NASA's Webb Telescope takes star-filled portrait of pillars of creation
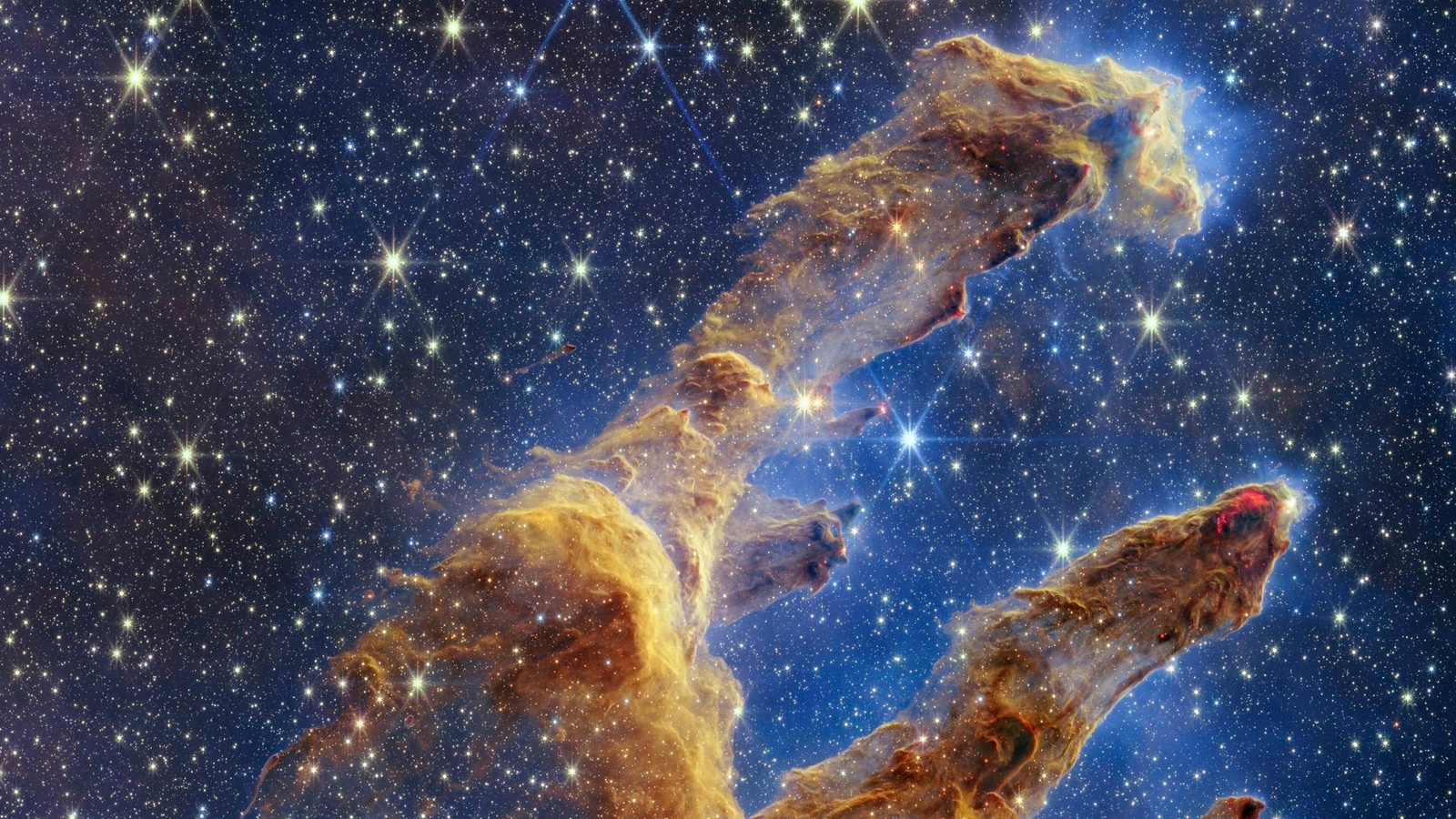
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has captured highly detailed landscape the Pillars of Creation where new stars are forming.


_1661230453587.jpg)



 View all Images
View all ImagesNASA's James Webb Space Telescope has captured a lush, highly detailed landscape the iconic Pillars of Creation where new stars are forming within dense clouds of gas and dust. The three-dimensional pillars look like majestic rock formations but are far more permeable. These columns are made up of cool interstellar gas and dust that appear at times semi-transparent in near-infrared light.
Webb's new view of the Pillars of Creation, which were first made famous when imaged by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope in 1995, will help researchers revamp their models of star formation by identifying far more precise counts of newly formed stars, along with the quantities of gas and dust in the region. Over time, they will begin to build a clearer understanding of how stars form and burst out of these dusty clouds over millions of years.
Newly formed stars are the scene-stealers in this image from Webb's Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam). These are the bright red orbs that typically have diffraction spikes and lie outside one of the dusty pillars. When knots with sufficient mass form within the pillars of gas and dust, they begin to collapse under their own gravity, slowly heat up, and eventually form new stars.
What about those wavy lines that look like lava at the edges of some pillars? These are ejections from stars that are still forming within the gas and dust. Young stars periodically shoot out supersonic jets that collide with clouds of material, like these thick pillars. This sometimes also results in bow shocks, which can form wavy patterns like a boat does as it moves through water. The crimson glow comes from the energetic hydrogen molecules that result from jets and shocks. This is evident in the second and third pillars from the top -- the NIRCam image is practically pulsing with their activity. These young stars are estimated to be only a few hundred thousand years old.
Although it may appear that near-infrared light has allowed Webb to "pierce through" the clouds to reveal great cosmic distances beyond the pillars, there are no galaxies in this view. Instead, a mix of translucent gas and dust known as the interstellar medium in the densest part of our Milky Way galaxy's disk blocks our view of the deeper universe.
This scene was first imaged by Hubble in 1995 and revisited in 2014, but many other observatories have also stared deeply at this region. Each advanced instrument offers researchers new details about this region, which is practically overflowing with stars.
This tightly cropped image is set within the vast Eagle Nebula, which lies 6,500 light-years away.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world's premier space science observatory. Webb will solve mysteries in our solar system, look beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probe the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.





























