Watch LIVE: NASA to deflect asteroid in key test of planetary defense
Watch LIVE: NASA will attempt a feat humanity has never before accomplished: smacking a spacecraft into an asteroid.







 View all Images
View all ImagesWatch LIVE on YouTube: NASA will on Monday attempt a feat humanity has never before accomplished: deliberately smacking a spacecraft into an asteroid to slightly deflect its orbit, in a key test of our ability to stop cosmic objects from devastating life on Earth.
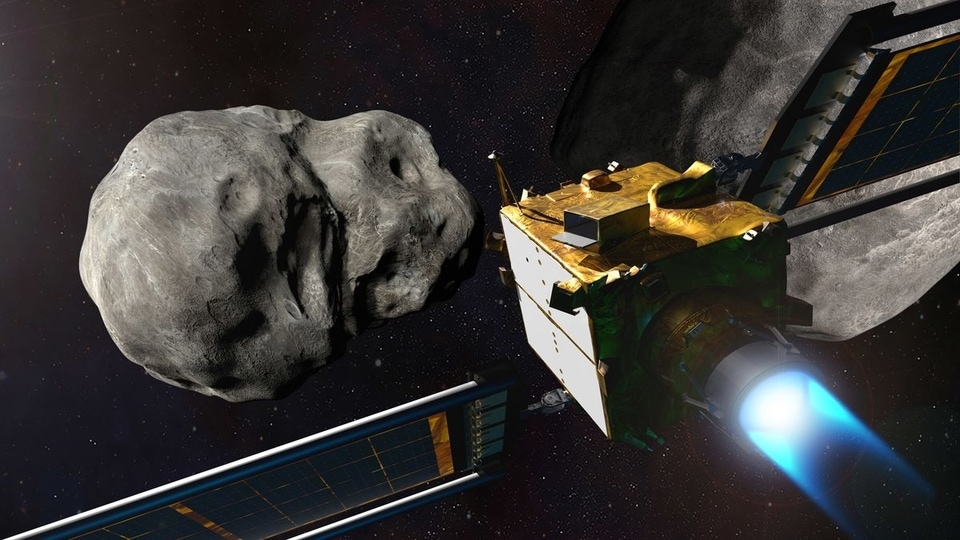
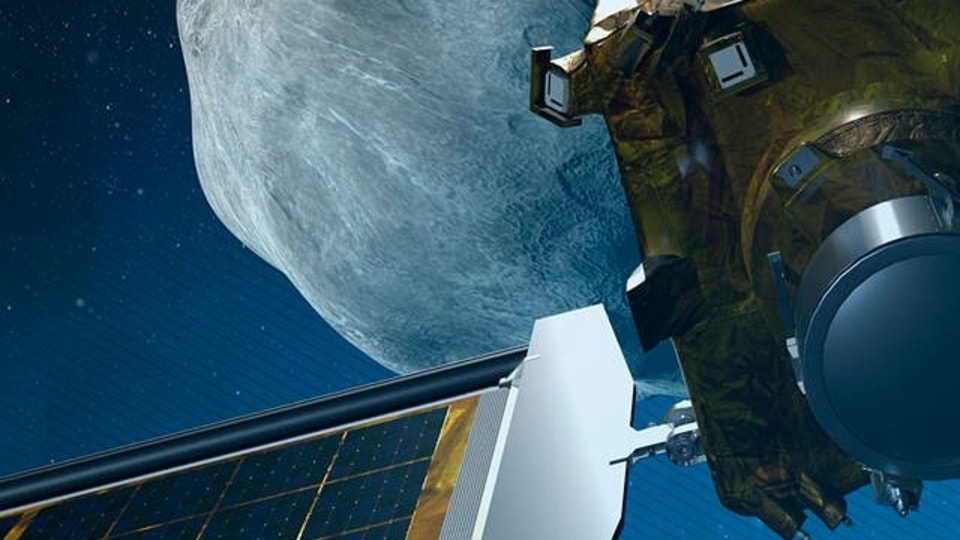
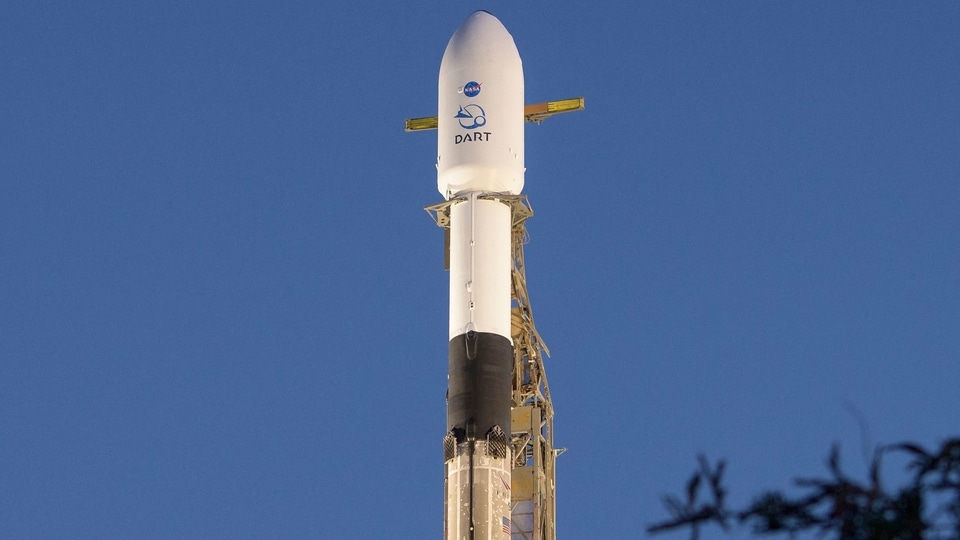
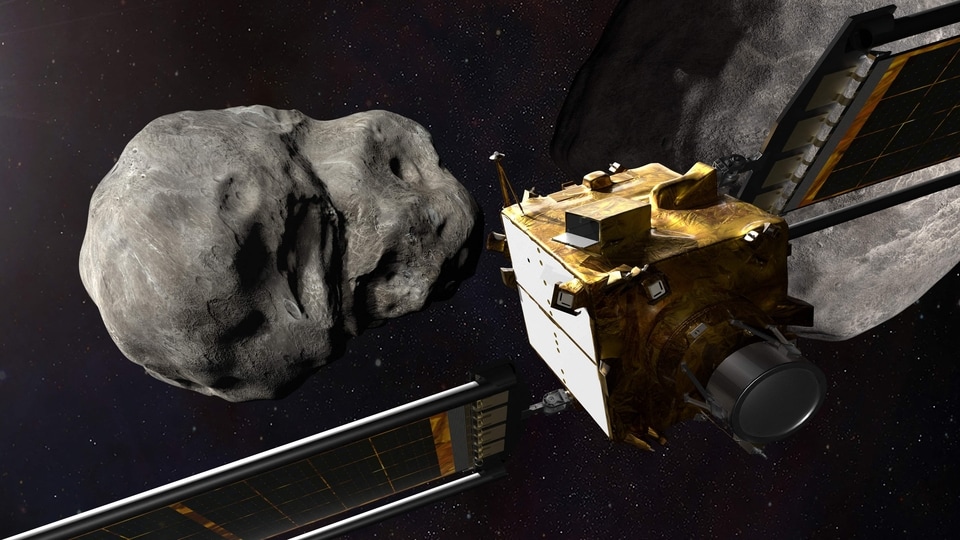
The Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) spaceship launched from California last November and is fast approaching its target, which it will strike at roughly 14,000 miles (22,500 kilometers) per hour.
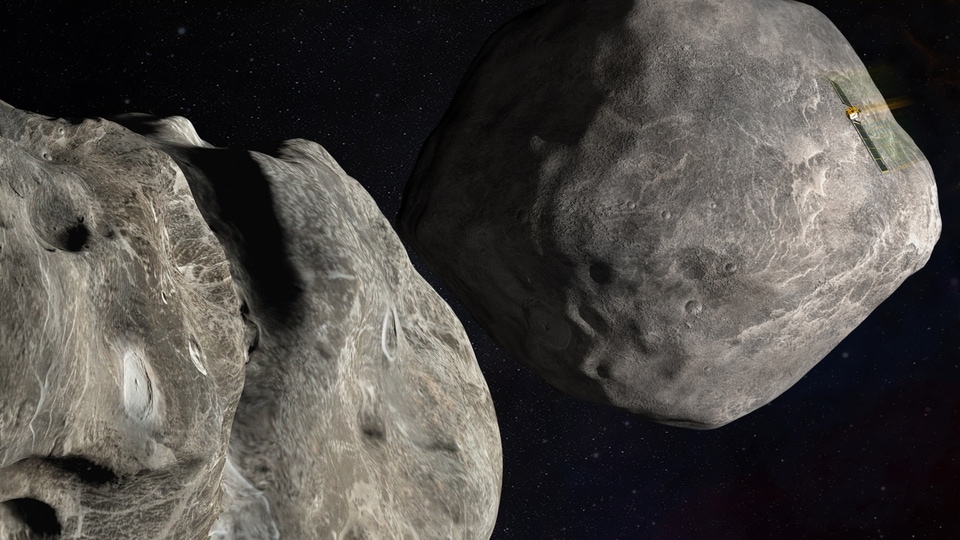
To be sure, neither the asteroid moonlet Dimorphos, nor the big brother it orbits, called Didymos, pose any threat as the pair loop the Sun, passing about seven million miles from Earth at nearest approach.
But NASA has deemed the experiment important to carry out before an actual need is discovered.
If all goes to plan, impact between the car-sized spacecraft, and the 530-foot (160 meters, or two Statues of Liberty) asteroid should take place at 7:14 pm Eastern Time (2314 GMT), and can be followed on a NASA livestream.
By striking Dimorphos head on, NASA hopes to push it into a smaller orbit, shaving ten minutes off the time it takes to encircle Didymos, which is currently 11 hours and 55 minutes -- a change that will be detected by ground telescopes in the days that follow.
The proof-of-concept experiment will make a reality of what has before only been attempted in science fiction -- notably films such as "Armageddon" and "Don't Look Up."
Watch NASA DART Spacecraft crash into asteroid LIVE on YouTube below:
- Technically challenging -
As the craft propels itself through space, flying autonomously for the mission's final phase, its camera system will start to beam down the very first pictures of Dimorphos.
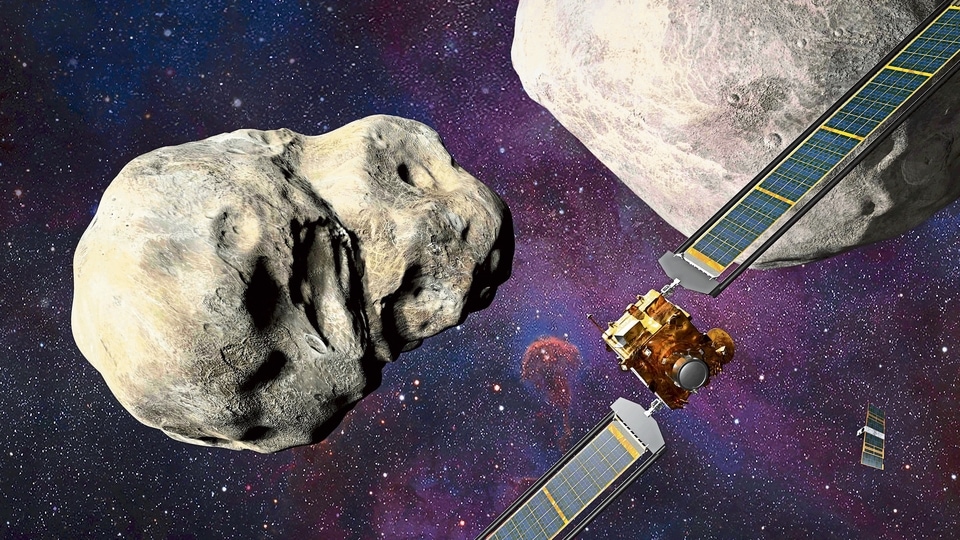
Minutes later, a toaster-sized satellite called LICIACube, which separated from DART a couple of weeks earlier, will make a close pass of the site to capture images of the collision and the ejecta -- the pulverized rock thrown off by impact.
LICIACube's pictures will be sent back in the weeks and months that follow.
Also watching the event: an array of telescopes, both on Earth and in space -- including the recently operational James Webb -- which might be able to see a brightening cloud of dust.
Finally, a full picture of what the system looks like will be revealed when a European Space Agency mission four years down the line called Hera arrives to survey Dimorphos's surface and measure its mass, which scientists can only guess at currently.
- Being prepared -
Very few of the billions of asteroids and comets in our solar system are considered potentially hazardous to our planet, and none are expected in the next hundred or so years.
But "I guarantee to you that if you wait long enough, there will be an object," said NASA's Thomas Zurbuchen.
We know that from the geological record -- for example, the six-mile wide Chicxulub asteroid struck Earth 66 million years ago, plunging the world into a long winter that led to the mass extinction of the dinosaurs along with 75 percent of all species.
An asteroid the size of Dimorphos, by contrast, would only cause a regional impact, such as devastating a city, albeit with greater force than any nuclear bomb in history.
How much momentum DART imparts on Dimorphos will depend on whether the asteroid is solid rock, or more like a "rubbish pile" of boulders bound by mutual gravity, a property that's not yet known.
The shape of the asteroid is also not known, but NASA engineers are confident DART's SmartNav guidance system will hit its target.
If it misses, NASA will have another shot in two years' time, with the spaceship containing just enough fuel for another pass.
But if it succeeds, Chabot said, the mission will mark the first step towards a world capable of defending itself from a future existential threat.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.