Pure GOLD! Where Earth's atmosphere meets space, NASA-funded gadget reveals big secrets
Between Earth and outer space, there is a critically important area.





 View all Images
View all ImagesBetween Earth and outer space, there is a critically important area. This is the atmosphere. Now, a NASA funded instrument has revealed some long-held secrets about the ionosphere.
The ionosphere stretches roughly 50 to 400 miles above Earth's surface. It is exactly at the edge of space. This is the dynamic region where the atmosphere meets space. Home to astronauts on the space station and to many satellites, the ionosphere constantly fluctuates and responds to changes from above and below.
A NASA-funded instrument is shedding new light on the invisible processes and rhythms at play in this intersection between Earth and space.
In the ionosphere, radiation from the Sun cooks some of the gases until they lose an electron or two. The result is a sea of electrically charged particles—ions—intermingled with the neutral upper atmosphere.
Not just energy from the Sun, but the ionosphere also responds to weather patterns that ripple up from the lower parts of Earth's atmosphere.
Such changes affect key communications systems such as high-frequency (HF) radio and GPS.
Atmospheric scientist Richard Eastes of the University of Colorado says the region is far more variable than scientists expected.
This is based on the insight from the Global-scale Observations of the Limb and Disk (GOLD) instrument, which images the ionosphere.
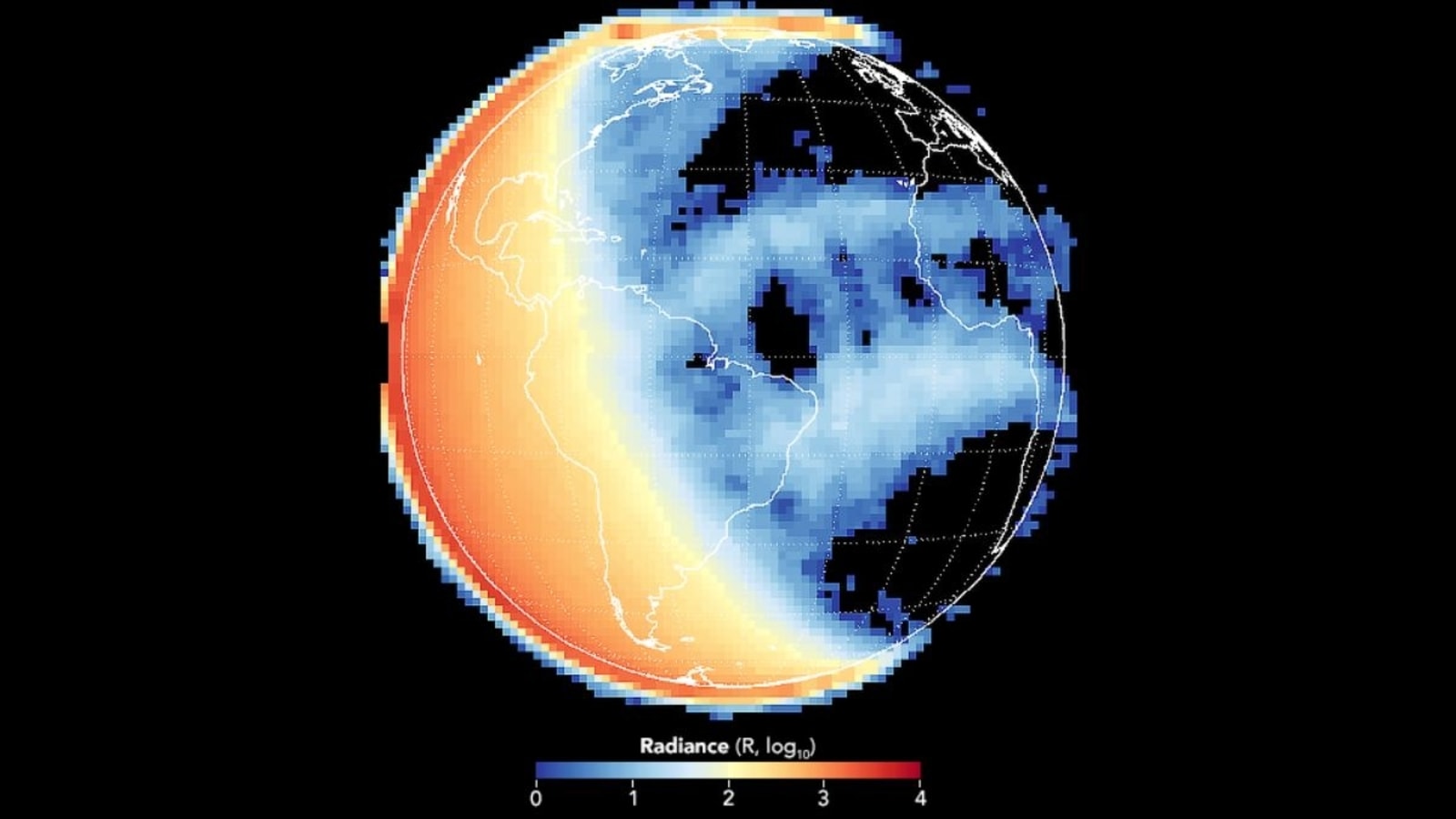
The image above was acquired by GOLD on December 19, 2018—a view of the entire Western Hemisphere as observed from geostationary orbit.
The left third of the sphere is still in daylight, while eastern North and South America were bathed in twilight or darkness.
The blue strips stretching across the Atlantic Ocean are known as the Appleton anomaly, a region of the ionosphere around the magnetic equator that stays activated for much of the night due to plasma rising from lower parts of the ionosphere.
Eastes noted that on one night, the crests may be evenly spaced over the equator; the next night, they can be far apart.
Notably, the paths that radio waves take—such as those used by GPS—depend on the density of the ionosphere. Sometimes changes in the density and location of these hot spots can interfere with communications signals.
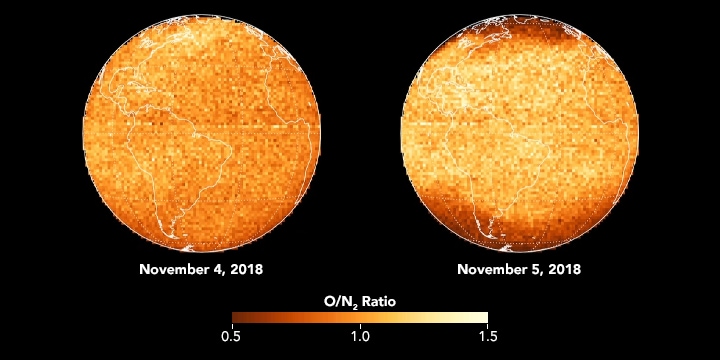

This image pair shows changes in the composition of the neutral atmosphere over the Western Hemisphere in full daylight, before and during a geomagnetic storm on November 4-5, 2018. Note how the ratio of atomic oxygen to nitrogen gas increases at low latitudes (becoming brighter in the image) and decreases at high latitudes (darker) in the wake of the storm.
During such storms, the neutral atmosphere near the magnetic poles is heated by energy coming from the magnetosphere, and the density ratio decreases dramatically. At lower latitudes, the opposite happens.
Since the neutral atmosphere and ionosphere are coupled, composition changes alter the ionosphere density and the behavior of radio communications signals.
NASA says that the GOLD research team was surprised by how much the ionosphere varies from night to night.
Catch all the Latest Tech News, Mobile News, Laptop News, Gaming news, Wearables News , How To News, also keep up with us on Whatsapp channel,Twitter, Facebook, Google News, and Instagram. For our latest videos, subscribe to our YouTube channel.





























