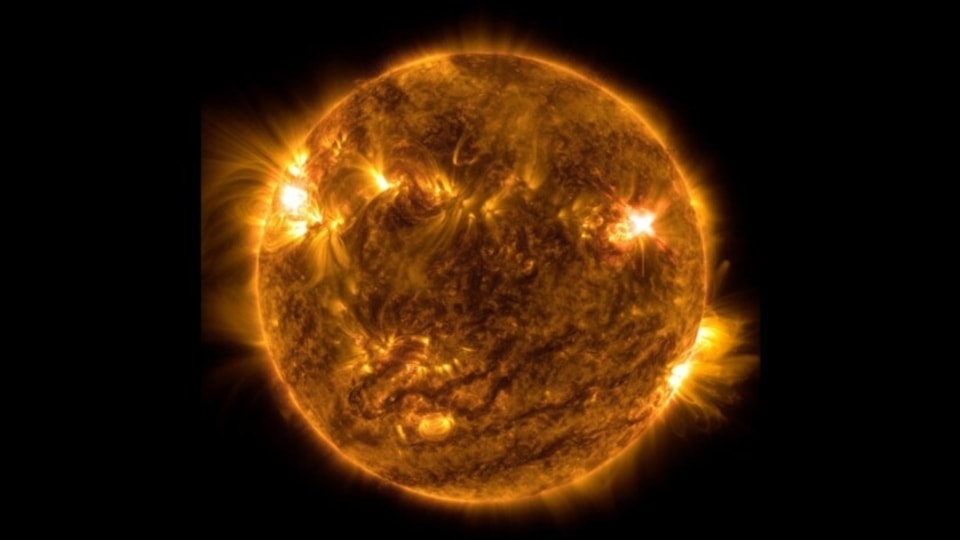
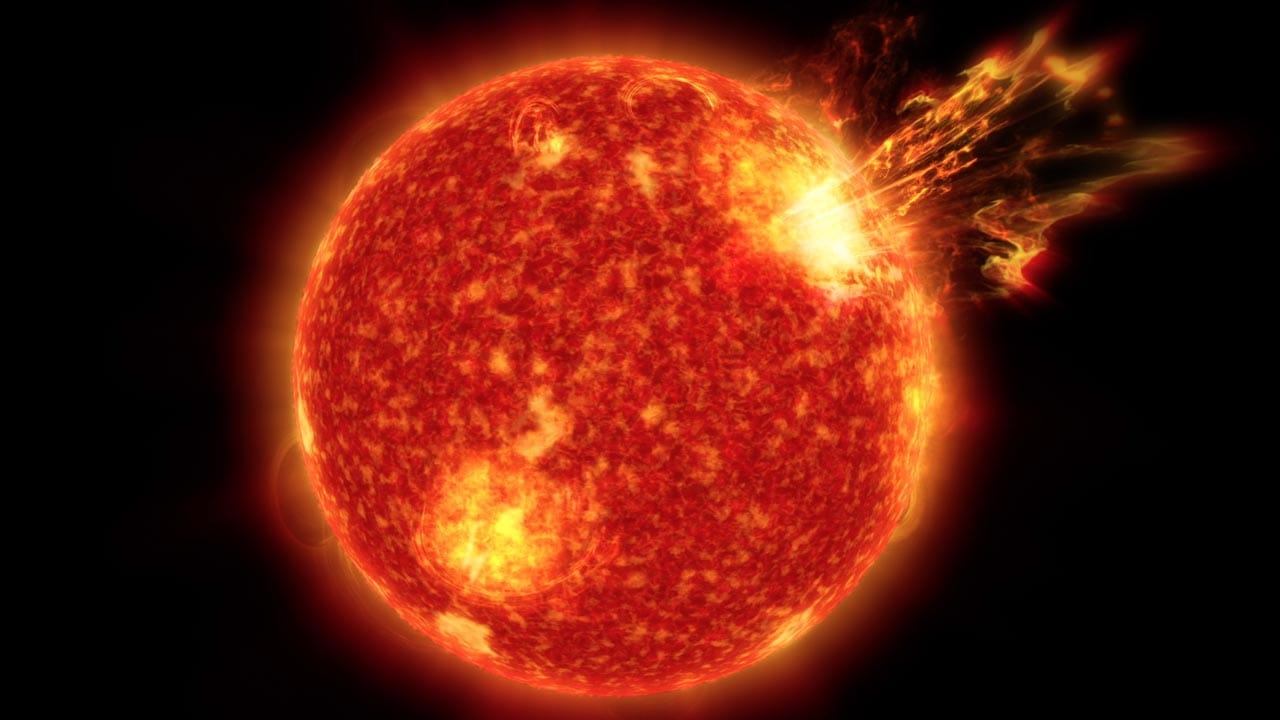
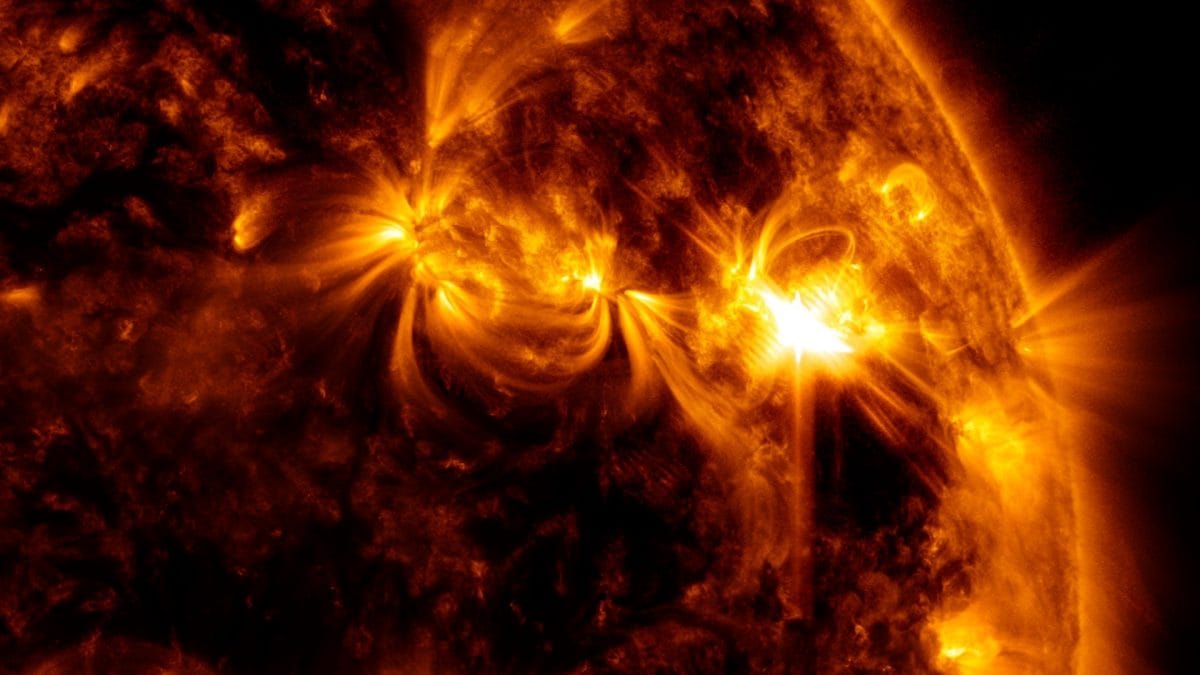
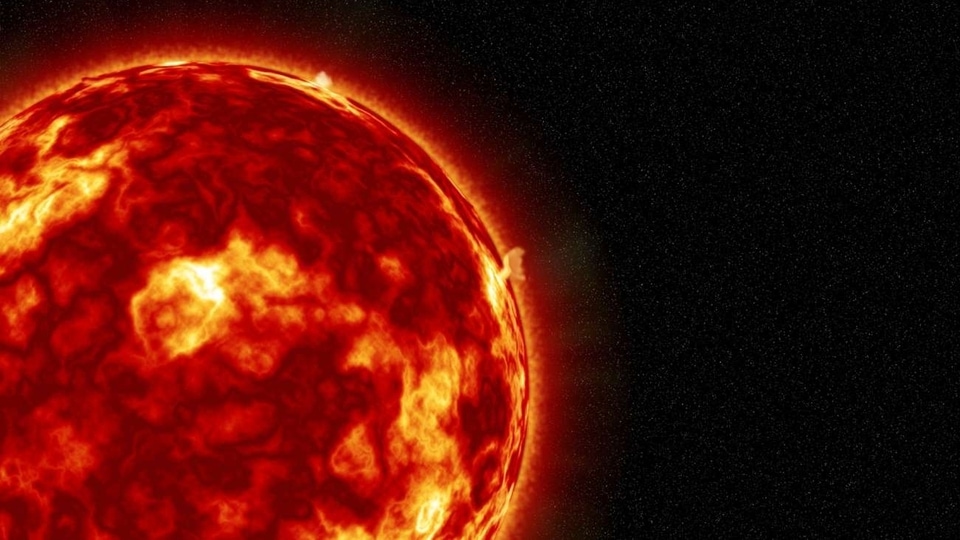
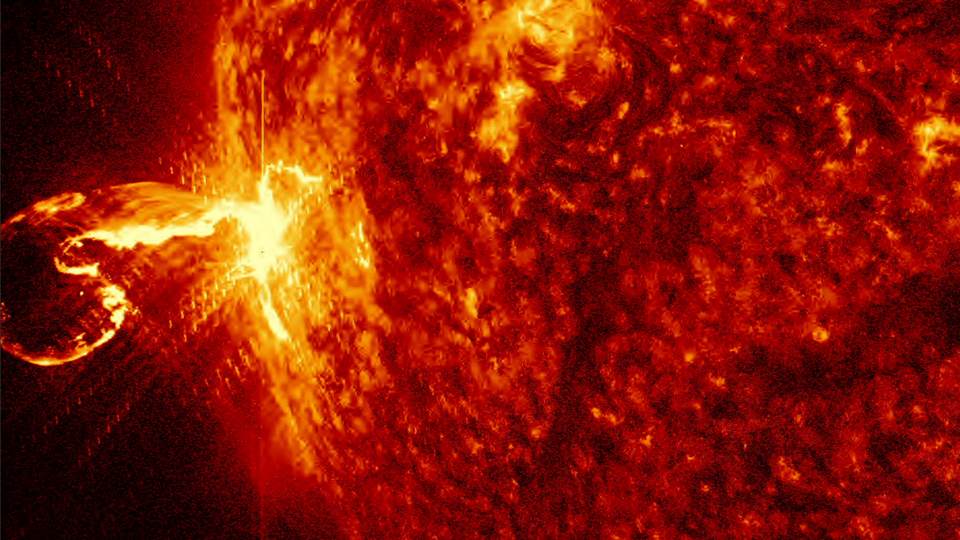
View all ImagesLast week, scientists observed a highly unstable sunspot emerge on the Earth-facing disk on the Sun. The sunspot, officially known as AR3165, has been experiencing multiple explosions and has erupted more than 18 M-class solar flares ever since December 15. However, the worst impact of it came yesterday, December 19, when a shockwave in the solar wind struck the magnetosphere of Earth and cracked open a hole in it, causing a dangerous solar storm event. Read on to know all about it.
The incident was reported by Spaceweather.com which noted on its website, “A shockwave in the solar wind hit Earth's magnetic field during the late hours of Dec. 18th. The impact opened a crack in our planet's magnetosphere, setting the stage for G1-class geomagnetic storms on Dec. 19th”. It is believed that the shockwave was part of the hyperactive emissions from the sunspot AR3165 and could have been a particularly powerful coronal mass ejection (CME).
Solar storm strikes the Earth
While the solar storm was not a major one, it was still responsible for temporary shortwave radio blackouts and GPS disruptions. However, the majority of the solar storm event fell on the oceanic region and as a result, the impact was limited to passing by ships and planes. However, this was a lucky escape and with the Sun flaring up as it reaches the peak of its solar cycle, it is expected that more solar storms will strike the Earth in coming days.
In fact, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) forecasters have revealed that there is a chance of another solar storm on December 21. This is likely to be caused by a side-by-side pair of solar wind streams that are expected to graze Earth's magnetic field. Incidentally, a different sunspot is responsible for the upcoming solar storm.
How NOAA keeps an eye on the Sun
NOAA monitors the solar storms and Sun's behavior using its DSCOVR satellite which became operational in 2016. The recovered data is then run through the Space Weather Prediction Center and the final analysis is prepared. The different measurements are done on temperature, speed, density, degree of orientation and frequency of the solar particles.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.