When a gigantic 6.4-km asteroid broke and pieces crashed on Earth
Seven years ago, a big chunk from a massive 6.4-kilometers wide asteroid broke apart and smashed into the Earth. The piece of asteroid has now offered a glimpse into the origin of life.



_1639115875543_1639115887157.jpg)


 View all Images
View all ImagesJust a few days ago, the Earth witnessed the Geminids meteor shower where the Earth annually passes by the debris left behind by the asteroid 3200 Phaethon. But what we look at as bright, glowing lights across the sky are actually small space rocks or meteors that could just as easily get pulled by the Earth and crash onto it. And this is not just a hypothetical possibility, this happens a lot around the planet. Just seven years ago, on November 13, 2015, a piece of a gigantic asteroid fell near the town of Kamargaon in Assam, India. While it did not cause any major destruction owing to the remote region, the meteorite, which weighed 12 kilograms, could have easily taken many lives. So, what caused this asteroid shard to hit the Earth and why has the Kamargaon meteorite become important for us? Find out.
According to a study published in the Journal of Geophysical Research-Planets, this broken asteroid has conveyed a very important piece of evidence to us that points us towards the origin of life itself. The research is conducted by a team at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kharagpur who claim that the composition and structure of the Kamargaon meteorite can reveal important information about the volatile gasses that help create and sustain life.
How the asteroid shard landed on Earth
The study theorizes that it belongs to the asteroid belt present between Mars and Jupiter. The region is filled with asteroids that revolve around the Sun in their independent orbits. After the parent asteroid, a 6.4-kilometers wide space rock, collided with another, this piece broke off and began moving towards our planet along with some smaller meteorites.
Why is the Kamargaon meteorite important
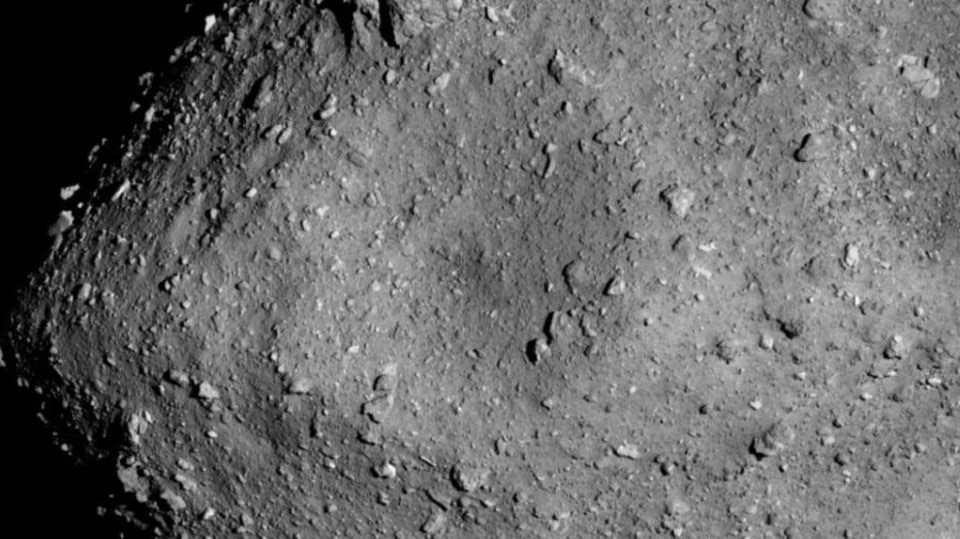
The researchers have found a systemic type of hole on the asteroid called a vesicle. These vesicles are formed when the gasses trapped within an asteroid begin expanding due to heat and try to escape. This probably happened when the meteorite came in contact with Earth's atmosphere and the friction caused it to heat up. But this has also highlighted that there was presence of volatile elements such as oxygen, carbon, sodium, manganese and sulfur which are also responsible for creating and sustaining life. Such evidence has been found for the first time in an asteroid belonging to the outer solar system.
This also tells us that these important elements responsible for the origin of life probably existed right at the beginning of the solar system and in fact came straight from stars and star dusts. While a definitive answer is still not possible, this is a big clue in the giant puzzle of our origin.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.