NASA Prepares Tiny Underwater Robots for Europa's Icy Oceans
NASA develops tiny underwater robots set to explore Europa’s icy oceans for signs of alien life





 View all Images
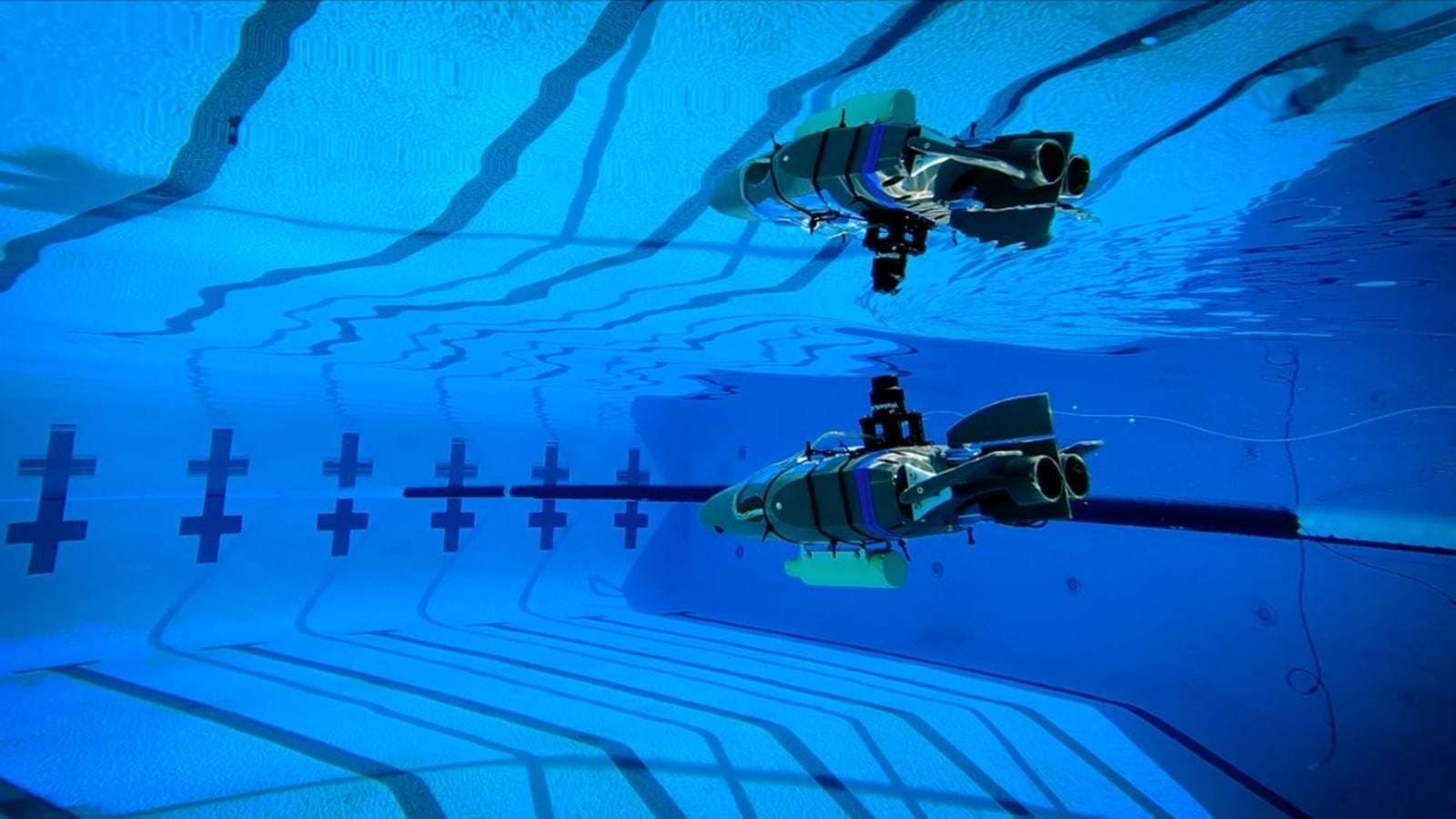
View all ImagesNASA is advancing its search for extraterrestrial life by developing miniature underwater robots designed to explore alien oceans. Known as the Sensing With Independent Micro-swimmers (SWIM) project, these robots have undergone initial testing in a Caltech swimming pool and could eventually dive into Jupiter's moon Europa's subsurface ocean.
Europa's Potential for Life
The SWIM initiative aligns with NASA's broader goal of examining whether environments beyond Earth could support life. Scheduled for a 2030 launch, the Europa Clipper mission will perform flybys to investigate the moon's ice-covered ocean. Building on this mission, SWIM envisions deploying a swarm of cell phone-sized robots beneath Europa's thick ice crust to search for chemical signals and temperature variations, key indicators of life.
Also read: Yeh Kaali Kaali Ankhein Season 2, The Piano Lesson and other top 7 OTT releases to watch today
Once delivered by an ice-penetrating cryobot, the robots would operate autonomously, fanning out to cover a wide area. Recent tests demonstrated their ability to perform search patterns in water and respond to simulated environmental cues. NASA engineers have also conducted simulations replicating Europa's harsh conditions to refine the robots' capabilities, ensuring they balance exploration efficiency with limited battery life.
Also read: Google must sell Chrome to restore competition in online search, DOJ argues
Advancements in Robot Design and Testing
Ethan Schaler, SWIM's principal investigator at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, highlighted the project's importance. He explained that finding environments suitable for life requires exploring water-based systems, which means creating autonomous robots capable of operating far from Earth.
The prototypes, measuring about 16.5 inches during testing, successfully navigated water and even performed complex movements like spelling "J-P-L." Future versions will be smaller, about 5 inches long, equipped with sensors to measure temperature, pressure, and chemical composition. Engineers at Georgia Tech are also contributing by developing a compact sensor chip to gather environmental data.
Also read: For the first time ever! This church is using ‘AI Jesus' to help you confess
The potential uses for SWIM robots extend beyond icy moons. They could aid oceanographic studies or explore under-polar ice on Earth, collecting critical data. Supported by NASA's Innovative Advanced Concepts program, the SWIM project represents a step forward in both space exploration and robotics technology, paving the way for future missions to distant ocean worlds.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.





























