Wow! NASA James Webb Telescope snaps unparalleled dusty disk near red dwarf
NASA's James Webb Telescope has snapped an image of dusty disk around the red dwarf star that was never viewed before. Know more details.


_1661230453587.jpg)


 View all Images
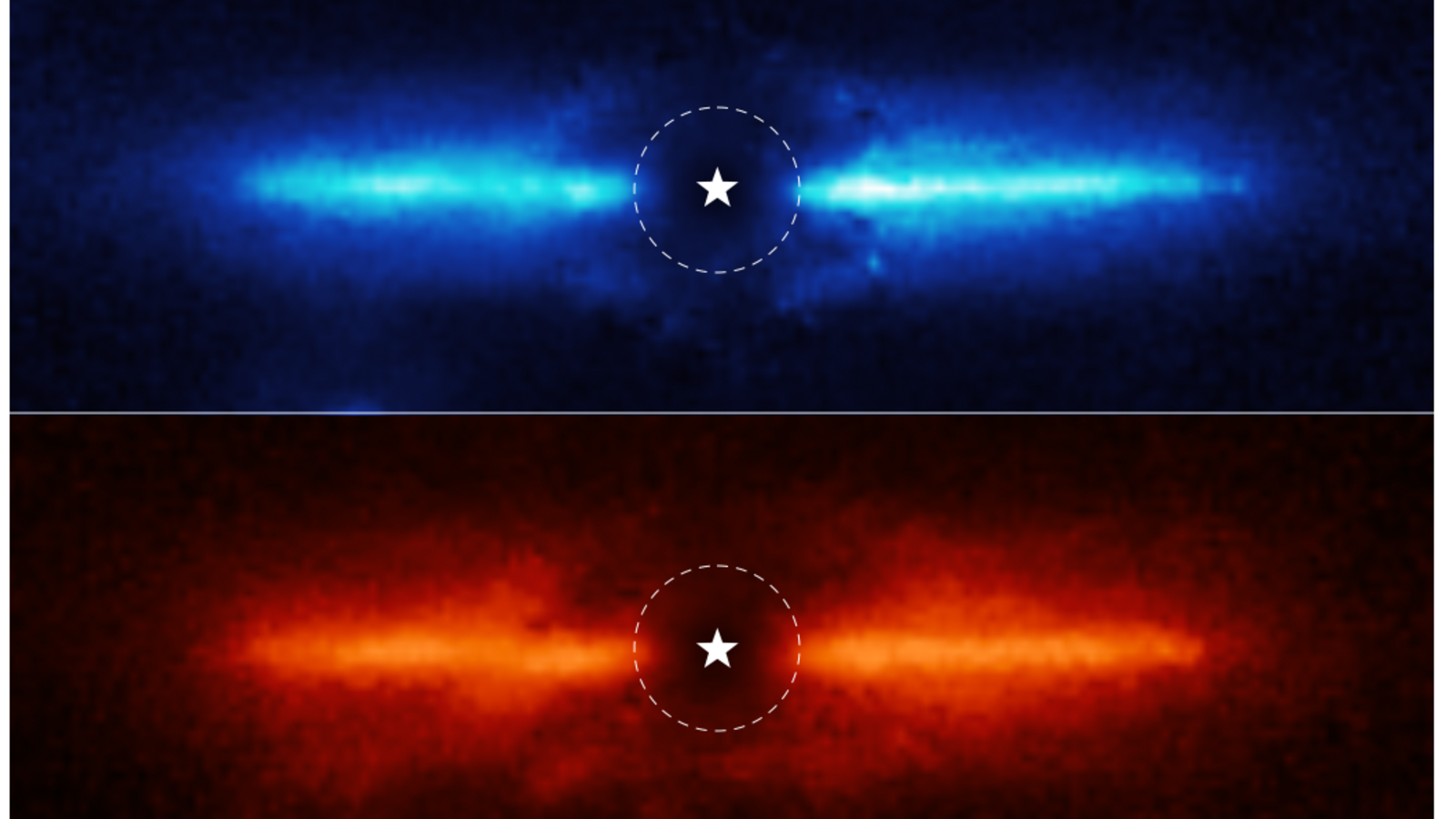
View all ImagesNASA's most expensive telescope, the James Webb Space Telescope has again amazed scientists by snapping till-now unseen images of the deep cosmos. Here again, the Webb Telescope has clicked the inner workings of a dusty disk surrounding a nearby red dwarf star. NASA says that these are the very first observations ever. The newly shared image by Webb Telescope provides clues to the composition of the disk.
“A debris disk is continuously replenished by collisions of planetesimals. By studying it, we get a unique window into the recent dynamical history of this system,” Kellen Lawson of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, lead author on the study of the star AU Mic said in a blog. This star system is also said to be one of the very few examples of a young star, with known exoplanets. And this near and bright debris disk is enough to study holistically using James Webb Telescope's uniquely powerful instruments, principal investigator of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center Josh Schliede said.
This star system named AU Microscopii or AU Mic is located 32 light-years away in the southern constellation Microscopium, which is approximately 23 million years old. This means planet formation has ended since that process typically takes less than 10 million years. This star has two known planets, while the dusty debris disk results from collisions between leftover planetesimals.
Tech behind Dusty disk near the Red dwarf star
The research team used NASA's James Webb Space Telescope's Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) to study this star system AU Mic. NASA says, “With the help of NIRCam's coronagraph, which blocks the intense light of the central star, they were able to study the region very close to the star.” This NIRCam of the Webb telescope allows researchers to trace the disk as close to the star as 5 astronomical units or 460 million miles, which is equivalent to Jupiter's orbit in our solar system.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.





























