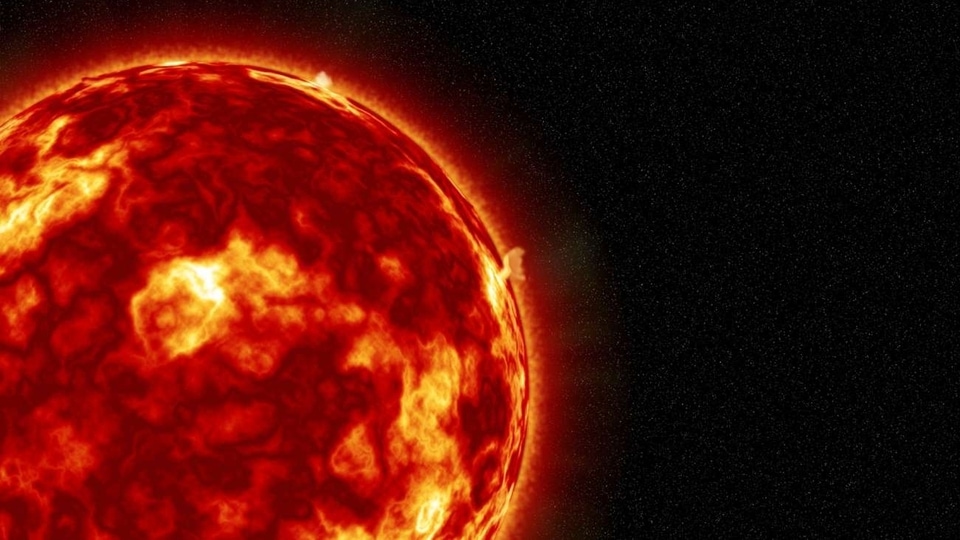
The solar storm that shook the solar system, know all about the shocking Bastille Day event
On July 15, 2000, Earth suffered one of the worst solar storms in history. The storm, known as the Bastille Day solar storm, was so intense that the shockwaves were felt at the edge of the solar system by the Voyager spacecraft.




 View all Images
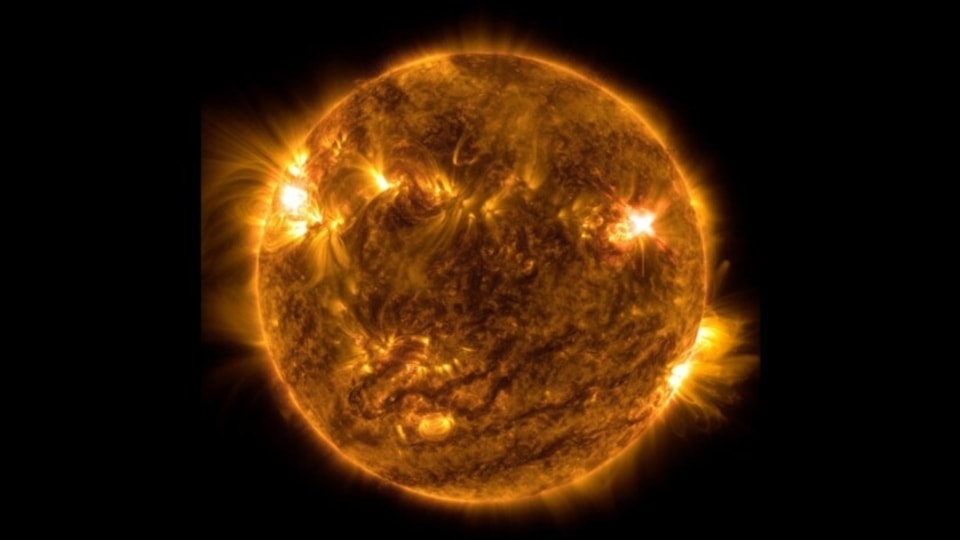
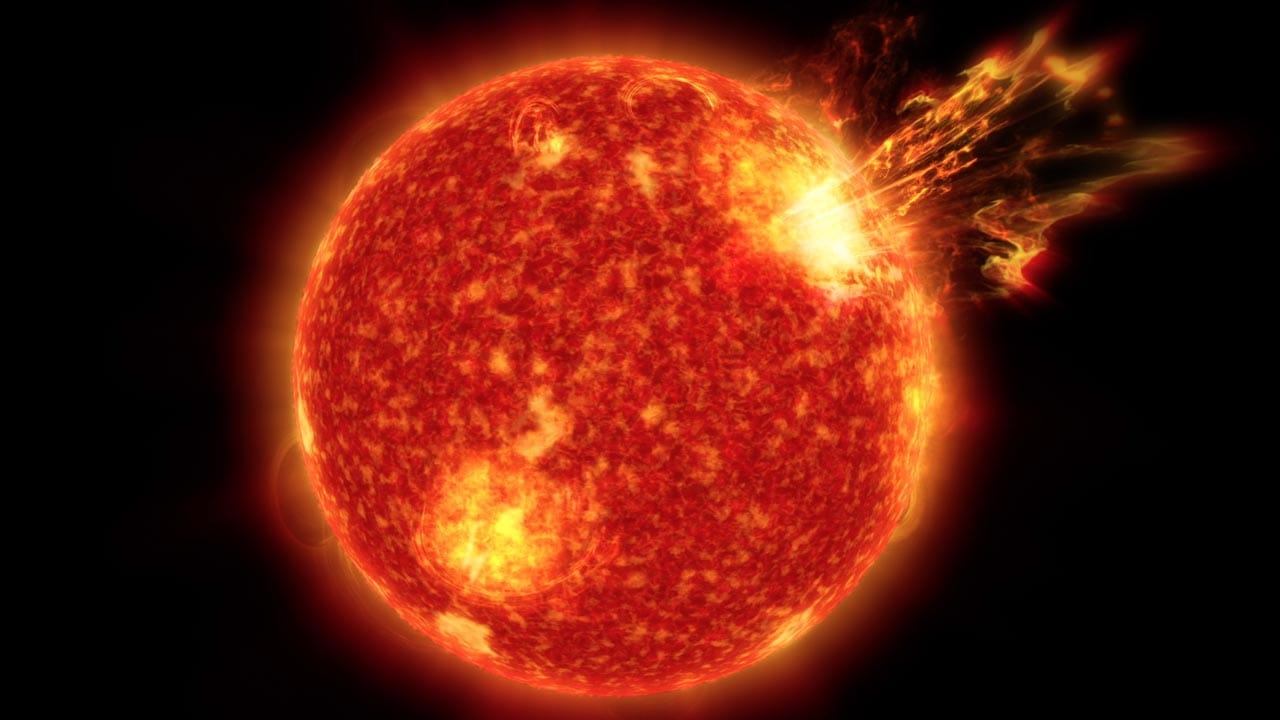
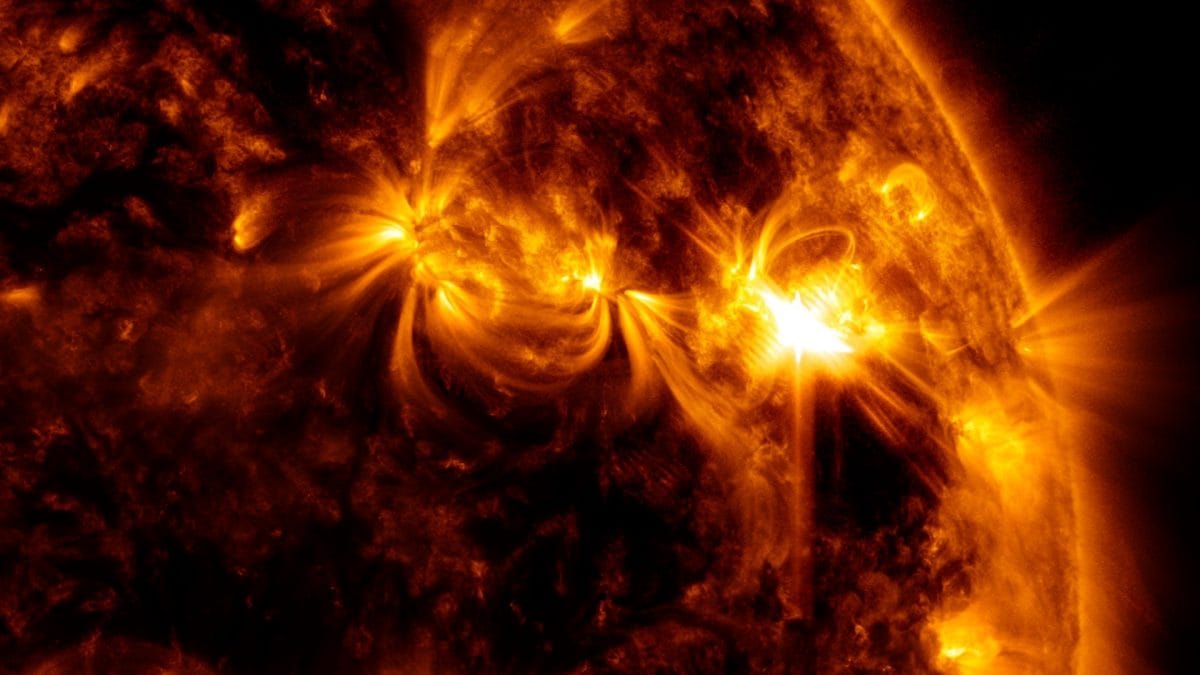
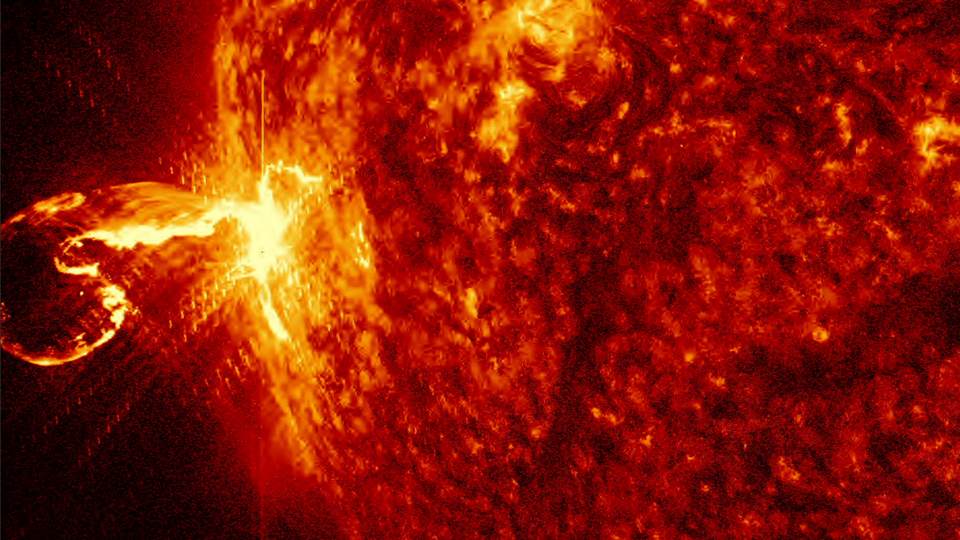
View all ImagesOn July 15, 2000, the Earth was hit by an unexpected solar storm. The storm was sparked by a coronal mass ejection (CME) that was released after an X5.7-class solar flare erupted on the Sun. The terrifying event was witnessed by the NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, which was launched just five years earlier. But that was not the only NASA spacecraft to witness the solar storm. The Voyager 1 spacecraft, which was placed at the edge of the solar system, also felt the shockwaves produced by the flare eruption. Today, this event is known as the Bastille Day solar storm, and as it completes its 23rd anniversary, let us know more about it.
According to a report by SpaceWeather.com, “Its impact on July 15, 2000, sparked an extreme (Kp=9) geomagnetic storm. By the time the storm subsided on July 16, 2000, auroras had been reported as far south as Texas, Florida and Mexico”. The report also revealed that the flare eruption released about 10 to the power of 33 ergs, or “about the same as a thousand billion WWII atomic bombs”.
The Bastille Day solar storm
The solar storm has been named Bastille Day because it coincides with the day when the city of Bastille fell in 1789. The day is also known as the national day of France.
As the strong magnetic waves engulfed the Earth, the solar storm started off causing aurora display in even the lower latitudes, highlighting its strength. It also damaged many satellites and caused radio blackouts and communication blockades. As in 2000 mobile phones were still gaining popularity, the effect on mobile networks and internet services is not clear.
Today, this solar storm event, along with other terrifying events such as the Carrington event, are reminders that solar storms can get very terrifying very quickly, and their damaging effects are not to be taken lightly.
The tech that enables NASA SOHO
NASA's SOHO (Solar and Heliospheric Observatory) is a satellite that was launched on December 2, 1995. It is a joint project between NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) to study the sun, its atmosphere, and its effects on the solar system. Equipped with 12 scientific instruments, such as an Extreme Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (EIT), Michelson Doppler Imager (MDI), LASCO (Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronagraph), and others, SOHO captures images of the sun's corona, measures the velocity and magnetic fields of the sun's surface, and observes the faint corona around the sun.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.