Crackling magnetic filament on Sun ready to explode; Solar storm danger looms
Near the equator of the Sun, a crackling magnetic filament has been spotted by astronomers which can explode at any time. This can bring yet another dangerous solar storm to Earth.





 View all Images
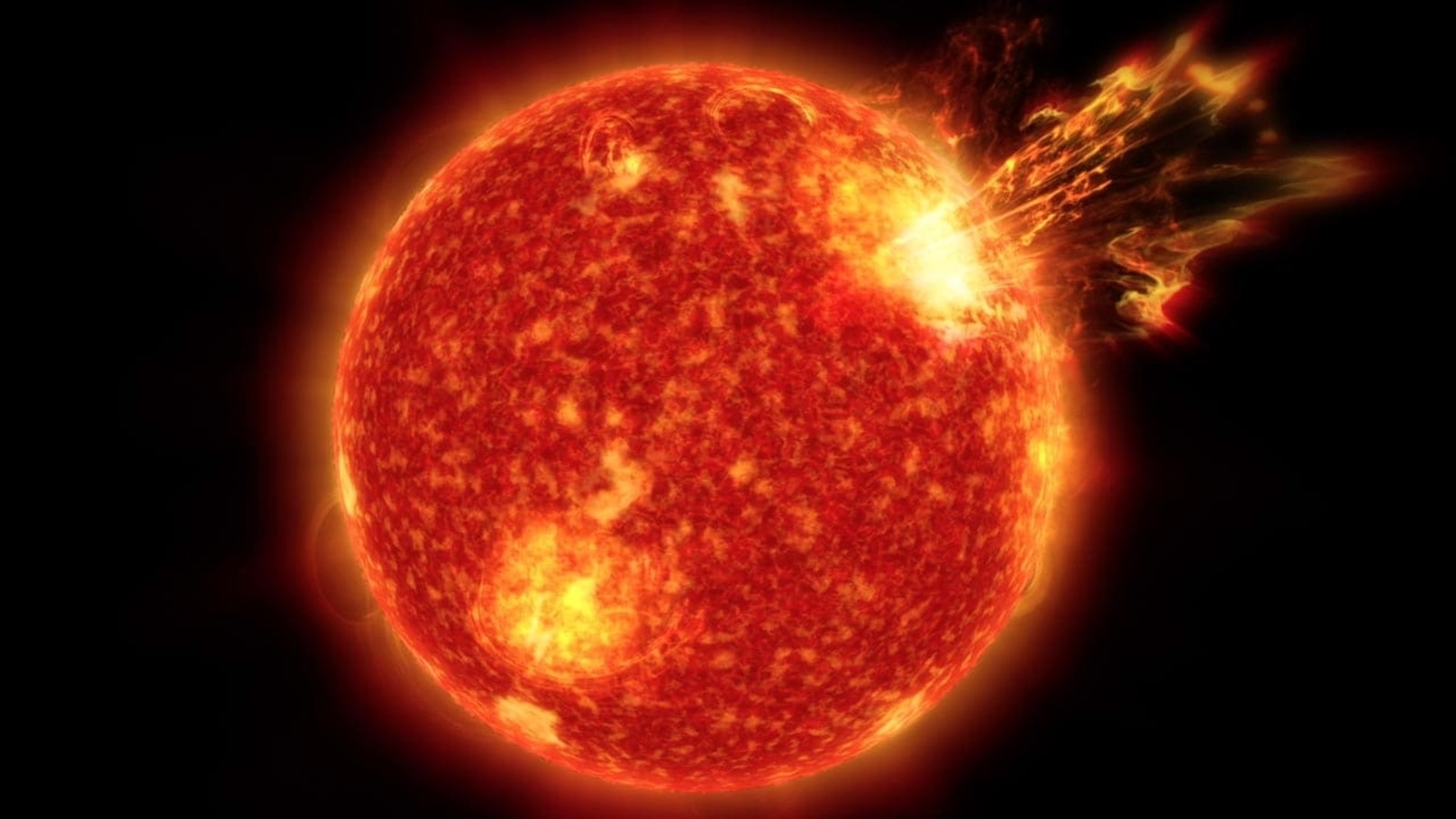
View all ImagesThe Earth cannot catch a break from the Sun's wrath. It has been hours since the Earth has passed the coronal mass ejection (CME) cloud that sideswiped our planet, creating a very weak aurora display, and the Sun is preparing another onslaught. An astronomer has observed a magnetic filament near the equator of the Sun which is bustling with a huge amount of magnetic field lines. This means it can soon erupt and send another wave of solar storm towards our planet. Check the details.
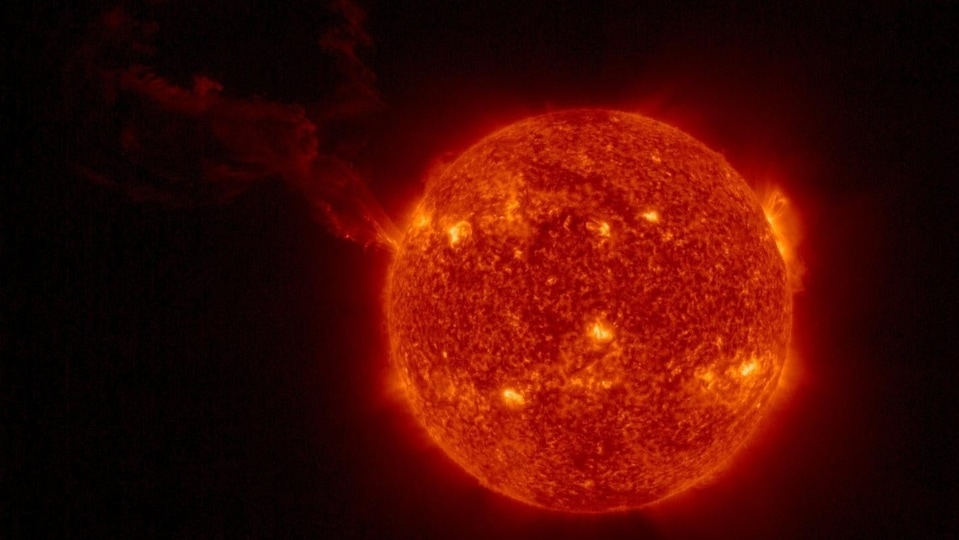
The development was captured by Dr. Erika Palmerio, a research scientist at Predictive Science, who focuses on the Sun and space weather. In a tweet, she revealed, “the eastern limb of the Earth-facing Sun is just gorgeous right now. A very clear pseudostreamer near the equator—see the plasma following the magnetic field in a cusp-like shape! And a filament off the SE limb that may erupt with another show”.
For the unaware, streamers are closed magnetic loops which lie above divisions between regions of opposite magnetic polarity on the Sun's surface. They resemble and act like a solar flare, only, they do not form within a sunspot.
Another solar storm to soon hit the Earth
Streamers are pretty common on the Sun and are very clearly visible during solar eclipses. They are of two types, a helmet streamer and a pseudo streamer. Helmet streamers are concentric loops on the surface of the Sun whereas pseudo streamers form alongside each other instead of within one another.
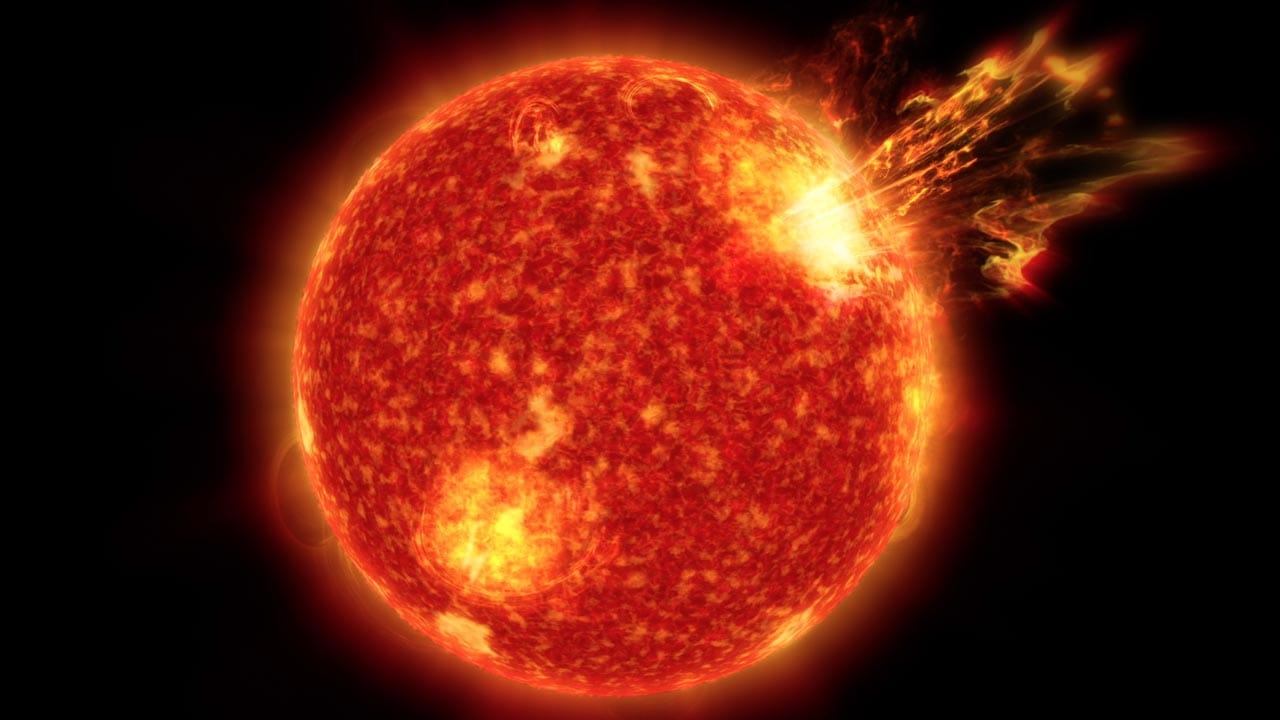
However, the presence of such powerful streamers is an indication of the increased solar activity. If this streamer goes out, it will release a huge amount of radiation and magnetic energy that can disrupt shortwave radio communication on Earth. Further, they can release CME particles and send them to cause a dangerous solar storm.
For now, the streamer seems to be crackling with magnetic field lines, which means that its energy is growing unstable. However, whether it explodes while in the view of Earth or not is something that cannot be determined at the moment.
Interestingly, many forecasters predicted Solar Cycle 25, the current one, to be a weak one. But as February 2023 witnessed 100 sunspots in a 28 day period, which has happened only three times since 2014, many astronomers now believe that this solar cycle is definitely going to exceed expectations.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.





























