Asteroids brought water on Earth: Study
In a quest to shed light on the origins of life and the formation of the universe, researchers are scrutinising material brought back to earth in 2020 from the asteroid Ryugu.


_1661230453587.jpg)
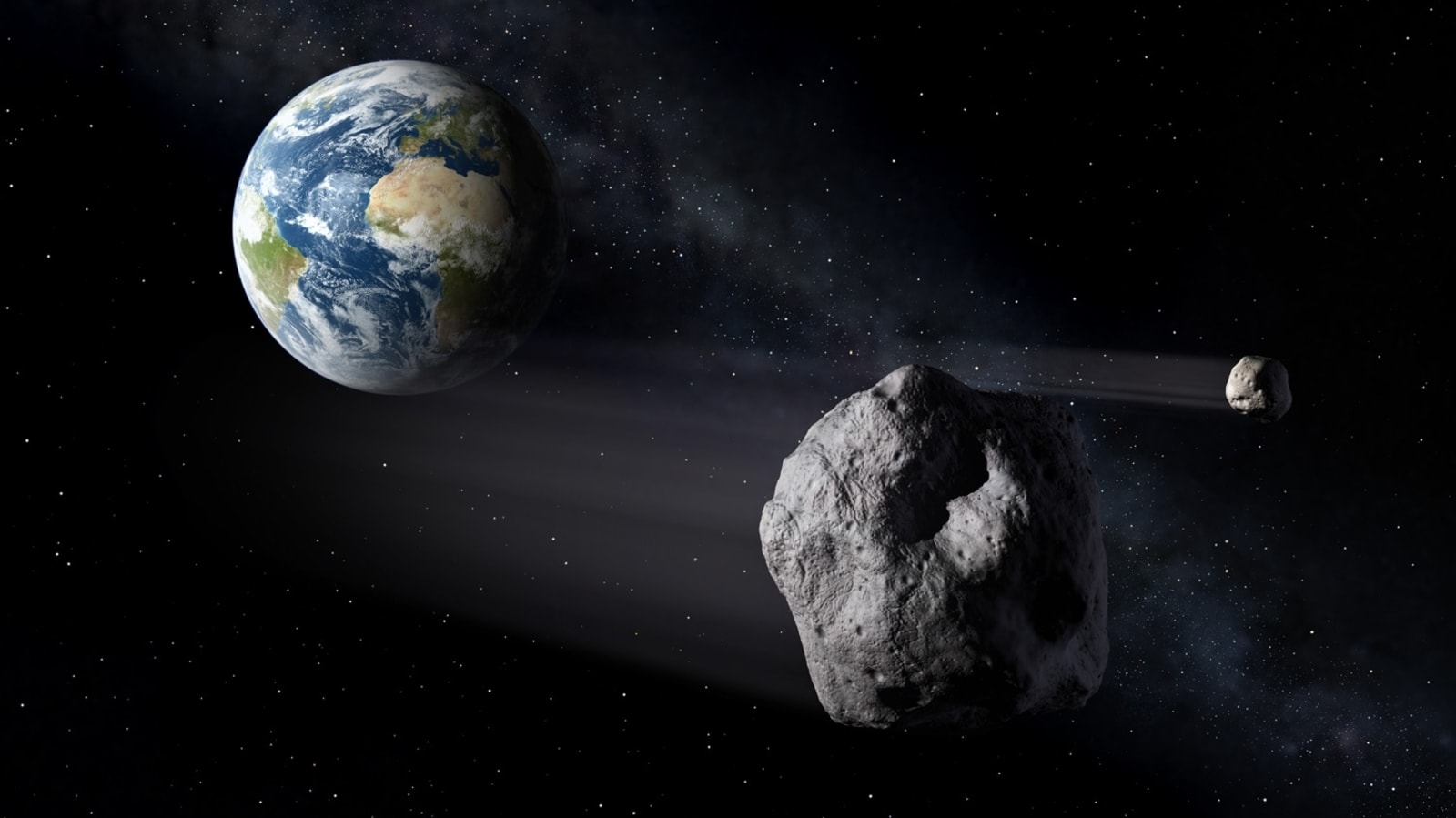



 View all Images
View all ImagesWater may have been brought to Earth by asteroids from the outer edges of the solar system, scientists said after analysing rare samples collected on a six-year Japanese space mission.
In a quest to shed light on the origins of life and the formation of the universe, researchers are scrutinising material brought back to earth in 2020 from the asteroid Ryugu.
The 5.4 grams (0.2 ounces) of rocks and dust were gathered by a Japanese space probe, called Hayabusa-2, that landed on the celestial body and fired an "impactor" into its surface.
Studies on the material are beginning to be published, and in June, one group of researchers said they had found organic material which showed that some of the building blocks of life on Earth, amino acids, may have been formed in space.
In a new paper published in the journal Nature Astronomy, scientists said the Ryugu samples could give clues to the mystery of how oceans appeared on Earth billions of years ago.
"Volatile and organic-rich C-type asteroids may have been one of the main sources of Earth's water," said the study by scientists from Japan and other countries, published Monday.
"The delivery of volatiles (that is, organics and water) to the Earth is still a subject of notable debate," it said.
But the organic materials found "in Ryugu particles, identified in this study, probably represent one important source of volatiles".
The scientists hypothesised that such material probably has an "outer Solar System origin", but said it was "unlikely to be the only source of volatiles delivered to the early Earth".
Hayabusa-2 was launched in 2014 on its mission to Ryugu, around 300 million kilometres away, and returned to Earth's orbit two years ago to drop off a capsule containing the sample.
In the Nature Astronomy study, the researchers again hailed the findings made possible by the mission.
"Ryugu particles are undoubtedly among the most uncontaminated Solar System materials available for laboratory study and ongoing investigations of these precious samples will certainly expand our understanding of early Solar System processes," the study said.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.